Debugging Oracle PL/SQL from Visual Studio
Purpose
This tutorial describes how you can debug Oracle PL/SQL from Visual Studio .
Time to Complete
Approximately 30 minutes
Overview
The integrated PL/SQL debugger in Oracle Developer Tools (ODT) allows you to remain inside of Visual Studio for end-to-end debugging of your .NET and Oracle solution. You can debug PL/SQL code such as procedures and functions (both stand-alone and packaged), object methods, and triggers from within the Visual Studio environment in the same way as you would debug your C# or VB.NET code. With the ODT integrated PL/SQL debugger, you can use traditional debugging features such as setting break points, viewing and modifying variable values, and examining the call stack.
You use the PL/SQL debugger in one of three modes:.
In this tutorial, you use the Multi-tier Application Debugging mode. This mode allows you, as a developer, to work with both .NET and PL/SQL code simultaneously during a debugging session.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you should:
|
. |
Install Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 |
|---|---|
|
. |
Install Oracle Database 9.2 or later or Oracle Database XE |
|
. |
Install Oracle 11g Oracle Data Access Components (ODAC) with Oracle Developer Tools for Visual Studio version 11.2.0.1.2 or later from OTN |
|
. |
Extract these files into your working directory. |
Creating an Oracle Connection
Before you begin creating your application, you open Visual Studio and create a connection. Perform the following steps:
|
. |
Open Visual Studio.. |
|---|---|
|
. |
Select View > Server Explorer.
|
|
. |
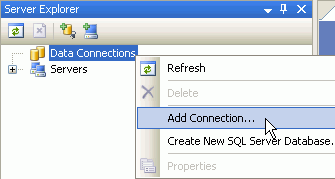
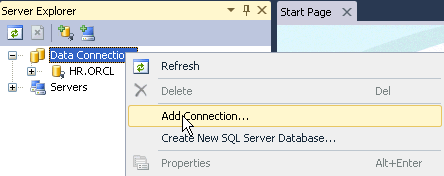
Right-click Data Connections and select Add Connection....
|
|
. |
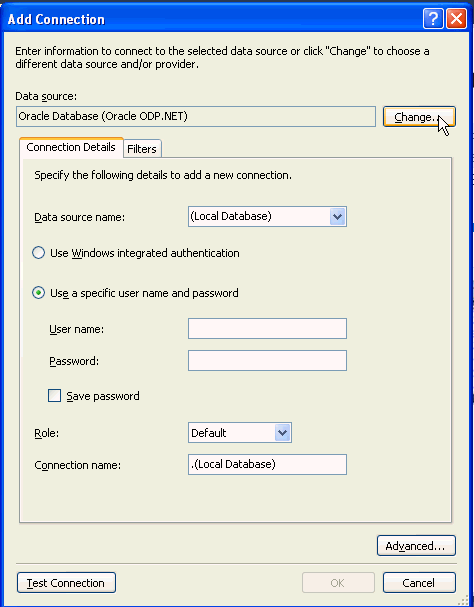
In Add Connection dialog box, first select the appropriate Data Source provider. Note: If the Data source is already set to Oracle Database Server(Oracle ODP.NET), then move to next step or click Change to select the Data Source provider
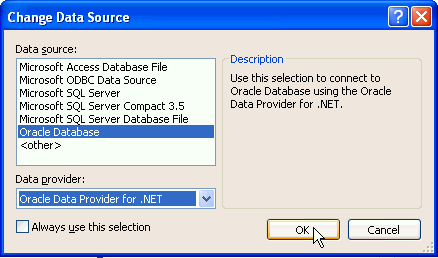
In the Change Data Source dialog box, select Oracle Database Server as the Data Source and Oracle Data Provider for .NET as the Data Provider. Click OK.
|
|
. |
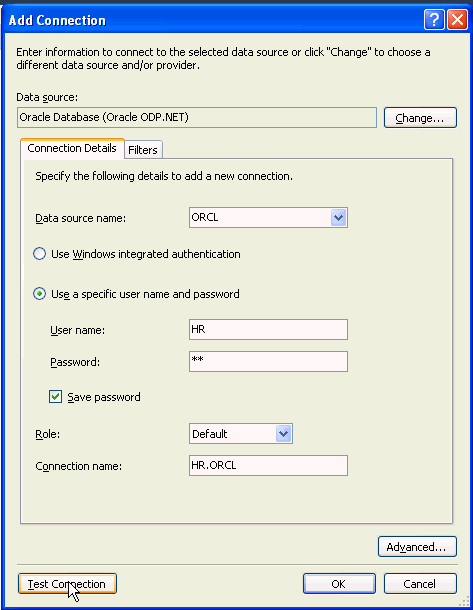
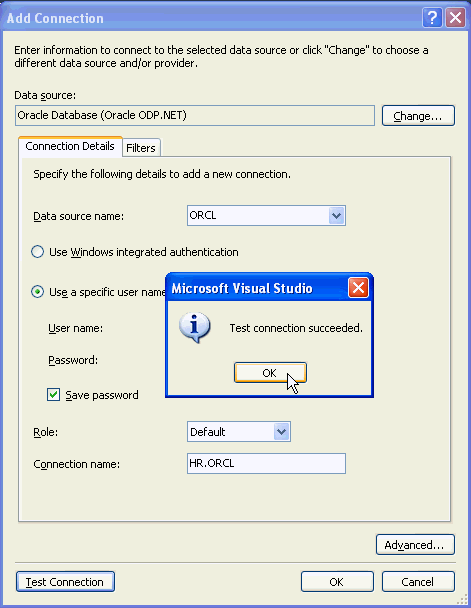
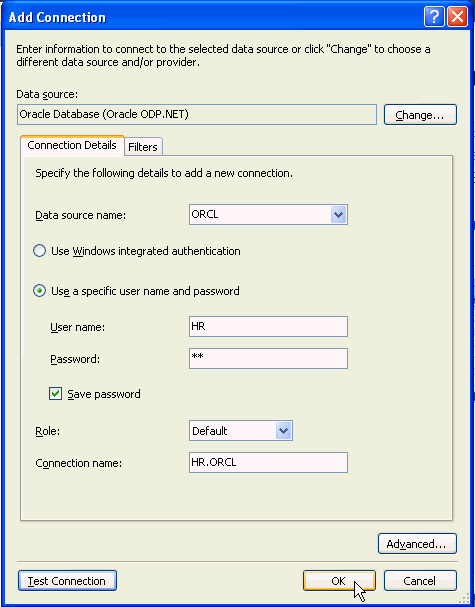
From the Data source name drop down, select the <SID> of your Oracle Database instance. Enter hr for the User name and Password, click Save password and click Test connection.
|
|
. |
Test connection was successful. Click OK.
|
|
. |
Click OK.
|
|
. |
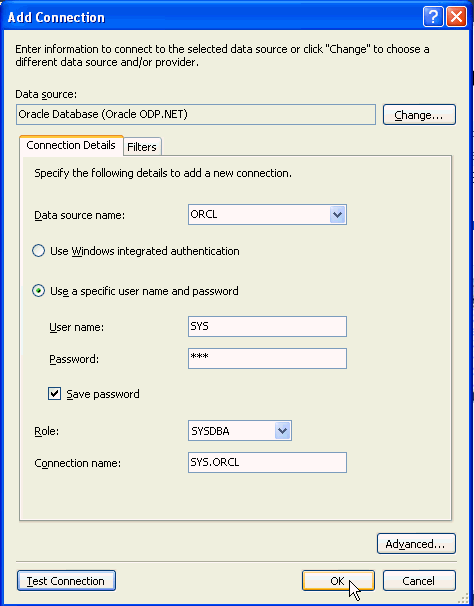
Your HR connection has been created. Similarly, you also need to create a SYS connection. Right-click Data Connections and select Add Connection...
|
|
. |
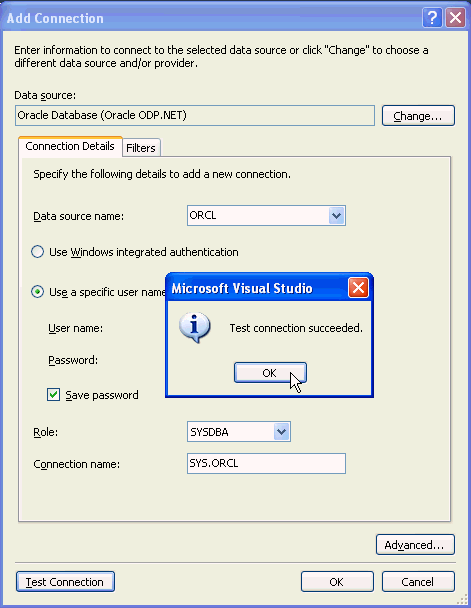
The Data source provider should be set to Oracle Database Server(Oracle ODP.NET). From the Data source name drop down, select the <SID> of your Oracle Database instance. Enter SYS for the User name and enter your sys Password, click Save password, select SYSDBA for the Role and click Test connection
|
|
. |
Test connection was successful. Click OK.
|
|
. |
Click OK.
|
|
. |
The SYS connection was created. Expand both hr.ORCL and SYS.ORCL to make the connection.
|
Granting Privileges for Debugging
Before you can use the debugger, you need to grant debug connect session and debug any procedure to the HR user. Perform the following steps:
|
. |
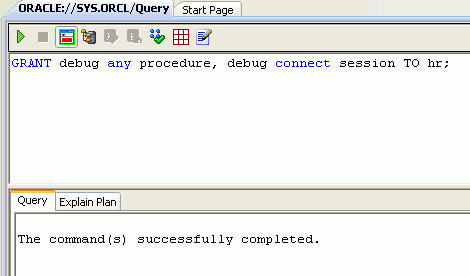
In the Server Explorer panel, right-click SYS.ORCL connection and select Query Window.
|
|---|---|
|
. |
Enter the following command and click Execute. GRANT debug any procedure, debug connect session TO hr;
Note: If you are using Oracle Database Release 9.2, you should execute grant debug any procedure to hr;
|
|
. |
The statement was executed successfully.
|
Creating the PL/SQL Package and Package Body
In this topic, you create a PL/SQL Package and Package Body that determines whether each number in a PL/SQL array is a prime number and then create a new row in the JOBS table using a PL/SQL record. Perform the following steps:
|
. |
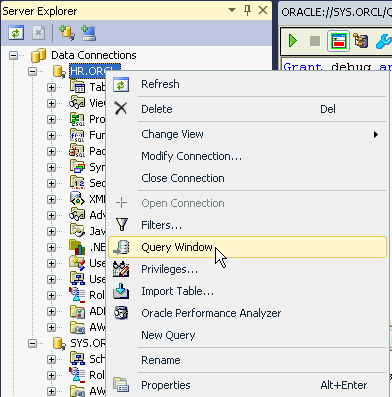
In the Server Explorer panel, right-click HR.ORCL and select Query Window.
|
|---|---|
|
. |
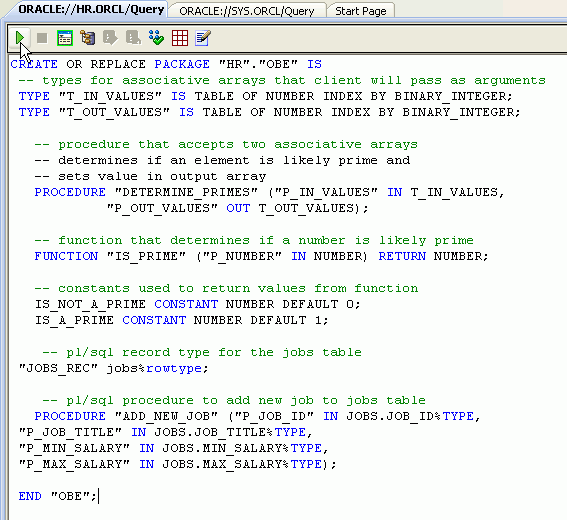
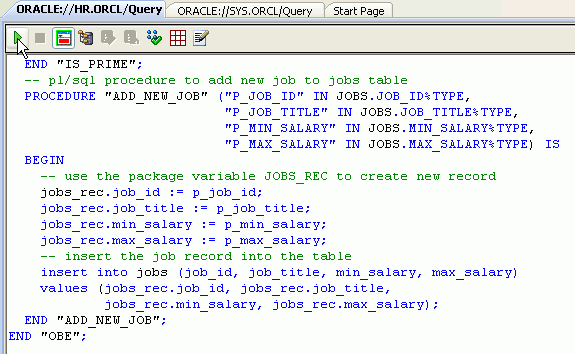
Copy the code in the PLSQL_Debug_Package.txt file from the files downloaded into your working directory and paste into the Query Window and click Execute. CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE
"HR"."OBE" IS -- pl/sql record type for
the jobs table -- pl/sql procedure to
add new job to jobs table END "OBE";
|
|
. |
The PL/SQL Package was executed successfully.
|
|
. |
Copy the code in the PLSQL_Debug_Packagebody.txt file from the files downloaded into your working directory and paste into the Query Window and click Execute. CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE
BODY "HR"."OBE" IS
|
|
. |
The PL/SQL Package Body was executed successfully.
|
|
. |
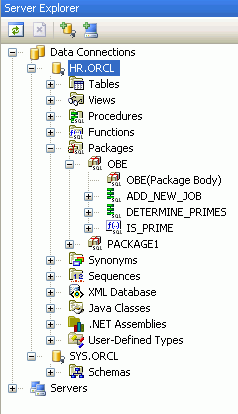
In the Server Explorer for the HR.ORCL Connection, expand Packages > OBE to see the list of objects that were created.
|
|
. |
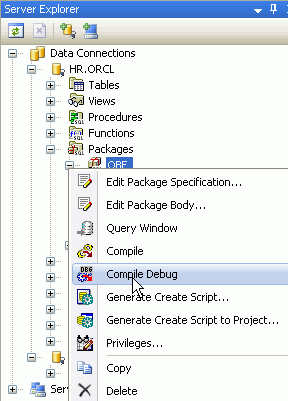
Right-click the OBE Package and select Compile Debug. This action enables debugging of the package.
|
|
. |
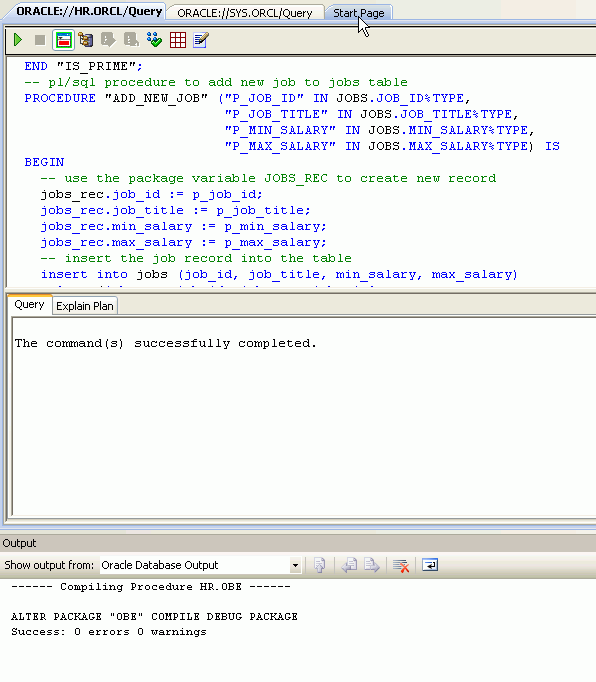
The package compiled successfully. Close the Output window. And then click the Start Page tab.
|
Creating a Project in Visual Studio
Now you can create a new project. Perform the following steps:
|
. |
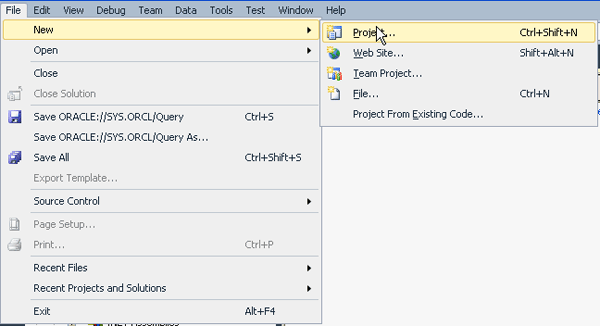
From the File menu, select New Project.
|
|---|---|
|
. |
Choose Project Type Visual C# : Windows, select the Template Console Application , enter plsqldebugobe1 for the Name and enter the directory where you want the files stored in the location field (Note: if the directory does not exist, it is created). Then click OK.
|
|
. |
The project has been created. Now you can add a reference.
|
|
. |
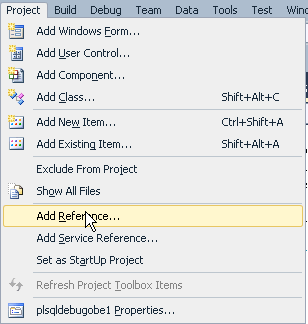
Select Project > Add Reference...
|
|
. |
Scroll down the list of References and select Oracle.DataAccess and click OK.
|
|
. |
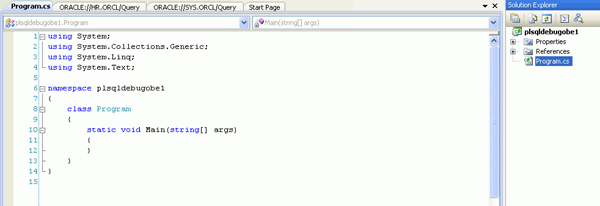
Copy the code in the PLSQL_Debug_csharpcode.txt file from the files downloaded into your working directory and paste into the Program.cs window in Visual Studio. Then right-click on the Program.cs tab and select Save Program.cs. using
System;
|
Configuring the Debugging Environment
There are a few properties and options that need to be configured before you can use the debugging environment. Perform the following steps:
|
. |
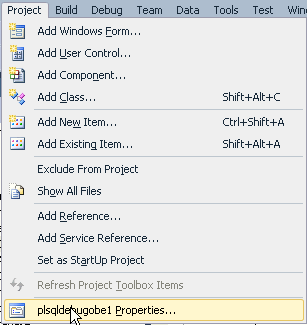
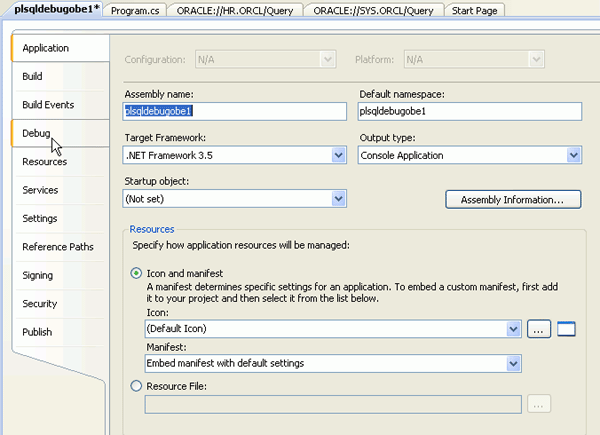
Select Project > plsqldebugobe1 Properties...
|
|---|---|
|
. |
Select Debug.
|
|
. |
Deselect Enable the Visual Studio hosting process and right-click the plsqldebugobe1 tab and select Save Selected Items
|
|
. |
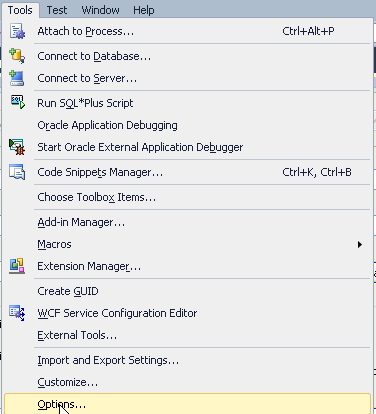
Select Tools > Options....
|
|
. |
Click the Show all settings check box. Note: You may not see this checkbox which means that it was already set. Scroll down and expand Oracle Developer Tools. Select PL/SQL Debugging. In the available Database Connections, click the checkbox in front of the HR.ORCL connection. Notice that you see an IP address dropdown box and a TCP/IP port range. During PL/SQL debugging, the Oracle Database connects to Visual Studio via TCP/IP on an IP address and on a random port within this range. If your machine has multiple IP addresses make sure to choose one that the Oracle database can connect to. Make sure the port range specified represents open ports on your machine and that they are not blocked by a firewall.
|
|
. |
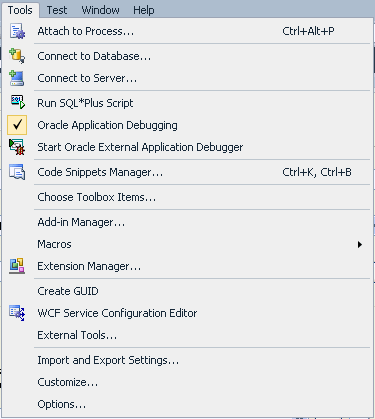
Select Tools > Oracle Application Debugging.
If you select the Tools menu again, you should see a checkmark in front of the menu item.
|
Setting Breakpoints
In this topic, you set some breakpoints in both your C# and PL/SQL code to stop the debugger during execution. Perform the following steps:
|
. |
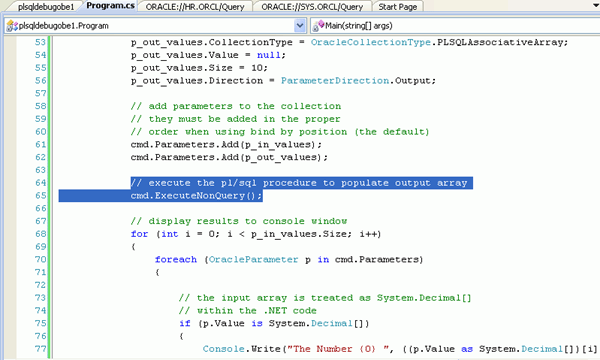
Click the Program.cs tab and locate the cmd.ExecuteNonQuery() statement.
|
|---|---|
|
. |
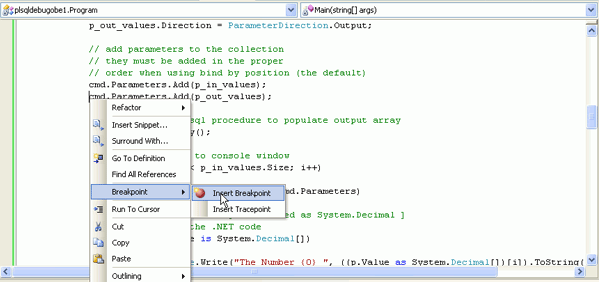
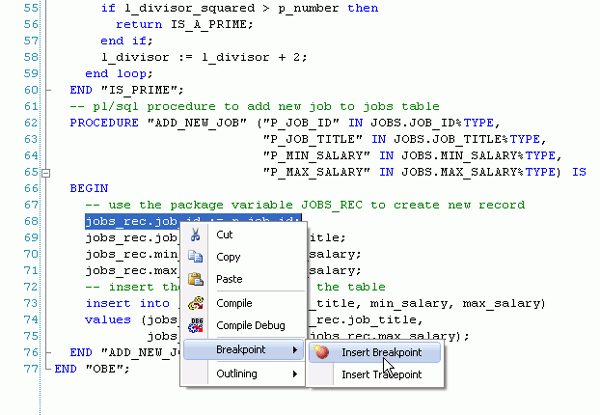
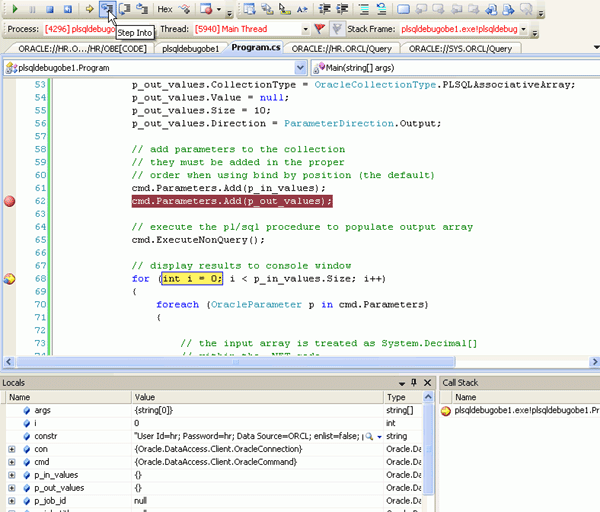
In the Program.cs code,at the cmd.Parameters.Add(p_out_values) statement, you want to create a breakpoint. Click anywhere on the line, right-click and select Breakpoint, then select Insert Breakpoint. Alternatively, you can click on the grey leftmost edge of the code window at the location where you would like to set the breakpoint.
|
|
. |
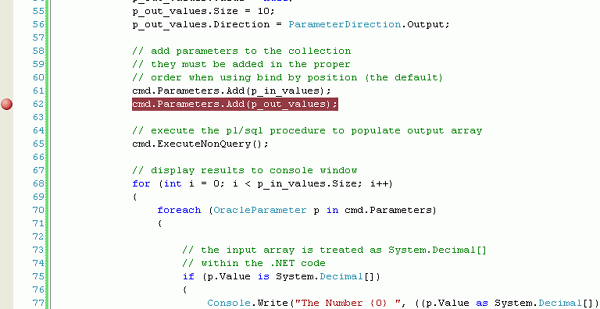
The breakpoint indicator is shown.
|
|
. |
Create another breakpoint after the package is executed.
|
|
. |
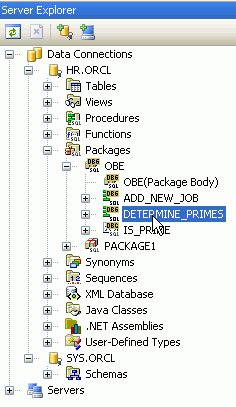
In the Server Explorer, double-click DETERMINE_PRIMES to open the code.
|
|
. |
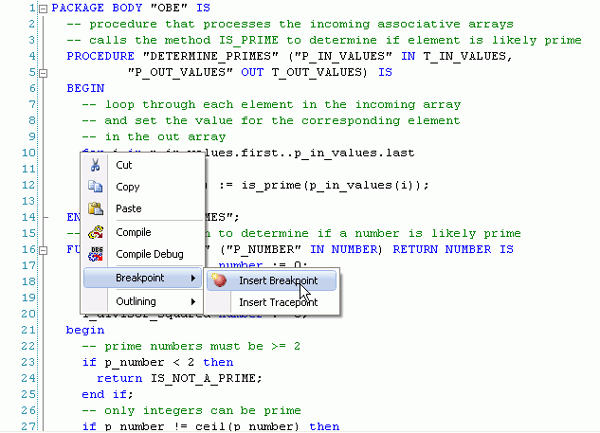
Create a breakpoint at the first statement after the BEGIN statement in the DETERMINE_PRIMES procedure.
|
|
. |
From the list of procedures, select ADD_NEW_JOB.
|
|
. |
Create a breakpoint at the first statement after the BEGIN statement.
|
|
. |
Click the Program.cs tab.
|
Debugging PL/SQL
In this topic, you execute the program using the debugger. Perform the following steps:
|
. |
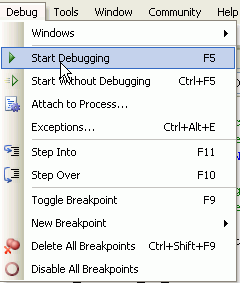
Now you are ready to debug your program. Select Debug > Start Debugging...
|
|---|---|
|
. |
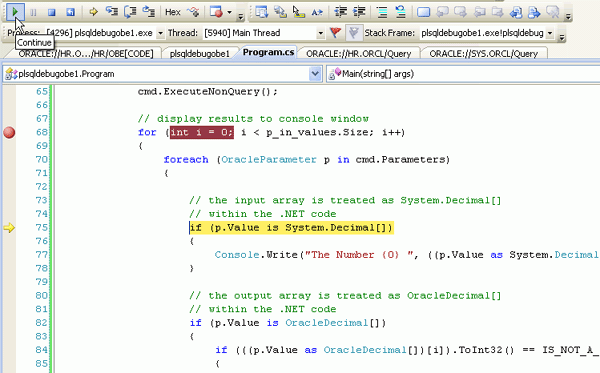
The debugger stops at the first breakpoint. To see the variables and their values, click the Local tab at the bottom of the window. Have a look at the code leading up to this breakpoint to understand how an array bind parameter is set up.
|
|
. |
To move to the next line, click the Step Into icon.
|
|
. |
You are at the statement that executes the PL/SQL Procedure. Click the Step Into icon.
|
|
. |
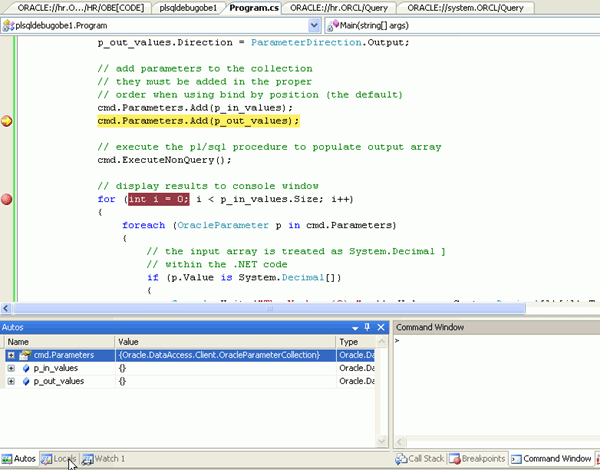
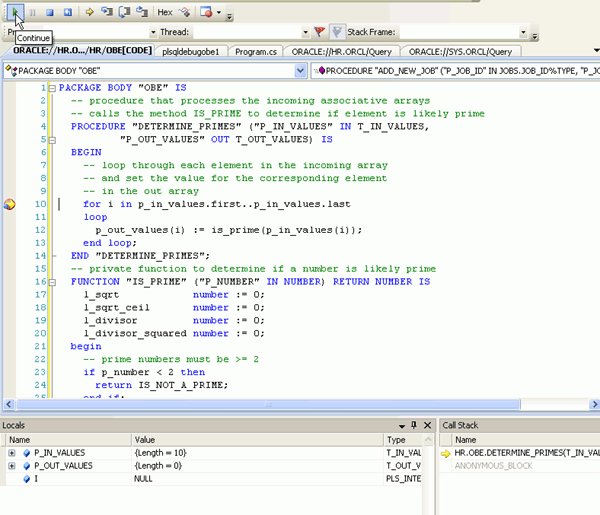
The next breakpoint is reached in the DETERMINE_PRIMES procedure. Notice that the P_IN_VALUES is an array of length 10 so the loop will be performed 10 times. Click the Continue icon a couple of times to see the values in the Local window change.
|
|
. |
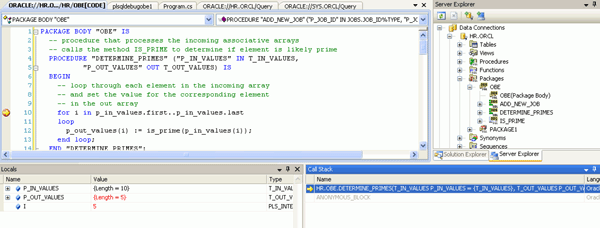
Click on the + icon next to the P_IN_VALUES variable name in the Locals window to view the contents of the input array. This is the array of values that was passed into this stored procedure from the C# application. Continue stepping through the code for a while. You can also expand the P_OUT_VALUES array to watch as it gets filled with values that are eventually returned by this stored procedure.
|
|
. |
Click the Call Stack tab in the lower right window. By examining the call stack, you can determine the code path to the current point in the execution of your program.
|
|
. |
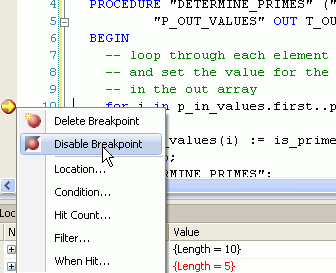
Disable this breakpoint so the program continues to the next breakpoint. Right-click the breakpoint and select Disable Breakpoint. You can also click directly on the red circle breakpoint icon to delete the breakpoint.
|
|
. |
Click the Continue icon so that the program executes until the next Breakpoint.
|
|
. |
The code performs the logic to produce what gets displayed to the user. Click Step Into a few more times.
|
|
. |
Click the Continue icon again to go to the next Breakpoint.
|
|
. |
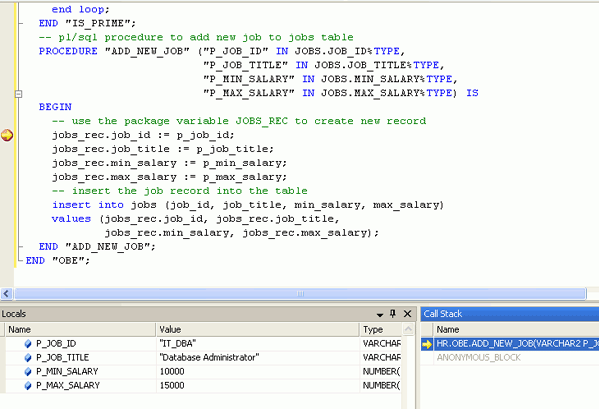
The ADD_NEW_JOB procedure breakpoint is reached.
|
|
. |
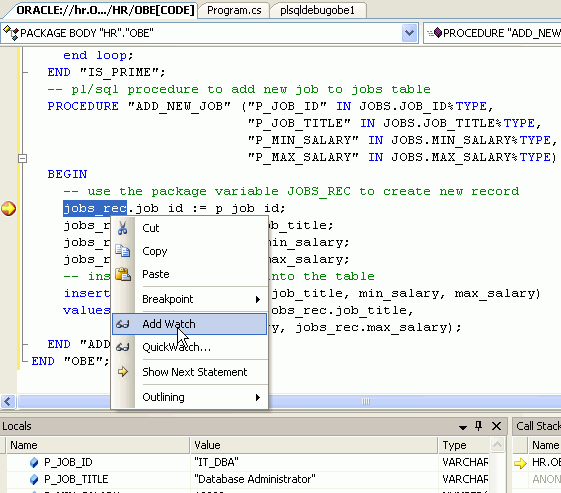
If you want to view the JOBS_REC PL/SQL record global variable, you need to create a watch. Select JOBS_REC and right-click, then select Add Watch. Then select the Watch tab at the bottom of the window.
|
|
. |
The Watch window is a built-in window in Visual Studio that allows you to examine specific program variables. Expand the JOBS_REC Watch.
|
|
. |
Click Step Into 4 times to see the Watch get populated. Then click Continue.
|
|
. |
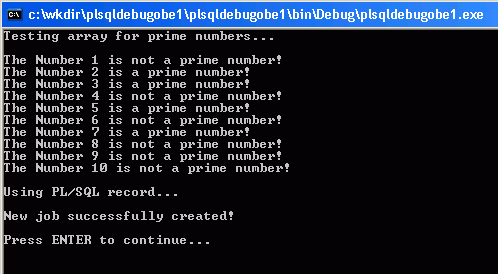
When the program finishes executing the results are shown.
|
Summary
In this tutorial, you have learned how to:
- Add a connection to the database and grant privileges for debugging
- Create a package and package body
- Create a project and configure the debug environment
- Debug PL/SQL
- Lead Curriculum Developer: Anupama Mandya, Pallavi Rajan
- Other Contributors: Marcie Young, Christian Shay
![]()

|
About
Oracle |Oracle and Sun | |