Oracle GoldenGate: HP NonStop Audited Enscribe to IBM DB2
Overview
- Prepare your environment to configure the GoldenGate processes.
- Configure and execute the initial data load process.
- Configure and start the change capture of database operations.
- Configure and start the change delivery of database operations.
- Manager:
- There is a Manager on the source host and a separate Manager on the target host. The Manager starts and stops the other processes on the source and target instances. The Manager is not required for passing traffic once the Extract or Replicat is running.
- Initial Load:
- Optional. Used to populate the target tables one time. It can read either from the source tables directly or from ASCII files.
- Extract:
- Runs on the source to capture transaction data to trail files. There are two versions of Extract: Classic (this OBE) and Integrated.
- Data Pump:
- Optional, but highly recommended. The Data Pump sends trail files from the source instance to the target instance over an IP network. Technically the Data Pump is a secondary Extract. This OBE does not have a Data Pump.
- Replicat:
- Delivers data to the target database. Normally the Replicat runs on the target.
- Some_Command
- You type this as a command or a value. Example:
Enter ./ggsci to start the command line interpreter.
- Some_Prompt
- The system responds with this as a prompt or reply. Example:
After the welcome splash banner, you can enter commands at the GGSCI (host01) 1> prompt.
- Some_Button
- Click this on-screen button. Example:
After selecting the version you want, click Continue to start the download.
- Some_Variable
- A variable that you substitute with a real value. Example:
Enter your userid/password at the prompt.
- Some_Filename
- A filename, path, or folder/directory. Example:
Edit the hosts file in the /etc directory.
- Some_Code
- A keyword or code element. Example:
Change the parameter HandleCollisions to NoHandleCollisions after the initial load.
- p=process=
- e(xtract), p(ump), r(eplicat), i(nitial), d(efgen), s(tartup).
- xxxx=project=
- All files related to a common project xxxx, for example hr, sales, engr, test.
- hh=host-to-host=
- aa, ab, ba, bb, as indicated by source and target host names where a=host01, and b=host02. Later on you will see that you cannot use numbers as part of some file names, so better not to go there at all.
- ext=extension=
- prm=parameter (stored in dirprm/), dsc=discard, rpt=report (stored in dirrpt/), def=definition (stored in dirdef/), oby=obey (stored in installation directory), sql=SQL (stored in dirsql/).
Purpose
Upon completion of this Oracle-By-Example (OBE) tutorial, you will be able to keep two heterogeneous databases synchronized; in this case an HP NonStop audited Enscribe database (source) to an IBM DB2 database (target) using Oracle GoldenGate.
During this lesson, you will learn how to:
Time to Complete
Approximately 2 hours
Introduction
Using Oracle GoldenGate for HP NonStop Audited Enscribe to IBM DB2 Database Synchronization
Oracle GoldenGate provides very fast replication of heterogeneous databases by reading transaction logs and writing the changes to one or more target databases. There are five processes involved in a typical environment:
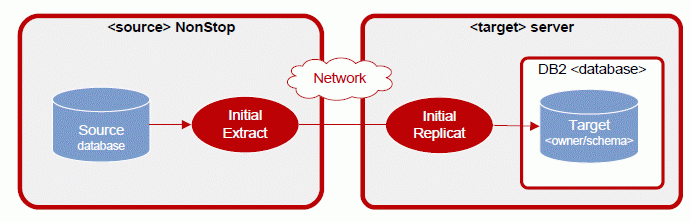
NonStop Audited Enscribe to DB2 configuration

The following diagram illustrates GoldenGate a configuration with NonStop audited source data being replicated to a DB2 target database.
In summary, the environment is:
| Host Name | Color | OS | Database | Source/Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| host01 | Green | HP | NonStop | Source |
| host02 | Blue | IBM | DB2 | Target |
Prerequisites
The source is an audited Enscribe database on HP NonStop and the target is an IBM DB2 database.
Bear in mind that there are two hosts: host01 and host02; and that each host has three environment prompts: OS, GGSCI, and SQL. That makes six different places in which you could be typing! Try to be extra careful about which command you enter in which location. The wrong command in the wrong context is the most common error.
Overview of Tasks
Prepare the Environment
In order to execute this lesson, the GoldenGate application must be installed on both the source and target systems. The installation includes a sample database and scripts to generate initial data as well as subsequent update operations. The source and target tables are created and loaded with initial data. The GoldenGate Manager processes are also started so that other processes may be configured and started.
Configure Initial Data Load
Initial database synchronization is almost always required. To initially load data across heterogeneous databases, you have limited choices. GoldenGate provides the ability to perform initial data synchronization while your application remains active. The capture process also provides flexible output options, including the capability to format the data to be loaded with bulk load utilities, such as DB2 Load.
This lesson demonstrates using the direct load method to capture data directly from the source tables and send the data directly to the delivery process on the target system.
Configure Change Capture (Extract)
For audited tables, the Extract process is configured to capture change data directly from the TMF audit trails and store the changes in a data queue known as GoldenGate remote trails.
Configure Change Delivery (Replicat)
Once the tables have been initially loaded with data, the delivery process is configured to synchronize the captured change data into the target database.
Typographic Conventions
Text color and font in the directions and in the screens should be interpreted as follows:
File and Process Naming Conventions
File and process naming conventions can be whatever works for you or your company. Here are the sample conventions used in this OBE:
pxxxxhh.ext
where:
1. Prepare your Environment to Configure the GoldenGate Processes
- Configure and start the Manager processes.
- Prepare the source and target sample databases.
Objective
The goals of this exercise are to:
1.1 Prepare the Source NSK Environment
Configure a GLOBALS parameter file on the source.
Execute the following commands on the source system unless a $<prefix> is not needed for your installation.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
TACL> VOLUME <install_vol>.<install_subvol> TACL> TEDIT GLOBALS ADD DEFINE =GGS_PREFIX, CLASS MAP, FILE $<prefix> |
A GLOBALS parameter can be used to uniquely identify each GoldenGate instance when multiple environments exist on single NSK node. Use the two-character <prefix> that was defined in the Lab Preparation.
Configure the Manager process on the source system.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
TACL> VOLUME <install_vol>.<install_subvol> TACL> RUN GGSCI GGSCI> TEDIT PARAMS MGRPARM -- GoldenGate Manager Parameter file TCPIPPROCESSNAME <tcpip_process> PORT <port> GGSCI> START MANAGER, CPU 1, PRI 180 (Verify the results:) GGSCI> INFO MANAGER |
The Manager process is responsible for starting and monitoring all of the other GoldenGate processes. You will always have one manager process per GoldenGate instance.
Create and load source files.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
(Move the script to the source data volume:) TACL> VOLUME <install_vol>.GGSSOU TACL> FUP DUP <install_subvol>.DEMOLDEO,* (Run the scripts:) TACL> VOLUME <install_vol>.GGSDDL TACL> DDL/IN <install_vol>.GGSSOU.DEMOLDEO/ (Create files and turn audit on:) TACL> FUP /IN <install_vol>.<install_subvol>.DEMOFUPS/ TACL> FUP ALTER ECUSTMER, AUDIT TACL> FUP ALTER ECUSTORD, AUDIT (Load the files:) TACL> RUN <install_vol>.<install_subvol>.DEMOLDEO (Within DEMOLDEO the following prompts and replies are issued:) To perform an initial load enter (I), to update the database enter (U) or to exit the program enter (E). ?I To perform an initial load enter (I), to update the database enter (U) or to exit the program enter (E). ?E (Verify the results:) TACL> FUP COPY ECUSTMER TACL> FUP COPY ECUSTORD |
The installation includes scripts to create sample tables and generate initial data.
Note that your <prefix> may need to be substituted for the GG in subvolumes GGSSOU and GGSDEF used in this section.
Generate source definitions.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
TACL> VOLUME <install_vol>.<install_subvol> TACL> RUN DEFGEN (Within DEFGEN, the following prompts and replies are issued:) Enter definitions filename (or Exit): <install_vol>.GGSDEF.ECUSTDEF File/Table to create definition for: <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTMER Include DDL record definition (Y/N)? Y DDL Dictionary: <install_vol>.GGSDDL DDL record or definition name ECUSTOMER.REC Definition retrieved. File/Table to create definition for (or Exit): <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTORD Include DDL record definition (Y/N)? Y DDL Dictionary: <install_vol>.GGSDDL DDL record or definition name ECUSTORD.REC Definition retrieved. File/Table to create definition for (or Exit): EXIT |
The DEFGEN utility is an interactive program that generates a source definition file describing the layouts of the files/tables that are to be replicated.
Move the source definitions to the target.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
[OS prompt] ftp ogg_user@target_host
put filename.def
|
After exiting, FTP the file <install_vol>.GGSDEF.ECUSTDEF in ASCII format to the target <install_location>/dirdef/source.def
Generate target database scripts based on your source layouts.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
TACL> VOLUME <install_vol>.<install_subvol> TACL> RUN DDLGEN -d <install_vol>.GGSDEFS.ECUSTDEF (This initiates an interactive DDLGEN session with the following prompts and replies: Enter definitions filename (or Exit): <install_vol>.GGSDEF.ECUSTSQL DDL template file name (or Exit): TMPLDB2 File/Table to create definition for (or Exit): <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTORD Definition retrieved. File/Table to create definition for (or Exit): <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTMER Definition retrieved. File/Table to create definition for (or Exit): EXIT |
The DDLGEN utility is an interactive program that generates a script containing table create statements for your target database based on the layouts of your source files/tables.
Move the scripts.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
[OS prompt] ftp ogg_user@target_host
put filename.sql
|
After exiting, FTP the file <install_vol>.GGSDEF.ECUSTSQL in ASCII format to the target file <install_location>/dirsql/ecust.sql.
This concludes Preparing the Source NSK Environment.
1.2 Prepare your Target DB2 Environment
Configure the Manager process on the target system.
Execute the following commands on the target system.
| Host02 - DB2 |
(Start the command interface:) Shell> cd <install_location> Shell> ggsci (Specify the port that the Manager should use:) GGSCI> EDIT PARAMS MGR -- GoldenGate Manager Parameter file PORT <port> (Start Manager:) GGSCI> START MANAGER (Verify the results:) GGSCI> INFO MANAGER |
The Manager should have a STATUS of RUNNING.
Create target DB2 tables.
Execute the following commands on the target system to run the script that creates the tables.
You are advised to edit the table create scripts, tcust.sql, and update the database connection information to match your system. For example, on the first line add:
CONNECT TO <database>
| Host02 - DB2 |
Shell> cd <install_location> Shell> db2 -tf <install_location>/dirsql/ecust.sql (Verify the results:) Shell> db2 db2 => connect to <database> db2 => describe table ECUSTMER db2 => describe table ECUSTORD db2 => quit |
The two sample ECUST* tables should exist, but be empty. Additional table create scripts for the sample database can be found in the GoldenGate for DB2 installation directory named demo_db2_create.sql.
This concludes preparing the target DB2 environment.
2. Initial Data Load
- Configure the initial load capture task.
- Configure the delivery of the data to the target system.
- Execute and verify the initial load of data.
Objective
The goals of this exercise are to:
2.1 Configure Initial Load Capture
Add the initial load capture batch task group.
Execute the following commands on the source system to add an Extract process called EINI<unique_id>. *
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
GGSCI> ADD EXTRACT EINI<unique_id>, SOURCEISTABLE (Verify the results:) GGSCI> INFO EXTRACT *, TASKS |
* The process names used in lab exercises, for example EINIBD1, are made up of
1) One character for the GoldenGate process (E for Extract, R for Replicat);
2) Three or four characters to describe the process type (INI for initial data load, ORA for capture from or delivery to an Oracle database, and so on) and
3) Three characters usually made up of the student's initials plus a sequential number to uniquely identify multiple occurrences of that type of process.
Create the initial load parameter file.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
GGSCI> EDIT PARAM EINI<unique_id> -- -- GoldenGate Initial Data Capture -- for ECUSTMER and ECUSTORD -- EXTRACT EINI<unique_id> RMTHOST <target>, MGRPORT <port> RMTTASK REPLICAT, GROUP RINI<unique_id> TABLE <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTMER; TABLE <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTORD; |
Examine the results to verify it was successful.
This completes the Initial Load Capture.
2.2 Configure Initial Load Delivery
Add the initial load delivery batch task group.
Execute the following command in GGSCI to create the batch task on the target system.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> ADD REPLICAT RINI<unique_id>, SPECIALRUN (Verify the results:) GGSCI> INFO REPLICAT *, TASKS |
Configure the initial load delivery parameter file.
Execute the following command in GGSCI to open the editor on the target system.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> EDIT PARAM RINI<unique_id> -- -- GoldenGate Initial Load Delivery REPLICAT RINI<unique_id> TARGETDB <database>, USERID <login>, PASSWORD <password> DISCARDFILE ./dirrpt/RINI<unique_id>.dsc, PURGE SOURCEDEFS ./dirdef/source.def MAP <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTMER, TARGET <owner/schema>.ECUSTMER; MAP <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTORD, TARGET <owner/schema>.ECUSTORD; |
Note: Remember to use <db_type>.def if you renamed source.def when you transferred it to the <target>.
This completes the Initial Load Delivery.
2.3 Execute the Initial Load
Execute the initial load task.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
GGSCI> START EXTRACT EINI<unique_id> (Verify the results:) GGSCI> VIEW REPORT EINI<unique_id> |
Verify the results.
Execute the following commands on the target system.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> VIEW REPORT RINI<unique_id>
|
This completes the Initial Data Load.
3. Configure Change Capture
- Configure and add the Extract process that will capture changes.
- Add the trail that will store these changes.
- Start the capture (Extract) process.
Objective
The goals of this exercise are to:
3.1 Configure Change Capture
Create the Extract parameter file.
Execute the following commands on the source system to define an Extract named EENS<unique_id> to pull data from the Enscribe TMF audit trails and route these changes to GoldenGate trails.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
GGSCI> EDIT PARAM EENS<unique_id> -- -- Change Capture parameter file to capture -- ECUSTMER and ECUSTORD Changes -- EXTRACT EENS<unique_id> TCPIPPROCESSNAME <tcpip_process> FETCHCOMPS RMTHOST <target>, MGRPORT <port> RMTTRAIL ./dirdat/<trail_id> TABLE <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTMER; TABLE <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTORD; |
Note: Record the two characters selected for your <trail_id>: ______. You will need this defining the remote trail and for identifying the trail to be read by Replicat.
Add the Extract group.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
GGSCI> ADD EXTRACT EENS<unique_id>, BEGIN NOW, CPU 1, PRI 160 (Verify the results:) GGSCI> INFO EXTRACT EENS<unique_id> |
The default CPU is the CPU in which the Manager runs.
Define the GoldenGate remote trail.
Execute the following commands on the source system to add the trail declared in the EENS<unique_id> Extract parameters. This will be located on the target system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
GGSCI> ADD RMTTRAIL ./dirdat/<trail_id>, EXTRACT EENS<unique_id>,
MEGABYTES 5
|
This completes configuring the extract.
3.2 Start the Extract Processes
Start the capture process.
Execute the following commands on the source system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
GGSCI> START EXTRACT EENS<unique_id> (Verify the results:) GGSCI> INFO EXTRACT EENS<unique_id> GGSCI> VIEW REPORT EXTRACT EENS<unique_id> |
The process STATUS should be RUNNING.
3.3 Discussion Points (Optional)
Identifying a remote system
What parameters are used to identify the remote target system?
Using the FETCHCOMPS parameter
What action is triggered by the FETCHCOMPS parameter? What type of input record is affected?
Hint: Search in the NSK Reference Guide for FETCHCOMPS | FETCHLASTIMAGE.
4. Configure Change Delivery (Replicat)
- Set up the checkpoint table on the target system.
- Create a named group that includes the Replicat process and the checkpoint tables.
- Configure the Replicat group by adding parameters.
- Start the Replicat group.
Objective
The goals of this exercise are to:
4.1 Set up the Checkpoint Table
Create a GLOBALS file on the target system.
Execute the following commands on the target system.
Create and edit the GLOBALS parameter file to add the checkpoint table:
| Host02 - DB2 |
Shell> cd <install_location> Shell> ggsci GGSCI> EDIT PARAMS ./GLOBALS CHECKPOINTTABLE <owner/schema>.ggschkpt |
Record the checkpoint table owner and name, then save and close the file.
Table owner ____________________ name ___________________
Note: You could name the table anything you want, but for training purposes we are using ggschkpt.
Verify that the GLOBALS file was created in the root GoldenGate directory, and remove any file extension that was added.
Activate the GLOBALS parameters.
For the GLOBALS configuration to take effect, you must exit the session in which the changes were made. Execute the following command to exit GGSCI.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> EXIT
|
Add a Replicat checkpoint table.
Execute the following commands on the target system.
| Host02 - DB2 |
Shell> cd <install_location> Shell> ggsci GGSCI> DBLOGIN SOURCEDB <database>, USERID <login>, PASSWORD <password> GGSCI> ADD CHECKPOINTTABLE |
This completes setting up the checkpoint table.
4.2 Configure Change Delivery
Add the Replicat group.
Execute the following commands on the target system to add a delivery group named RDB2<unique_id>.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> ADD REPLICAT RDB2<unique_id>, EXTTRAIL ./dirdat/<trail_id>
|
Note: Refer to your Extract set up for the correct two-character <trail_id>, referred to back then as <remote_trail>.
Create Replicat parameter file.
Execute the following commands on the target system to bring up the parameter file in the editor.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> EDIT PARAM RDB2<unique_id> (Type in the following parameters:) -- -- Change Delivery parameter file to apply -- ECUSTMER and ECUSTORD Changes -- REPLICAT RDB2<unique_id> USERID <login>, PASSWORD <password> HANDLECOLLISIONS SOURCEDEFS ./dirdef/source.def DISCARDFILE ./dirrpt/RDB2<unique_id>.DSC, PURGE MAP <source_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTMER, TARGET <owner/schema>.ECUSTMER; MAP <source_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTORD, TARGET <owner/schema>.ECUSTORD; |
Note: Remember to use <db_type>.def if you renamed the source.def when you transferred it to the <target>.
Start the Replicat process.
Execute the following commands on the target system.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> START REPLICAT RDB2<unique_id> (Verify the results:) GGSCI> INFO REPLICAT RDB2<unique_id> |
This completes configuring change delivery (Replicat).
4.3 Discussion Points (Optional)
When to use HANDLECOLLISIONS
For which stage of GoldenGate processing - change capture, initial data load, or change delivery - would you use HANDLECOLLISIONS? What does it do?
What information is supplied by SOURCEDEFS?
What is the purpose of the DISCARDFILE?
5. Generate Activity and Verify Results
- Execute miscellaneous update, insert, and delete operations on the source system.
- Verify the delivery of the changes to the target.
- Turn off the error handling used for the initial load.
Objective
The goals of this exercise are to:
5.1 Generate Database Operations
Execute miscellaneous update, insert, and delete operations.
Execute the following commands on the target system.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
TACL> VOLUME <install_vol>.GGSSOU; TACL> RUN <install_vol>.<install_subvol>.DEMOLDEO (Within DEMOLDEO the following prompts and replies are issued:) To perform an initial load enter (I), to update the database enter (U) or to exit the program enter (E). ?U To perform an initial load enter (I), to update the database enter (U) or to exit the program enter (E). ?E |
5.2 Verify Change Capture and Delivery
Verify your results on the source system.
Execute the following commands on the source system to view the contents of the source Enscribe files.
| Host01 - HP NonStop |
TACL> FUP COPY <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTMER TACL> FUP COPY <install_vol>.GGSSOU.ECUSTORD |
Verify your results on the target system to verify the target data.
| Host02 - DB2 |
Shell> cd <install_location> Shell> db2 db2 => connect to <database> db2 => select * from ECUSTMER db2 => select * from ECUSTORD db2 => quit Shell> ggsci GGSCI> SEND REPLICAT RDB2<unique_id>, REPORT GGSCI> VIEW REPORT RDB2<unique_id> |
5.3 Turn Off Error Handling
Turn off initial load error handling for the running delivery process.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> SEND REPLICAT RDB2<unique_id>, NOHANDLECOLLISIONS
|
Remove initial load error handling from the parameter file.
| Host02 - DB2 |
GGSCI> EDIT PARAM RDB2<unique_id>
|
Remove the HANDLECOLLISIONS parameter.
This completes the turning off of error handling.
This completes the generation of activity.
Summary
- Configure and start Extract and Replicat processes for Initial Load of tables
- Generate sample data and test the validity of the replication
- Manage the reports produced by the processes
- Oracle GoldenGate Product Documentation version 11.2.1 (E35209-01) and other older versions
- Courses from Oracle University
- External Web sites for related information
- To learn more about Oracle GoldenGate, refer to additional OBEs in the Oracle Learning Library
- The original PDF of this OBE locally. The HTML-based version supercedes the PDF-based version. You can see the original listed by going here, you can view the original online here.
- Lead Curriculum Developer: Steve Friedberg.
- Other Contributors: Doug Reid, Chris Lawless, Hadi Koesnodihardjo.
Oracle GoldenGate can do far more than was demonstrated in this simple exercise.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to:
Resources
Help topics relevant to the topic of this tutorial:
Credits
To help navigate this Oracle by Example, note the following:
- Hiding Header Buttons:
- Click the Title to hide the buttons in the header. To show the buttons again, simply click the Title again.
- Topic List Button:
- A list of all the topics. Click one of the topics to navigate to that section.
- Expand/Collapse All Topics:
- To show/hide all the detail for all the sections. By default, all topics are collapsed.
- Show/Hide All Images:
- To show/hide all the screenshots. By default, all images are displayed.
- Print:
- To print the content. The content currently displayed or hidden will be printed.
To navigate to a particular section in this tutorial, select the topic from the list.