Before You Begin
Purpose
This tutorial shows you how to connect a Java application to Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service using JDBC and how to deploy the application to Oracle Application Container Cloud Service.
Time to Complete
40 minutes
Background
This tutorial provides you the source code of a sample application that is used to show you how to connect a Java application using JDBC to Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service and then how to deploy it in Oracle Application Container Cloud Service. The application is a Java REST service developed using Jersey and Grizzly that implements the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations and uses Maven to administrate the project dependencies and create the builds.
The employee-service.zip file
provided in the section "What do you need?"
contains the following structure:
-
Project sources: Located under
src/main/java.Contains four classes in thecom.example.restpackage:-
The
Mainclass configures and deploys the project's JAX-RS application to the Grizzly container. It configures the Universal Resource Identifier (URI) where the Grizzly HTTP Server listens and the packages where the Grizzly HTTP Server scans for JAX-RS resources. It then starts a new instance of the Grizzly HTTP Server. TheMainclass reads the HOSTNAME and PORT from the environment variables if they aren't defined the default values arelocalhostand8080./* Copyright © 2016 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. */ package com.example.rest; import org.glassfish.grizzly.http.server.HttpServer; import org.glassfish.jersey.grizzly2.httpserver.GrizzlyHttpServerFactory; import org.glassfish.jersey.server.ResourceConfig; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; import java.util.Optional; /** * Main class. * */ public class Main{ // Base URI the Grizzly HTTP server will listen on public static final String BASE_URI; public static final String protocol; public static final OptionalHOSTNAME; public static final Optional PORT; static{ protocol = "http://"; HOSTNAME = Optional.ofNullable(System.getenv("HOSTNAME")); PORT = Optional.ofNullable(System.getenv("PORT")); BASE_URI = protocol + HOSTNAME.orElse("localhost") + ":" + PORT.orElse("8080") + "/" ; } /** * Starts Grizzly HTTP server exposing JAX-RS resources defined in this application. * @return Grizzly HTTP server. */ public static HttpServer startServer() { // create a resource config that scans for JAX-RS resources and providers // in com.example.rest package final ResourceConfig rc = new ResourceConfig().packages("com.example.rest"); // create and start a new instance of grizzly http server // exposing the Jersey application at BASE_URI return GrizzlyHttpServerFactory.createHttpServer(URI.create(BASE_URI), rc); } /** * Main method. * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { final HttpServer server = startServer(); System.out.println(String.format("Jersey app started with WADL available at " + "%sapplication.wadl\nHit enter to stop it...", BASE_URI)); System.in.read(); server.stop(); } } -
The
DBConnectionclass creates the database connection to Oracle Exadata Express Cloud Service. It gets the database user and password from the EECS_USER and EECS_PASSWORD environment variables, if the variables aren't define the value by default isoraclein both cases.The service name
(dbaccess)in the connection string is a reference to a connection definition in thetnsnames.orafile that is generated as part of the Oracle Exadata Express Cloud Service client credentials./* Copyright © 2016 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. */ package com.example.rest; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Optional; import java.util.Properties; import oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleConnection; import oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource; public class DBConnection { final static String DB_URL = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@dbaccess"; //Environment Variable Cloud public static final Optional<String> EECS_USER = Optional.ofNullable(System.getenv("EECS_USER")); public static final Optional<String> EECS_PASSWORD = Optional.ofNullable(System.getenv("EECS_PASSWORD")); private static Connection connection = null; private static DBConnection instance = null; private DBConnection() { } public static DBConnection getInstance() { if (connection == null) { instance = new DBConnection(); } return instance; } public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Properties info = new Properties(); info.put(OracleConnection.CONNECTION_PROPERTY_USER_NAME, EECS_USER.orElse("oracle")); info.put(OracleConnection.CONNECTION_PROPERTY_PASSWORD, EECS_PASSWORD.orElse("oracle")); if (connection == null) { OracleDataSource ods = new OracleDataSource(); ods.setURL(DB_URL); ods.setConnectionProperties(info); connection = (OracleConnection) ods.getConnection(); } return connection; } } -
The
Employeeclass is a Plain Old Java Object (POJO) that contains the employee properties to represent theEmployeetable and their getters and setters methods to access to the properties./* Copyright © 2016 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. */ package com.example.rest; import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement; @XmlRootElement public class Employee { private long id; private String firstName; private String lastName; private String birthDate; private String title; private String department; private String email; public Employee() { } public Employee(String firstName, String lastName, String birthDate, String title, String department, String email) { this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; this.birthDate = birthDate; this.title = title; this.department = department; this.email = email; } public Employee(long id, String firstName, String lastName, String birthDate, String title, String department, String email) { this(firstName, lastName, birthDate, title, department, email); this.id = id; } public long getId() { return id; } public void setId(long id) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getBirthDate() { return birthDate; } public void setBirthDate(String birthDate) { this.birthDate = birthDate; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public String getDepartment() { return department; } public void setDepartment(String department) { this.department = department; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } } -
The
EmployeeServiceclass is the employee resource class that contains the HTTP methods (GET, POST, DELETE, and PUT)./* Copyright©2015 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. */ package com.example.rest; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.logging.Level; import java.util.logging.Logger; import javax.ws.rs.DELETE; import javax.ws.rs.GET; import javax.ws.rs.POST; import javax.ws.rs.PUT; import javax.ws.rs.Path; import javax.ws.rs.PathParam; import javax.ws.rs.Produces; import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType; import javax.ws.rs.core.Response; @Path("/employees") public class EmployeeService { @GET @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) public Employee[] getAllEmployees() { ArrayList<Employee> cList = null; try { Connection conn = DBConnection.getInstance().getConnection(); String queryStr = "SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE "; cList = new ArrayList<>(); try (PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(queryStr)) { ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { cList.add(new Employee(rs.getLong("ID"), rs.getString("FIRSTNAME"), rs.getString("LASTNAME"), rs.getString("BIRTHDATE"), rs.getString("TITLE"), rs.getString("DEPARTMENT"), rs.getString("EMAIL"))); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (SQLException ex) { Logger.getLogger(EmployeeService.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } return cList.toArray(new Employee[0]); } @GET @Path("{id}") @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) public Employee getEmployee(@PathParam("id") long id) { Employee employee = null; try { Connection conn = DBConnection.getInstance().getConnection(); String queryStr = "SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE ID=" + id; try (PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement(queryStr)) { ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()) { employee = new Employee(rs.getLong("ID"), rs.getString("FIRSTNAME"), rs.getString("LASTNAME"), rs.getString("BIRTHDATE"), rs.getString("TITLE"), rs.getString("DEPARTMENT"), rs.getString("EMAIL")); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (SQLException ex) { Logger.getLogger(EmployeeService.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } return employee; } @POST @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) public Response addEmployee(Employee employee) { try { Connection conn = DBConnection.getInstance().getConnection(); String insertTableSQL = "INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE " + "(ID, FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, TITLE, DEPARTMENT, BIRTHDATE) " + "VALUES(EMPLOYEE_SEQ.NEXTVAL,?,?,?,?,?,?)"; try (PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn .prepareStatement(insertTableSQL)) { preparedStatement.setString(1, employee.getFirstName()); preparedStatement.setString(2, employee.getLastName()); preparedStatement.setString(3, employee.getEmail()); preparedStatement.setString(4, employee.getTitle()); preparedStatement.setString(5, employee.getDepartment()); preparedStatement.setString(6, employee.getBirthDate()); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { } catch (Exception e) { } } catch (SQLException ex) { Logger.getLogger(EmployeeService.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } return Response.status(Response.Status.OK).build(); } @PUT @Path("{id}") @Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) public Response updateEmployee(Employee employee, @PathParam("id") long id) { try { Connection conn = DBConnection.getInstance().getConnection(); String updateTableSQL = "UPDATE EMPLOYEE SET FIRSTNAME= ?, LASTNAME= ?, EMAIL=?, TITLE=?, DEPARTMENT=?, BIRTHDATE=? WHERE ID=?"; try (PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn .prepareStatement(updateTableSQL);) { preparedStatement.setString(1, employee.getFirstName()); preparedStatement.setString(2, employee.getLastName()); preparedStatement.setString(3, employee.getEmail()); preparedStatement.setString(4, employee.getTitle()); preparedStatement.setString(5, employee.getDepartment()); preparedStatement.setString(6, employee.getBirthDate()); preparedStatement.setLong(7, employee.getId()); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (SQLException ex) { Logger.getLogger(EmployeeService.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } return Response.status(Response.Status.OK).build(); } @DELETE @Path("{id}") public Response deleteEmployee(@PathParam("id") long id) { try { String deleteRowSQL = "DELETE FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE ID=?"; Connection conn = DBConnection.getInstance().getConnection(); try (PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn .prepareStatement(deleteRowSQL)) { preparedStatement.setLong(1, id); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { } catch (Exception e) { } } catch (SQLException ex) { Logger.getLogger(EmployeeService.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } return Response.status(Response.Status.OK).build(); } }
-
- Scripts:
Located under the
root directory.
Contains two
files:
-
The
replace_policy_jars.shscript detects if JAVA_HOME is JDK or JRE and copy thelocal_policy.jarandUS_export_policy.jarfiles into the correct security directory.#!/bin/sh if [ -z "$JAVA_HOME" ]; then echo "ERROR: JAVA_HOME not defined-cannot update policy jars!" exit -1 fi # Detect if JAVA_HOME is JDK or JRE and set correct security dir location if [ -d "$JAVA_HOME/jre" ]; then echo "JDK detected in ${JAVA_HOME}" security_dir="${JAVA_HOME}/jre/lib/security" else echo "JRE detected in ${JAVA_HOME}" security_dir="${JAVA_HOME}/lib/security" fi # Replace existing jars with Unlimited Strength Juristiction Policy jars echo "Updating local_policy.jar in ${security_dir}" cp -f ./policy_jars/local_policy.jar "${security_dir}" echo "Updating US_export_policy.jar in ${security_dir}" cp -f ./policy_jars/US_export_policy.jar "${security_dir}" exit -1 -
The
pom.xmlscript is the Maven script that contains the project dependencies and the plugin to build the fat jar.<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.example.rest</groupId> <artifactId>employee-service</artifactId> <packaging>jar</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>employee-service</name> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.glassfish.jersey</groupId> <artifactId>jersey-bom</artifactId> <version>${jersey.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.glassfish.jersey.containers</groupId> <artifactId>jersey-container-grizzly2-http</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.glassfish.jersey.media</groupId> <artifactId>jersey-media-json-jackson</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.oracle.jdbc</groupId> <artifactId>ojdbc7</artifactId> <version>12.1.0.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.9</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <properties> <jersey.version>2.17</jersey.version> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> <executions> <execution> <id>build-jar</id> <phase>package</phase> <goals> <goal>shade</goal> </goals> <configuration> <finalName>exadata-express-employees-${project.version}</finalName> <transformers> <transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ServicesResourceTransformer" /> <transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ManifestResourceTransformer"> <mainClass>com.example.rest.Main</mainClass> </transformer> </transformers> </configuration> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
-
What Do You Need?
- An Oracle Exadata Express Cloud Service account
- An Oracle Platform Cloud account with Oracle Application Cloud Container Service
- Maven
- Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy Jars
- Oracle Database JDBC Driver & UCP Downloads for Cloud Release
- Oracle SQL Developer Release 4.1.5 or later.
- employee-service.zip
Obtaining the Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service Client Credentials
-
Login into Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service.
-
Navigate to the Service Console for Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service and open the service console.
-
If Client Access is not currently enabled, click Enable Client Access.
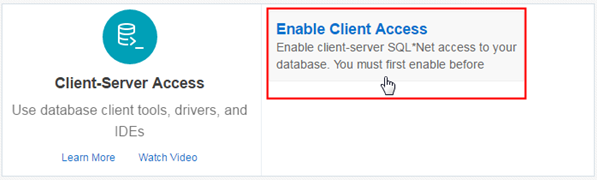
Description of this image -
Click Download Client Credentials.
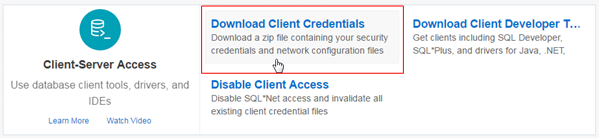
Description of this image -
Enter Password, Confirm password and click Download.
Note: Oracle Application Container Cloud Service limits the use of special characters in environment variable values but Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service requires you to use special characters in the JKS password. Use "!" as your special character to avoid compatibility issues.
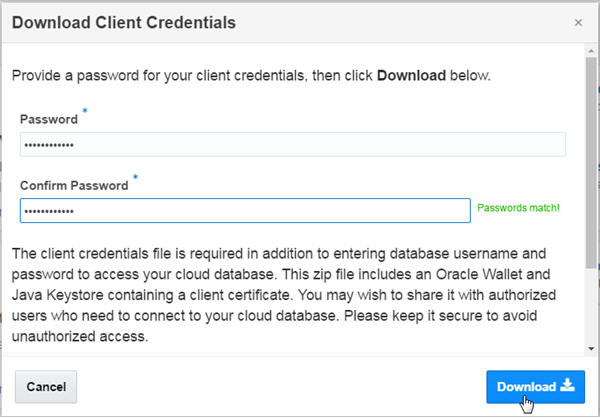
Description of this image -
Save the client wallet
client_credentials.zipfile.
Setting Up Your Application
-
Create the root folder for your project and extract the contents of the
employee_service.zipfile. - Create the
securityfolder in the root directory and extract the contents of theclient_credentials.zipfile. -
Create the
policy_jarssubfolder in the root directory, extracts the contents of the JCE file and putlocal_policy.jarandUS_export_policy.jarin thepolicy_jarsdirectory. -
Create the
libsubfolder in the root directory and put theojdbc7.jaranducp.jarfiles into thelibdirectory.
Connecting Oracle SQL Developer Cloud to Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service
Creating a Connection
-
Open Oracle SQL Developer.
-
Right click Connections and select New Connection...

Description of this image -
On the New/Select Database Connection dialog, make the following entries:
- Connection Name - Enter the name for this cloud connection.
- Username
- Enter the
default
administrator
database account
(PDB_ADMIN)provided as part of the service. - Password
- Enter the
(PDB_ADMIN)password. - Connection Type - Select Cloud PDB.
- Configuration File - Click Browse, and select the Client Credentials zip file, downloaded from the Oracle Exadata Express service console.
- Keystore Password - Enter the password generated while downloading the Client Credentials from the Oracle Exadata Express service console.
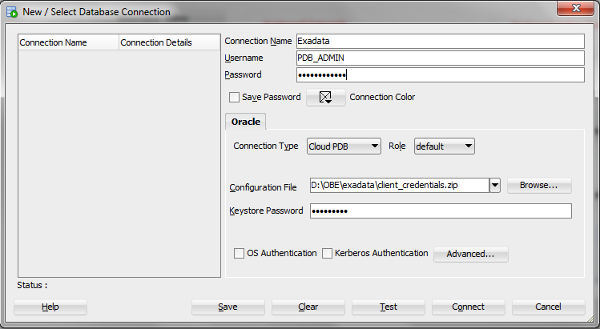
Description of this image -
Click Test.
-
Click Connect.
Creating the Database Objects
-
Copy the following script into the SQL worksheet to create the
EMPLOYEEtable and the sequence namedEMPLOYEE_SEQ:CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE ( ID INTEGER NOT NULL, FIRSTNAME VARCHAR(255), LASTNAME VARCHAR(255), EMAIL VARCHAR(255), PHONE VARCHAR(255), BIRTHDATE VARCHAR(10), TITLE VARCHAR(255), DEPARTMENT VARCHAR(255), PRIMARY KEY (ID) ); CREATE SEQUENCE EMPLOYEE_SEQ START WITH 100 INCREMENT BY 1; -
Click Run Script
 and then click Commit
and then click Commit  .
.
-
Copy and paste the following script to insert six employee records, then click Run script, and then click Commit.
INSERT INTO employee (FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES ('Hugh', 'Jast', 'Hugh.Jast@example.com', '730-715-4446', '1970-11-28' , 'National Data Strategist', 'Mobility'); INSERT INTO employee (FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES ('Toy', 'Herzog', 'Toy.Herzog@example.com', '769-569-1789','1961-08-08', 'Dynamic Operations Manager', 'Paradigm'); INSERT INTO employee (FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES ('Reed', 'Hahn', 'Reed.Hahn@example.com', '429-071-2018', '1977-02-05', 'Future Directives Facilitator', 'Quality'); INSERT INTO employee (FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES ('Novella', 'Bahringer', 'Novella.Bahringer@example.com', '293-596-3547', '1961-07-25' , 'Principal Factors Architect', 'Division'); INSERT INTO employee (FIRSTNAME, LASTNAME, EMAIL, PHONE, BIRTHDATE, TITLE, DEPARTMENT) VALUES ('Zora', 'Sawayn', 'Zora.Sawayn@example.com', '923-814-0502', '1978-03-18' , 'Dynamic Marketing Designer', 'Security');
Running the Application Locally
-
Open a command-line window and go to the root folder of your application.
-
Install the
ojdbc7.jaranducp.jarfiles in your Maven repository.mvn install:install-file -DgroupId=com.oracle.jdbc -DartifactId=ucp -Dversion=12.1.0.2 -Dpackaging=jar -Dfile=lib/ucp.jar mvn install:install-file -DgroupId=com.oracle.jdbc -DartifactId=ojdbc7 -Dversion=12.1.0.2 -Dpackaging=jar -Dfile=lib/ojdbc7.jar -
Run the
replace_policy_jars.shscript to replace the JCE files of yourJAVA_HOMEdirectory.replace_policy_jar.sh -
Build your application using the Maven command:
mvn clean package -
Create a script file named
local_start.sh, open the file in a text editor and copy and paste the following script:if [ -z "$1" ] || [ -z "$2" ] || [ -z "$3" ]; then echo "usage: ${0} <db user> <db password> <trust and key store password>"; exit -1; fi export EECS_USER=${1} export EECS_PASSWORD=${2} export STORE_PASSWORD=${3} echo "starting Example..." # Start the application referencing the security config files java \ -Doracle.net.tns_admin=./security \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=./security/truststore.jks \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=${3} \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=./security/keystore.jks \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=${3} \ -Doracle.net.ssl_server_dn_match=true \ -Doracle.net.ssl_version=1.2 \ -jar target/exadata-express-employees*.jar echo "exited Example"The script takes three parameters: the database user, the user password, and the trust and key store password then sets three environment variables with those values and calls the java command to execute the fat jar along with the properties needed to create the connection to Oracle Exadata Cloud Service.
-
Execute the
local_start.shscript in the command-line window.local_start.sh userDB passwordDB storePassword
Preparing the Application for Cloud Deployment
-
Create the
start.shscript file and add the following code to execute the application in Oracle Application Container Cloud Service.# Replace the default policy jars with the unlimited strength jars sh ./replace_policy_jars.sh echo "starting Example..." # Start the application referencing the security config files java -Doracle.net.tns_admin=./security \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=./security/truststore.jks \ -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=${JKS_PASSWORD} \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=./security/keystore.jks \ -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=${JKS_PASSWORD} \ -Doracle.net.ssl_server_dn_match=true \ -Doracle.net.ssl_version=1.2 \ -jar exadata-express-*.jar echo "exited Example" -
Create the
manifest.jsonfile in the root directory and add the following content:{ "runtime": { "majorVersion": "8" }, "command": "sh ./start.sh" } -
Create the
assemblydirectory into thesrcfolder. -
Create the
distribution.xmlfile in theassemblyfolder and add the following content:<assembly xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/assembly-1.1.3.xsd"> <id>dist</id> <formats> <format>zip</format> </formats> <includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory> <fileSets> <fileSet> <directory>${project.basedir}</directory> <outputDirectory>/</outputDirectory> <includes> <include>manifest.json</include> <include>start.sh</include> <include>replace_policy_jars.sh</include> </includes> </fileSet> <fileSet> <directory>${project.basedir}/security</directory> <outputDirectory>/security</outputDirectory> <includes> <include>*</include> </includes> </fileSet> <fileSet> <directory>${project.basedir}/policy_jars</directory> <outputDirectory>/policy_jars</outputDirectory> <includes> <include>*.jar</include> </includes> </fileSet> <fileSet> <directory>${project.build.directory}</directory> <outputDirectory>/</outputDirectory> <includes> <include>exadata-express-employees*.jar</include> </includes> <excludes> <exclude>*.zip</exclude> </excludes> </fileSet> </fileSets> </assembly> -
Open the
pom.xmlfile in a text editor and add following code inside the<plugins>tags.<plugin> <artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5.5</version> <configuration> <appendAssemblyId>false</appendAssemblyId> <descriptors> <descriptor>src/assembly/distribution.xml</descriptor> </descriptors> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <phase>package</phase> <goals> <goal>single</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> -
In the command-line window, build your application using the Maven command:
mvn clean package Look at the
targetdirectory and you'll find theemployee-service-1.0-SNAPSHOT.zipfile which will be used to deploy the application to Oracle Application Container Cloud Service.
The distribution.xml
script creates a zip
file that includes
the fat jar, the manifest.json
file, the replace_policy_jars.sh
script file, and the
start.sh
script file.
Deploying the Application to Oracle Application Container Cloud Service
-
Log in to Oracle Cloud at http://cloud.oracle.com/. Enter the identity domain, user name, and password for your account.
-
In the Oracle Cloud Services dashboard, click the Action menu
 , and select
Application Container.
, and select
Application Container. -
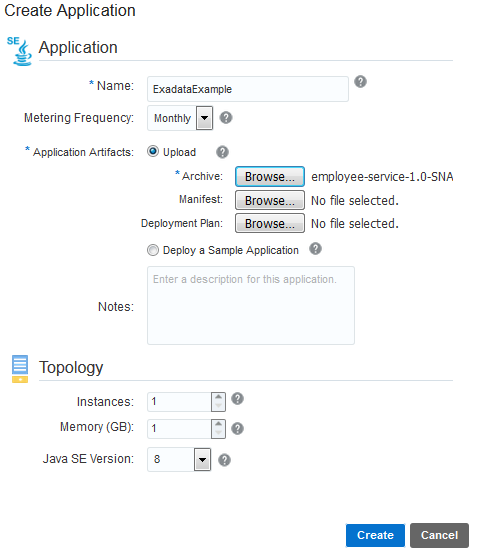
In the Applications list view, click Create Application and select Java SE.
-
In the Application section, enter a name for your application and click Browse next to Archive.
-
On the File Upload page, select the
employee-service-1.0-SNAPSHOT.ziparchive and click Open. -
Keep the default values in the Topology section and click Create.
Description of this image -
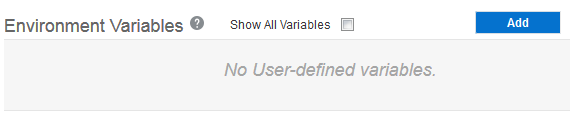
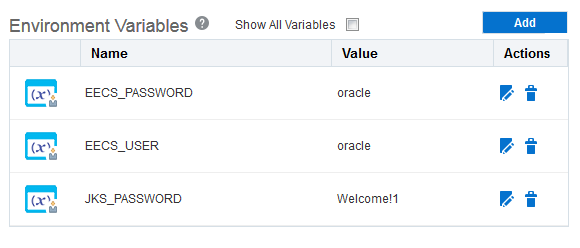
Wait until the application is created, go to the Deployments tab, and define three environment variables:
JKS_PASSWORD, EECS_USER,andEECS_PASSWORD.Name Value JKS_PASSWORD Enter the Java keystore password that you defined when you download the Oracle Exadata Express Cloud Service credentials. EECS_USER Enter the database user. For example, PDB_ADMIN.EECS_PASSWORD Enter the password of the database user to log into the Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service instance. -
In the Environment Variables section click Add.
Description of this image -
Enter the Name and Value
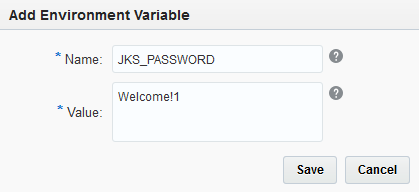
Description of this image -
Repeat the process with the other two environment variables.
Description of this image
-
-
Click Apply Edits.
Wait until the application is restarted and then click to the application URL.
Description of this image Add to the URL
/employees.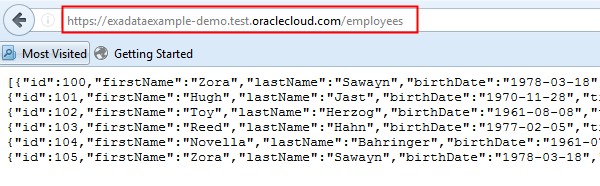
Description of this image
Want to Learn More?
- Oracle Application Container Cloud Service in the Oracle Help Center
- Oracle Database Exadata Express Cloud Service in the Oracle Help Center