Before You Begin
Purpose
This tutorial shows how to use the Oracle WebLogic Server 12c administration console to configure a JDBC data source.
Time to Complete
Approximately 1/2 hour
Background
A data source is an object that enables a Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) client to obtain a database connection. The data source has a collection of database connections called a connection pool. An application can request a connection from the data source, use the connection to access the database, and then close the connection. Rather than actually close the connection, however, the data source places it back in the connection pool to be used again. Data sources can be created as part of the configuration of an instance of WebLogic Server. When that server comes up, (or the data source is deployed), the server creates database connections to fill the connection pool of its data source.
Scenario
This tutorial covers using the Oracle WebLogic Server 12c (12.2.1) administration console to create a data source and its connection pool. The connections are to an Oracle Database.
Context
Before starting this tutorial, you should have completed the Oracle by Example tutorials titled Oracle WebLogic Server 12c: Installing WebLogic Server and Creating a Domain and Oracle WebLogic Server 12c: Configuring Managed Servers.
What Do You Need?
The following is a list of software requirements:
- Oracle WebLogic Server 12c (12.2.1)
- Oracle Database 12c or later (Express Edition
may work as well but has not been tested.
Note: In this tutorial Oracle Database XE 11.2 is used.
Setting Up the Schema in the Oracle Database
To set up the database schema required by the JDBC client application, perform the following steps:
-
Download the jdbc_obe.zip file to the machine where your WebLogic Server domain and servers are. Extract the file contents to a local drive. In this tutorial, the files are extracted into the
/u01/jdbc_obe/testdsdirectory. The zip file contains three files:testds_oracle.sql
A SQL script to configure the required schema in the Oracle Databasetestds.war
A simple web application used to test the configured data sourcedeploy_testds.py
A WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) script used to deploy the web application
-
Log in to the system as the user that started the Oracle Database. Open a Terminal window and navigate to the location of the SQL script file,
testds_oracle.sql. In this tutorial that is:cd /u01/jdbc_obe/testds
-
Make sure that the database environment variables are set by printing them out:
echo $ORACLE_HOME
/u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0/dbhome 1
echo $ORACLE_SID
orcl
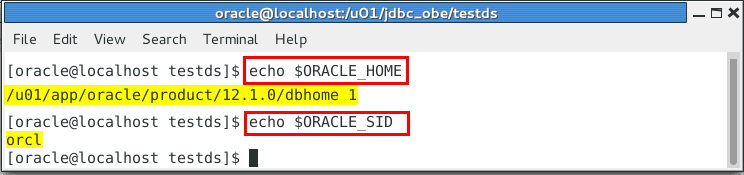
Note: The values of your environment variables may be different. If there are no values printed, then set the variables to the proper values with:
export ORACLE_HOME=<valid_value>
export ORACLE_SID=<valid_value> -
Then invoke SQL Plus as the
sysdbauser:$ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplus / as sysdba
-
Connect to the database as the
systemuser. You can give the password and the name of the database as you connect. In this tutorial the command is:connect system/welcome1 as sysdba
-
Then run the SQL script with this command:
@testds_oracle.sql
The script,
testds_oracle.sql, creates a user calledDBTESTERwith the passwordwelcome1. It grants that user the abilities to create sessions, tables, and so on. It then connects to the database as that user and creates three tables:EMPLOYEE,WLS_CATALOG_ITEMS, andWLS_CLIENT_INFO. Finally, it inserts rows into those tables and exits.
Starting WebLogic Server
- If Node Manager is not already running, it needs
to be started. To start it, in a Terminal window,
navigate to the domain directory, and enter the
command:
./startNodeManager.sh
-
If the administration server of the domain is not already running, it needs to be started. To start it, in another Terminal window, navigate to the domain directory, then
cdinto thebinsubdirectory. Enter the command:./startWebLogic.sh
-
The managed server
server1should also be running. If it is not already running, start it. In another Terminal window, navigate to the domain directory, thencdinto thebinsubdirectory. Note: Use the host name and port of the administration server of your domain. Enter the command:./startManagedWebLogic.sh server1 http://localhost:7001This runs the script to start the managed server named
server1. Also notice the argument that gives the URL of the domain's administration server:
http://localhost:7001.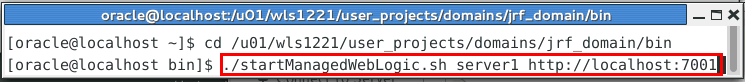
-
When prompted for a username and password, enter the credentials of the domain administrator.
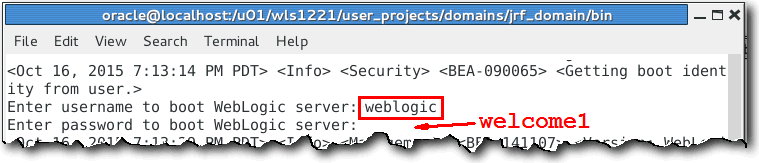
To start the administration server and the server1 managed server of the domain, perform the following steps:
Configuring a JDBC Data Source
To configure a JDBC data source by using the WebLogic Server administration console, perform the following steps:
-
After the servers are up and running, access the WebLogic Server administration console. Open a web browser and enter its URL:
http://<hostname>:<port>/consoleIn this tutorial, that is:
http://localhost:7001/consoleNote: Use the host name and port of the administration server of your domain.

-
On the Welcome screen, log in using the Username and Password entered to start the servers.

-
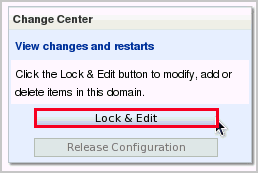
Creating a data source is a change to the domain's configuration, so the configuration must first be locked. In the Change Center, click the Lock & Edit button.
-
In the administration console under Domain Structure, expand Services (by clicking the + next to it). Then click Data Sources.

On the right, notice that the Summary of JDBC Data Sources section appears.
-
Under the Data Sources table heading, click the New drop-down list. Then select Generic Data Source.

-
On the first page of the Create a New JDBC Data Source wizard, enter the Name of the data source as
myNewDS.Enter the JNDI Name of the data source as
myNewDS.Note: There is no requirement that the data source name and the JNDI name match. The JNDI name is the one to make note of, because it is used by JDBC clients to access the data source.
Use the Database Type drop-down list to select
Oracle.Then click Next.

-
On the second page of the wizard, use the Database Driver drop-down list to select
*Oracle's Driver (Thin) for Instance connections; Versions:9.0.1 and later.Then click Next.

-
On the next page of the wizard, keep all the default Transaction Options, and click Next.

-
On the next page of the wizard, enter the Database Name. In this tutorial it is
orclYour database name may be different.Enter the Host Name of the server1 managed server. In this tutorial it is
localhost. Use the host name where your server1 server resides.Leave the database Port at the default of
1521. (Unless it is different for your database.)Enter the Database User Name of
DBTESTER. This is the user that was created by the SQL script.Enter the database user's password twice, in the Password and Confirm Password fields. The password is
welcome1.Then click Next.

-
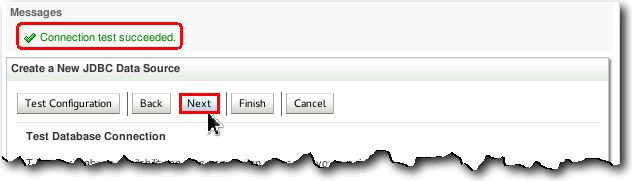
On the next page of the wizard, click the Test Configuration button to check if a connection to the Database can be made, based upon the information entered.

If the connection test fails, use the Back button to review the entries made for the data source and correct any errors. If there are no errors in the entries and the test still fails, make sure your database is running.
If the message "Connection test succeeded" is displayed, click Next.
-
On the last page of the wizard, the data source is targeted. Targeting a data source to a server means that the server will manage that data source and it will be available as one of the resources of that server.
Select the check box next to server1.
Then click Finish.

-
In the Change Center click the Activate Changes button.
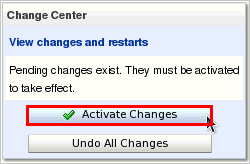
The message "All changes have been activated. No restarts are necessary." is displayed.
-
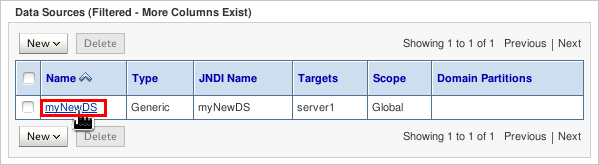
In the Summary of JDBC Data Sources area, in the Data Sources table, the new data source, myNewDS, is listed.

-
To modify the configuration of the new data source, click its name, myNewDS, in the table.
-
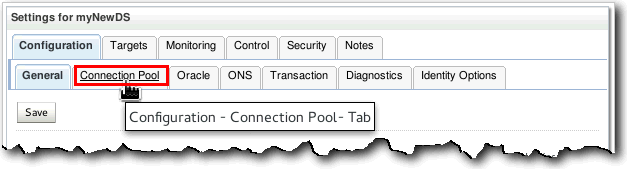
Under the Settings for myNewDS, click the Connection Pool tab under the Configuration tab.
Scroll down to find the "capacity" fields.
For Initial Capacity enter
2.For Maximum Capacity enter
20.For Minimum Capacity enter
2.Then click Save.

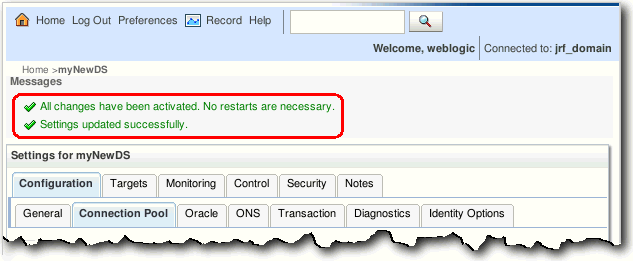
In the Change Center click the Activate Changes button.

The messages "All changes have been activated. No restarts are necessary." and "Settings updated successfully." are displayed.
-
Under Domain Structure, expand Environment and then click Servers.

-
In the Servers table, click the server server1.

-
In the Settings for server1, under the Configuration tab and the General subtab, click the link View JNDI Tree.

The JNDI tree opens in a new browser window (or tab). Notice that myNewDS appears in the JNDI tree.
Note: Other entries in the JNDI tree of your server can be very different from what is shown here. It all depends upon what resources your server has.

Testing the JDBC Data Source
To test the JDBC data source with a simple web application, perform the following steps:
-
Open a new Terminal window and navigate to the
/server/bindirectory under the WebLogic installation directory. In this tutorial, that is:
/u01/wls1221/wlserver/server/bin -
Then run the
setWLSEnv.shscript as follows:source setWLSEnv.shThis will set the
PATHand theCLASSPATHso the WLST deployment script can be executed.
-
Next navigate to the directory where the
testds.warfile resides. This file was part of the zip file extracted earlier. In this tutorial, the zip file was extracted into the/u01/jdbc_obe/testdsdirectory.
-
Before running the supplied
WLSTscript,deploy_testds.py, you may need to edit it. The first line of the script uses theconnect()command. The first argument of that command is the domain administrator's username, the second argument is that user's password, and the third argument is the host and port of the administration server of the domain. Make sure the values for these arguments are correct for your domain before running this script.Make any changes required to the script, and save the file.
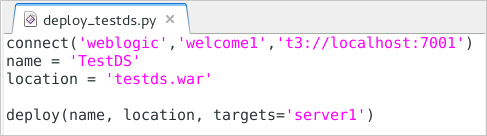
-
Run the
deploy_testds.pyscript to deploy the web application in thetestds.warfile and target it to theserver1server. Do this by entering the following command:java weblogic.WLST deploy_testds.py
You should see a message that the deploy operation has succeeded.
Note: You can ignore the warning about
Context.close(). That warning is always displayed when running aWLSTscript and is not an issue. -
To verify the deployment was successful, go the the administration console, and under Domain Structure, click Deployments. Then in the Deployments table, find TestDS with the "Active" State.

-
To use the deployed application, in another web browser, enter the host and port for the server1 managed server, followed by
/testds.In this tutorial, the URL entered is:
http://localhost:7003/testds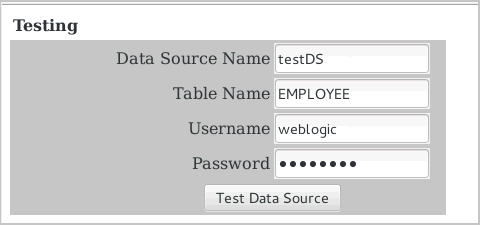
-
When the application comes up, enter the following:
Data Source Name: myNewDSTable Name: EMPLOYEEUsername: weblogic(use your domain administrator's username)Password: welcome1. (use your domain administrator's password) -
Then click the Test Data Source button.

The rows in the
EMPLOYEEtable are displayed below the fields.
The application uses the Data Source Name entered (
myNewDS) as the JNDI name to look up the data source from server1, retrieves a database connection from that data source, and executes the SQL to select all the rows in the table entered in the Table Name field (EMPLOYEE).If you want to test the data source again, try a different table in the Table Name field. The other two tables are
WLS_CATALOG_ITEMSandWLS_CLIENT_INFO.
Want to learn more?
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Run a SQL script to set up a schema in an Oracle database
- Start instances of WebLogic Server
- Configure a JDBC data source by using the administration console
- Test that data source by using a simple web application
- For documentation on Oracle WebLogic Server 12c, visit the Documentation Library.
- For more information on creating JDBC data sources, see the Configuring and Managing JDBC Data Sources document.
- To learn more about Oracle WebLogic Server, refer to additional OBEs in the OLL website.
- Lead Curriculum Developer: Bill Bell
- Original OBE Created By: TJ Palazzolo