Before You Begin
Purpose
This tutorial guides you through the setup of SQL Developer to connect and use SQL for your cloud or non-cloud Oracle databases.
Time to Complete
Approximately 15 minutes.
Background
Oracle SQL Developer is a development environment for using SQL for Oracle databases. If you have an Oracle Database Cloud Service or a non-cloud Oracle database, either way you can use SQL Developer to create users, run queries and load and update your databases. First you setup your SQL Developer connection information to connect to your databases and then you create all your users and run your queries. This tutorial goes through the steps of connecting to a database. For cloud databases, you have an extra step to setup an SSH connection with the database.
What Do You Need?
Oracle SQL Developer that's version 4.1 or later
An Oracle Database or an Oracle Database Cloud Service instance
Setup Connection to Cloud Database
If you have a non-cloud Oracle database, then skip this section.
Find the IP Address and Service Name for the Cloud Database
In My Services Dashboard asociated to your Oracle Cloud account, click the menu icon for Database and then click Open Service Console. If you need help, go to Find the IP address of an Oracle Public Cloud Service VM.
-
Click the name of the database cloud service instance you want to connect to. In this tutorial, it's
DB12C-ABC.
-
Copy the IP address from the Nodes section's Public IP field and save it for the next section. For this tutorial, the IP address is
11.111.111.11.
-
Click show more in the Additional Information section.

-
In the Connect String field, copy the Service name, which is the value after the slash and save it for the SQL Developer section. For this tutorial, the Service Name which is for the pluggable database
PDB1 is PDB1.ggcs.oraclecloud.internal. Rememeber to use your own service name for your environment.
Setup an SSH Connection to the Database
Start Oracle SQL Developer.

-
From the toolbar, go to View > SSH.

-
In the SSH Hosts section, right click SSH Hosts and select New SSH Host... .

-
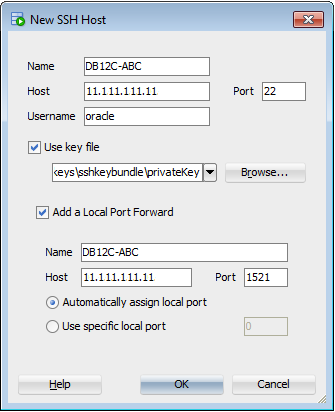
In the New SSH Host window, enter or select the following information and then click OK:
Name:
DB12C-ABCHost:
<Database IP address such as 11.111.111.11>Port:
22Username:
oracleUse key file: Select check box.
- Click Browse and find and select the private key associated to your service instance. For this tutorial, it's called privateKey which was created through the Create Service wizard of Oracle Database Cloud Service, located in the unzipped folder of sshkeybundle. If you don't remember where the private key is, refer to Update Public/Private Key Pairs of Oracle Public Cloud Services to create a new pair of keys specific to this database instance.
Add a Local Port Forward: Select check box.
Name:
DB12C-ABCHost:
<Database IP address such as 11.111.111.11>Port:
1521Automatically assign local port: Select radio button
-
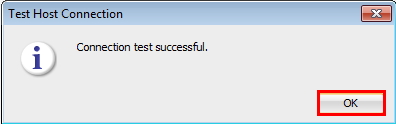
Right click the SSH host, DB12C-ABC and click Test.

-
Ensure that the message is Connection test successful and click OK.
-
In the Connections section, click the New Connection dropdown menu and select New Connection... .

-
In the New /Select Database Connection window, enter or select the following information and then click Test:
Connection Name:
PDB1_SYSUsername:
SYSPassword:
<Database SYS password>Save Password: Select check box.
Connection Type: SSH
Role: SYSDBA (If your user is not a system administrator, then select an appropriate role from the Role drop-down menu.)
Port Forward: DB12C-ABC (DB12C-ABC)
Service Name: <Your Service mame, such as PDB1.ggcs.oraclecloud.internal>

-
Confirm that the Status displays Success.
-
Click Save.
-
Click Connect.
-
Ensure that PDB1_SYS displays in the list of Connections.

-
Enter your SQL scripts in the worksheet that opens for this connection.
-
Run your scripts with F5.
Setup Connection to Non-Cloud Database
If you have a non-cloud Oracle database, perform the steps in this section.
Find the IP Address and Service Name for the Non-Cloud Database
In the environment where the Oracle database is installed find the service name and port number for the database from tnsnames.ora. For example, in this tutorial, it's located in $TNSADMIN which is /scratch/rdbms/product/12.1.0/dbhome/network/admin/ and it displays the he service name of orcl.us.oracle.com and the port of 1521.
$ cat $TNSADMIN/tnsnames.ora
# tnsnames.ora Network Configuration File: /scratch/rdbms/product/12.1.0/dbhome_1/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
# Generated by Oracle configuration tools.
LISTENER_ORCL =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = localhost)(PORT = 1521))
ORCL =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = localhost)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = orcl.us.oracle.com)
)
)
-
Validate that your administrator can connect to the database. In this tutorial, the administrator is called SYS and its password is oracle and the database is ORCL. (The database name is not case sensitive.)
$ sqlplus SYS/oracle@orcl SQL*Plus: Release 12.1.0.2.0 Production on Wed Sep 21 15:31:57 2016 Copyright (c) 1982, 2014, Oracle. All rights reserved. Last Successful login time: Wed Sep 21 2016 15:31:35 -04:00 Connected to: Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.1.0.2.0 - 64bit Production SQL> exit Disconnected from Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.1.0.2.0 - 64 bit Production
-
Find the IP address for the environment that the database is installed from ifconfig's inet addr value.
$ /sbin/ifconfig ...inet addr:xx.xxx.xx.xx...Have the service name, port number and IP address available for the next section.
Setup a Basic Connection to the Database
Start Oracle SQL Developer.

-
In the Connections section, click the New Connection dropdown menu and select New Connection... .

-
In the New /Select Database Connection window, enter or select the following information and then click Test:
Connection Name:
Source_SYSUsername:
SYSPassword:
<Database SYS password>Save Password: Select check box.
Connection Type: Basic
Role: SYSDBA (If your user is not a system administrator, then select an appropriate role from the Role drop-down menu.)
Hostname: <IP address of the environment that the non-cloud database is installed>
Port: 1521 <Find this port name from the tnsnames.ora described in the previous section>
Service Name: <Your Service mame, such as PDB1.ggcs.oraclecloud.internal>

-
Click Save.
-
Click Connect.
-
Ensure that Source_SYS displays in the list of Connections.

-
Right click Source_SYS and then click Connect.
-
Enter your SQL scripts in the worksheet that opens for this connection.
-
Run your scripts with F5.