Oracle Enterprise Manager 12c Enterprise Ready Framework: Create and Use Credentials
Purpose
In this tutorial, you learn how to create and use a named credential, as well as setup a preferred credential, in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control 12c.
Time to Complete
Approximately 1 hour.
Overview
Security has always been an important part of Enterprise Manager. In this tutorial you familiarize yourself with the enhancements to the security model in the latest release.
Scenario
In this tutorial, you will:
- Create and use a named credential to access a monitored database.
- Set up a preferred credential that uses the named credential to access a database.
Software Requirements
The following is a list of software requirements:
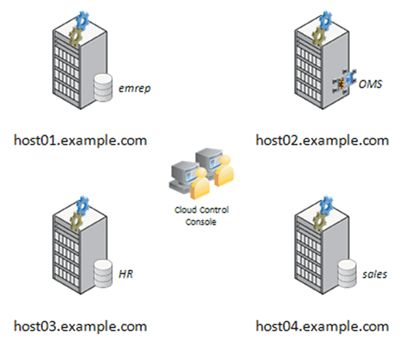
- Download and install the Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control 12c software, available from OTN at this link. You can either install the Oracle Management Repository (OMR) and Oracle Management Server (OMS) on a single host, or on two separate hosts. The examples used in this series of hands-on exercises have the OMR installed in a database called emrep on a host named host01.example.com, with the OMS running on the host host02.example.com.
- Add two hosts as targets, each of which also has an Oracle database installed. Our example architecture has the HR database running on host03.example.com, and the Sales database running on host04.example.com.
This example architecture is shown diagrammatically below:
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you should:
- Have the software installed as listed under Software Requirements
- Have created your own super administrator account in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control12.1 as shown here.
Note: Screen captures for this tutorial were taken in a Linux environment; if you are using a different operating system the browser look and feel will vary slightly.
Named Credentials
A named credential specifies a user's authentication information on a system. It can be a username/password, or a public key-private key pair, or an X509v3 certificate and is used for performing operations such as running jobs, patching and other system management tasks.
Creating Named Credentials
The first step in looking at the enhancements to security is to create a named credential.
|
. |
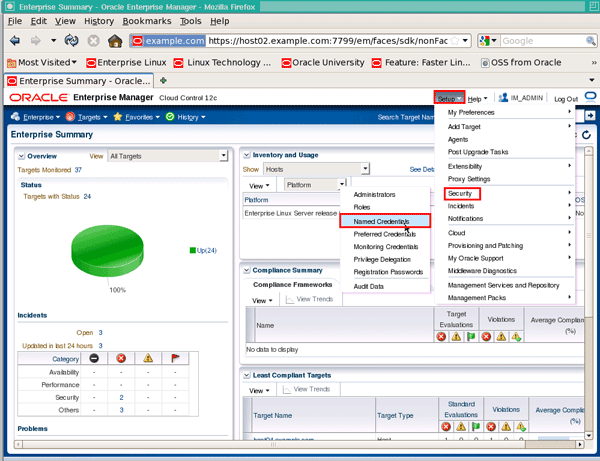
To create a named credential, first login to Enterprise Manager using the super-administrator account you created earlier, then from the Setup menu choose Security followed by Named Credentials:
|
|---|---|
|
. |
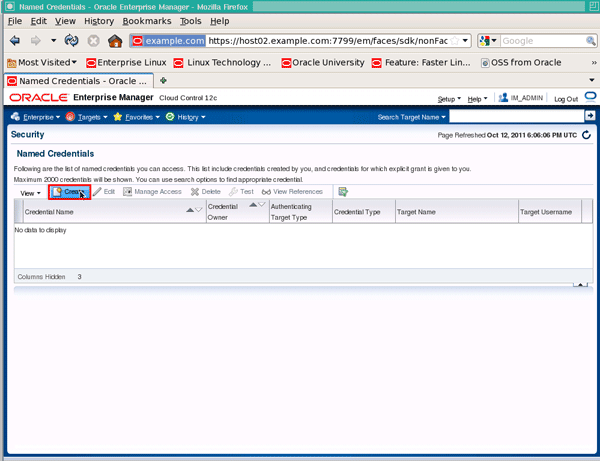
On the "Security" page, click the Create button:
|
|
. |
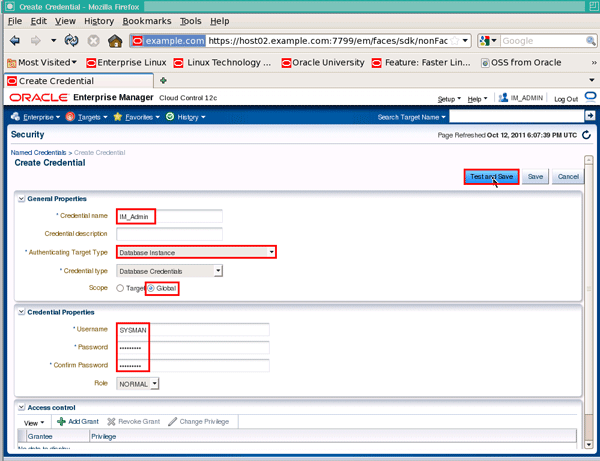
In the "Create Credential" region, enter a credential name of IM_Admin (or the super-administrator you created earlier) and from the "Authenticating Target Type" dropdown list, select Database Instance. Change the "Scope" radio button to Global, enter a username of SYSMAN, and the password for the SYSMAN database account, then click the Test and Save button. Note: The SYSMAN database account is locked by default. Make sure you unlock the SYSMAN database account first before you move on to the next step. To unlock the account, you can either use the Database Management console in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, or connect to the database as SYS using SQL*Plus and issue the ALTER USER sysman ACCOUNT UNLOCK command.
|
|
. |
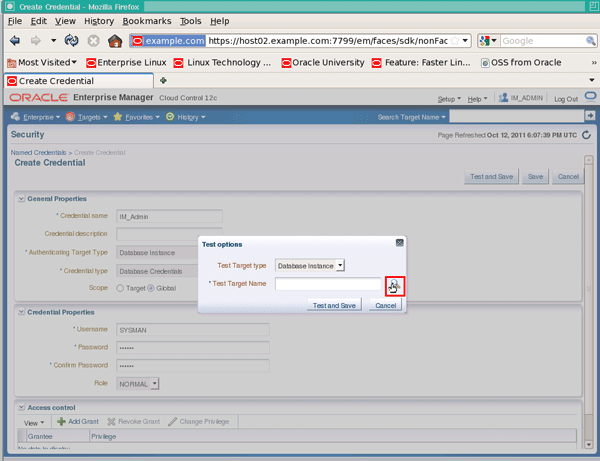
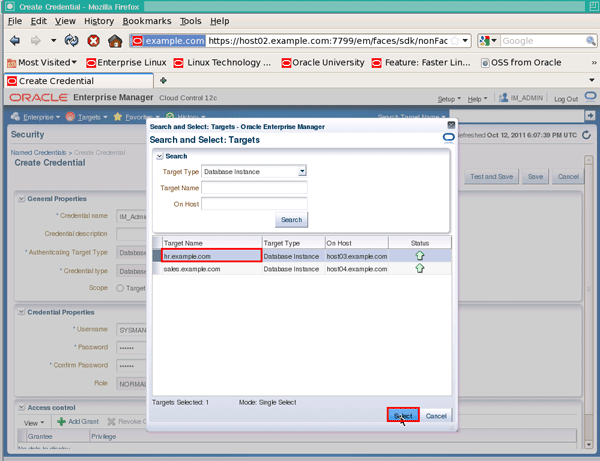
On the "Test options" pop-up, click the selector icon to the right of the "Test Target Name" field:
|
|
. |
Next, select the target name hr.example.com, followed by Select:
|
|
. |
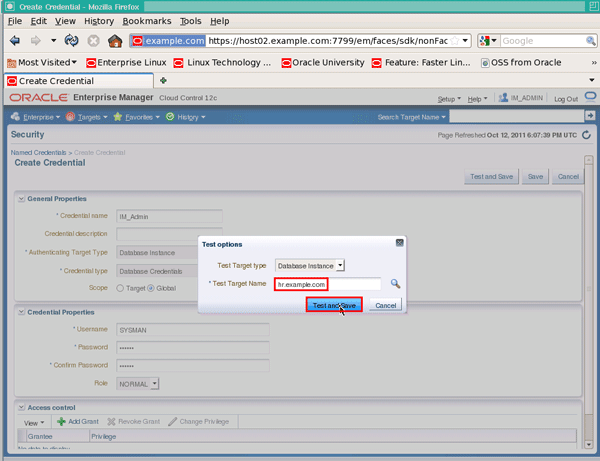
The "Target Name" field should now be populated with "hr.example.com". Click the Test and Save button:
|
|
. |
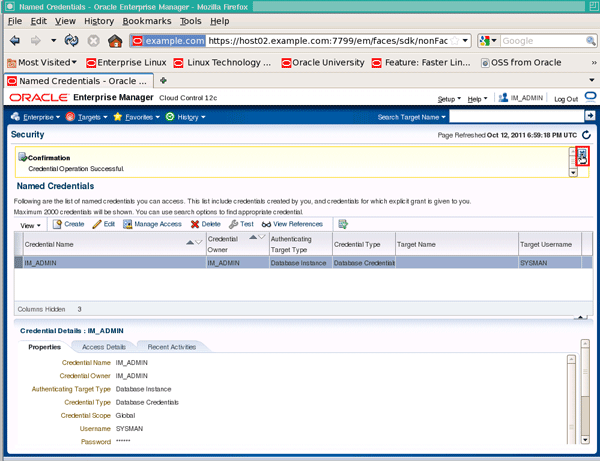
Click the close icon to close the confirmation message:
|
|
. |
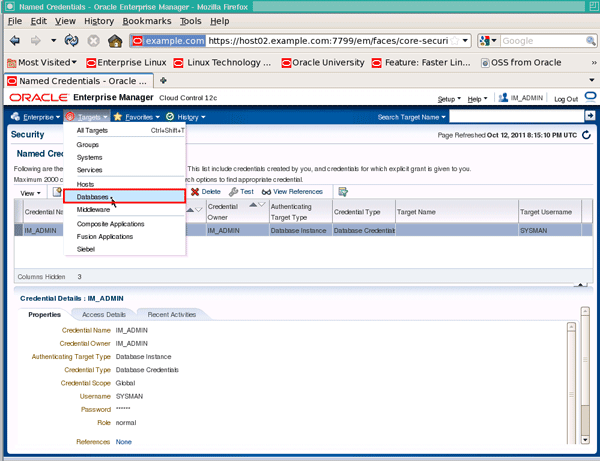
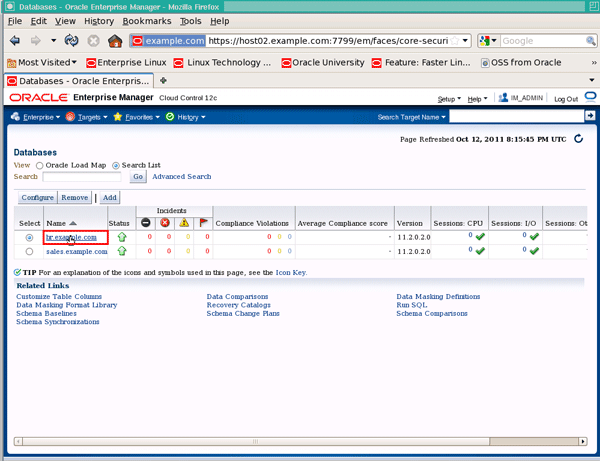
To verify the credential works, let's login with the credential. Click the Targets menu and select Databases:
|
|
. |
Click the database name hr.example.com (you may need to switch to Search List mode instead of the Oracle Load Map for this):
|
|
. |
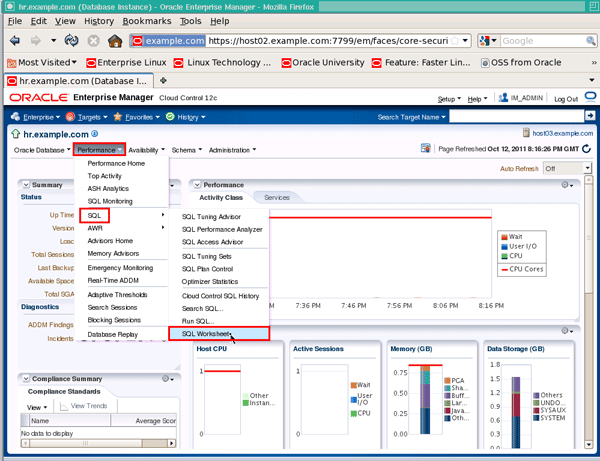
Click the Performance menu, then choose SQL and SQL Worksheet. Note: Make sure your browser's popup-blocker is turned off for this site.
|
|
. |
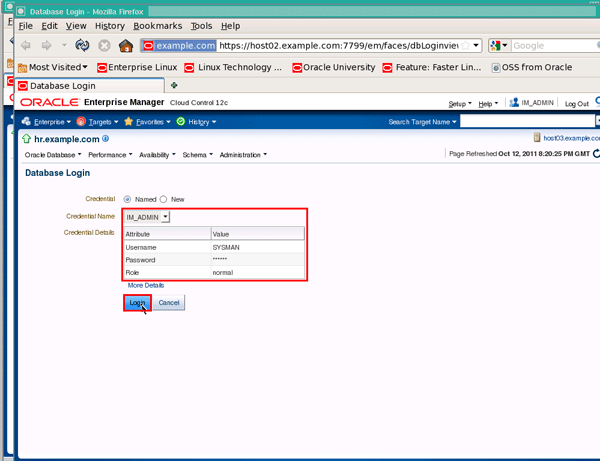
The named credential should be chosen by default and credentials populated, so just click the Login button:
|
|
. |
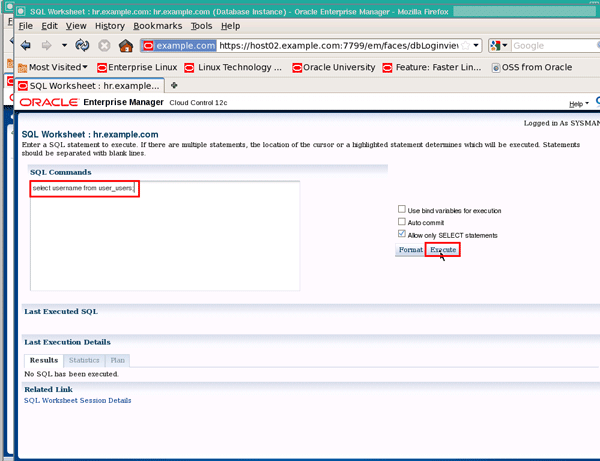
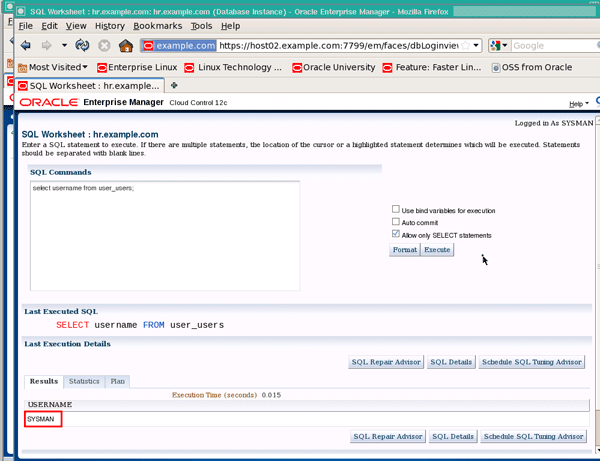
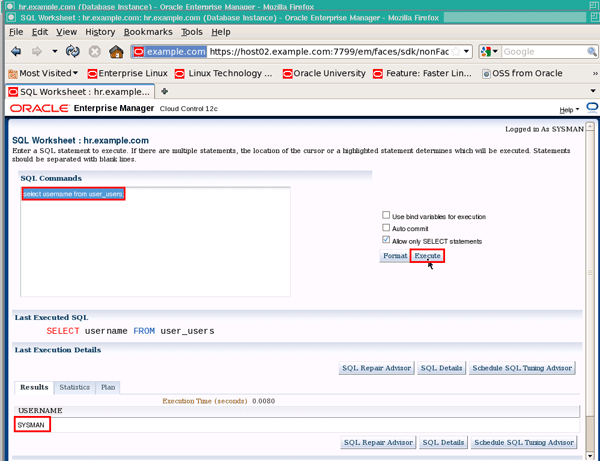
Enter the SQL command select username from user_users; and click the Execute button:
|
|
. |
You should see the value "SYSMAN" displayed in the Results region. Close the SQL Worksheet window when you are finished:
|
Using Named Credentials
Now that we've created a named credential, let's look at an example of where it can be used.
|
. |
Named credentials can be used to execute jobs. Click the Enterprise menu, followed by Job and then Activity:
|
|---|---|
|
. |
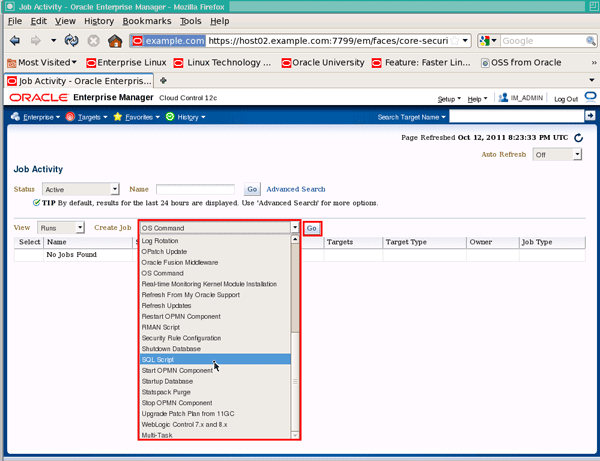
This will bring you to the Job Activity page. Click on the Create Job dropdown list, select SQL Script and then click Go:
|
|
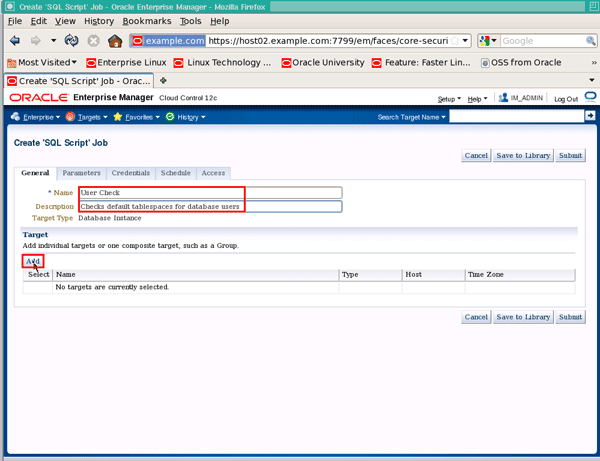
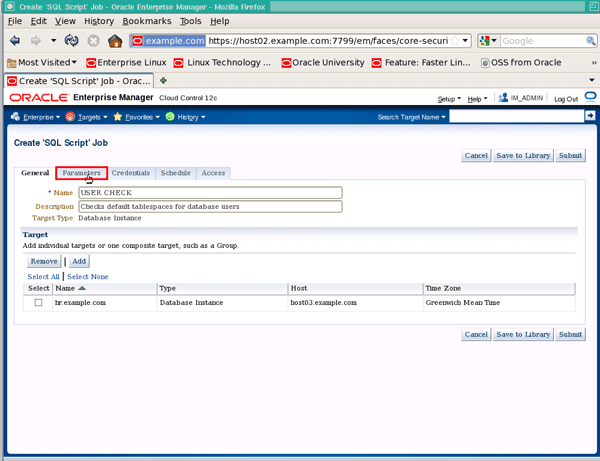
On the "Create 'SQL Script' Job" page, enter a name of User Check, a description of Checks default tablespaces for database users and click Add to add targets to the job:
|
|
|
Click the check box next to hr.example.com, then click the Select button:
|
|
|
. |
Click on the Parameters tab:
|
|
. |
In the "SQL Script" text box, enter the text select username, default_tablespace from dba_users; after the existing text, then click the Credentials tab:
|
|
. |
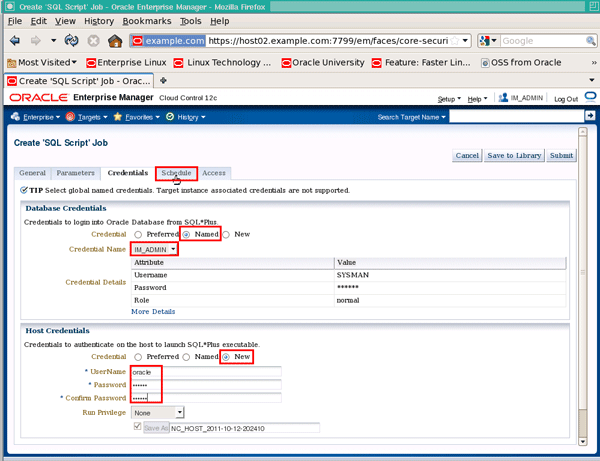
On the "Credentials" tab page, click the Named Credential radio button. If the credential name "IM_Admin" doesn't appear by default, select it from the Credential Name dropdown list (if there are no named credentials here, it probably means you created the named credential as target specific, rather than global, so you will need to edit the named credential to be global before proceeding). In the "Host Credentials" region, click New Credential since we have not yet created any host credentials, and enter a username and password of oracle (or if this is not the username and password for the ORACLE user defined on your host, enter the values that match your system here). Then click the Schedule tab:
|
|
. |
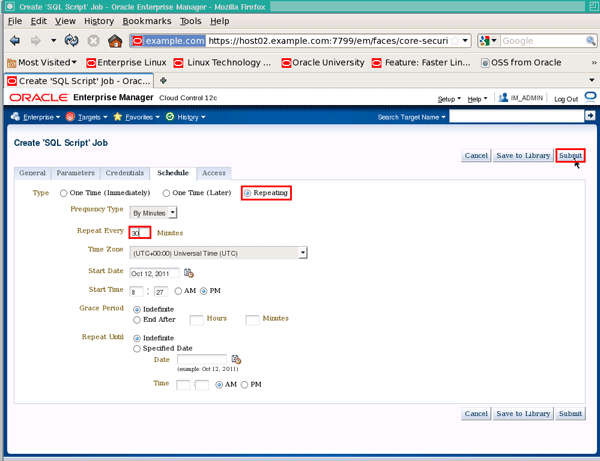
The default schedule is to run the job immediately, so click the Repeating radio button and enter a "Repeat Every" value of 30 minutes, then click the Submit button. Note: For the purposes of this tutorial, you could also just use the default schedule of One Time (Immediately) so that you can more quickly see the results from the job run.
|
|
. |
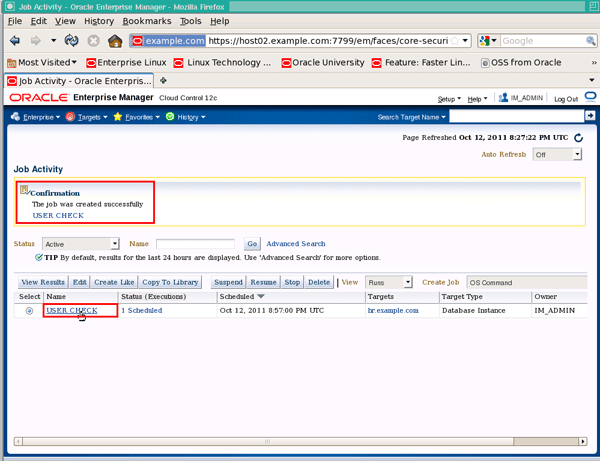
You should see confirmation window, and the job "USER CHECK" should be listed with a status of "1 Scheduled". Click the job name to drill into the "Job Run: USER CHECK" page:
|
|
. |
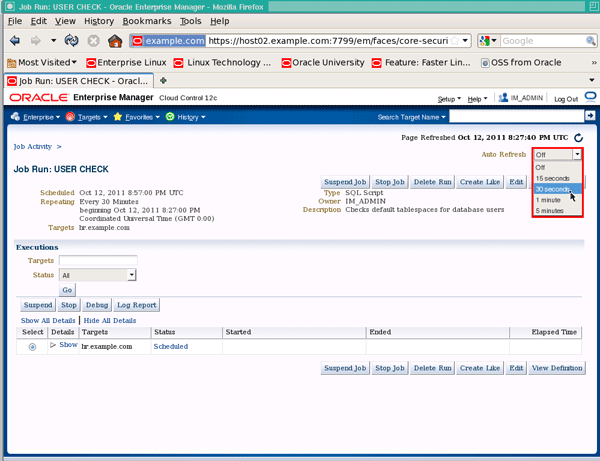
The job will stay in scheduled status until the time it was scheduled to execute next. You can change the value of the Auto Refresh drop down to 30 seconds, then wait for the job status to change to "Succeeded":
|
|
. |
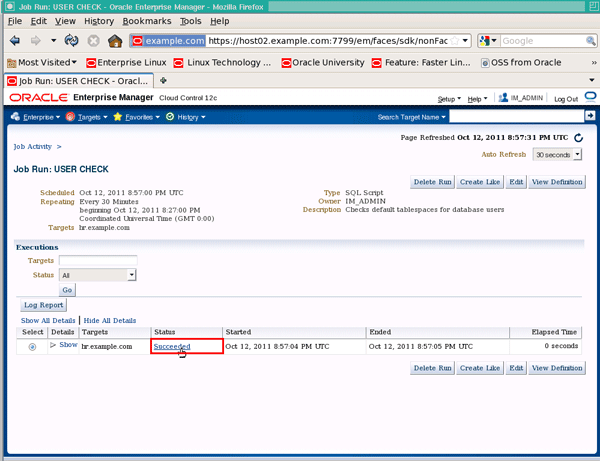
Once the status changes to "Succeeded" click the Succeeded status to drill into the job execution:
|
|
. |
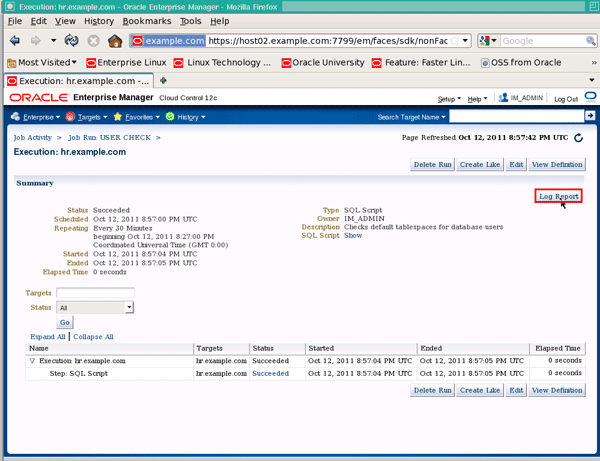
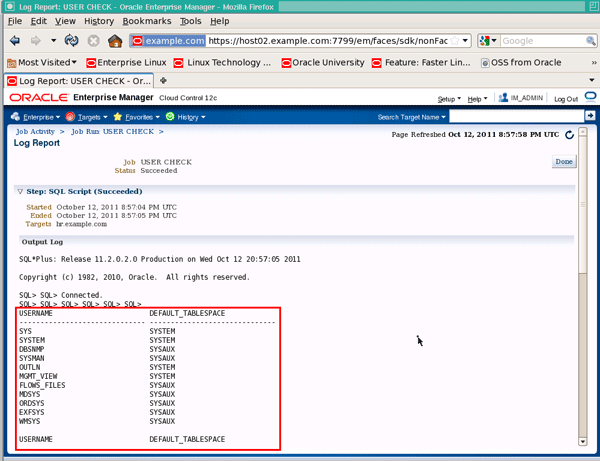
Click the Log Report button to show the job results:
|
|
. |
You should see a list of usernames and their default tablespaces:
|
Preferred Credentials
Named credentials can also be used as preferred credentials once they have been created. Let's look at how that is done.
|
. |
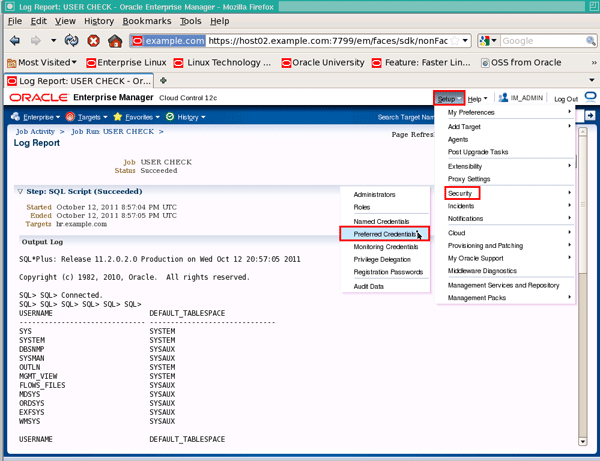
To setup a preferred credential, we again start by clicking the Setup menu, followed by Security and then Preferred Credentials:
|
|---|---|
|
. |
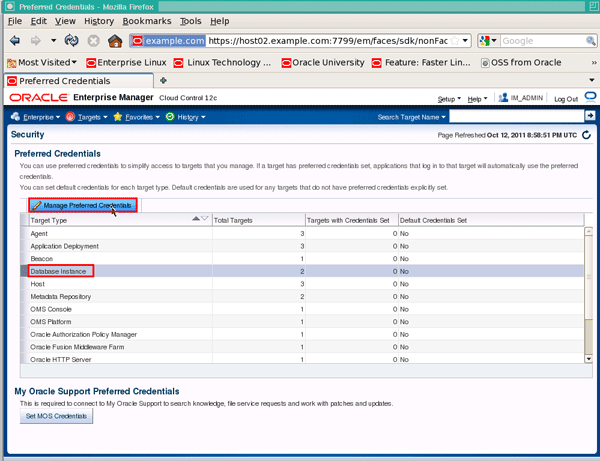
On the "Preferred Credentials" page, click the target type Database Instance and then click Manage Preferred Credentials:
|
|
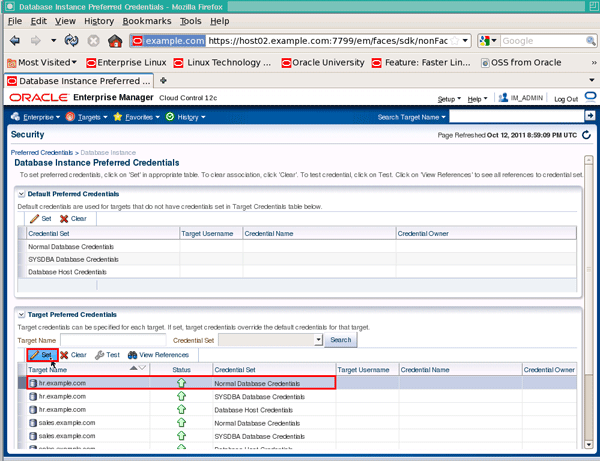
On the "Database Instance Preferred Credentials" page, select the target name hr.example.com row that has a credential set of "Normal Database Credentials" and click Set:
|
|
|
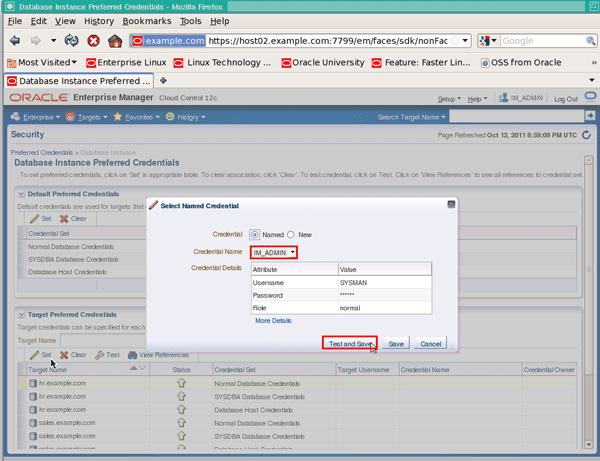
On the "Select Named Credential" popup, choose a credential name of IM_ADMIN (or the super-administrator you created earlier) from the dropdown list if not automatically selected, then click the Test and Save button:
|
|
|
. |
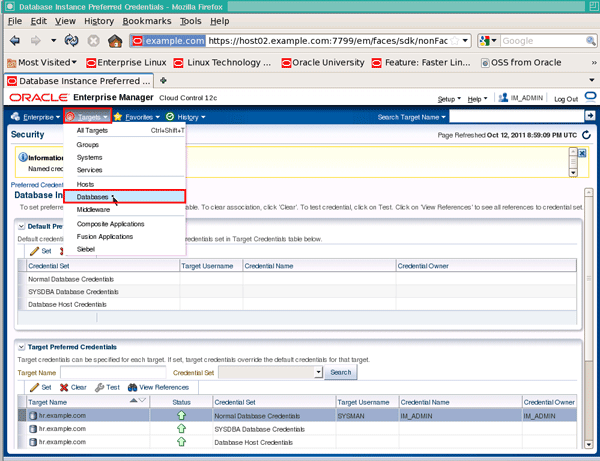
A confirmation message should be displayed. To validate the setting, click the Targets menu, then Databases:
|
|
. |
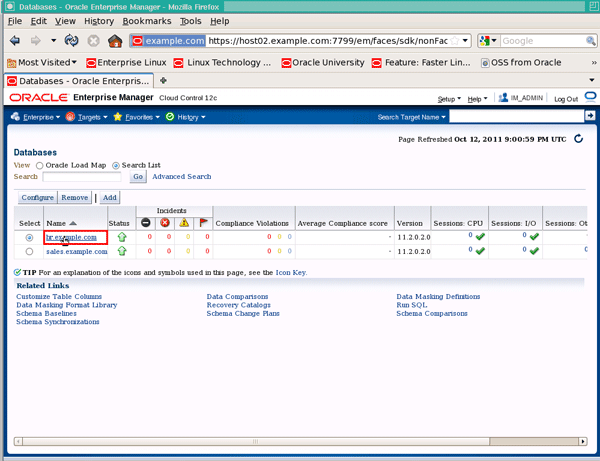
From the "Search List", click hr.example.com:
|
|
. |
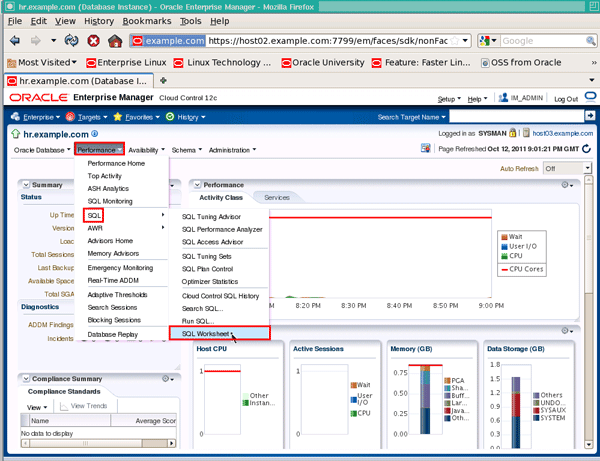
Next, select the Performance menu, followed by SQL and SQL Worksheet. Note: Make sure your browser's popup-blocker is turned off for this site.
|
|
. |
Enter the SQL command select username from user_users; (if not already entered for you) then click the Execute button. The "Results" region should show a value of "SYSMAN":
|
Summary
The security enhancements in the latest release of Enterprise Manager are designed to secure your enterprise infrastructure even further than previous releases.
In this tutorial, you should have learned how to:
- Create and use a named credential to access a monitored database.
- Set up a preferred credential that uses the named credential to access a database.
Resources
- Oracle Enterprise Manager documentation set
- To learn more about Oracle Enterprise Manager, refer to additional OBEs in the Oracle Learning Library
![]()