Creating ASO Reporting Cubes in Essbase 11.1.2
Purpose
This tutorial shows you how to create ASO reporting cubes in Essbase 11.1.2.
Time to Complete
Approximately 45 minutes
Overview
For analytical applications spanning a variety of businesses, Essbase block storage (BSO) cubes provide a world class analytical engine for complex modeling. BSO cubes typically contain fewer (and smaller) dimensions than aggregate storage (ASO) cubes and can perform numerous and complex calculations on the smaller outlines. ASO cubes are designed to provide rapid aggregation capabilities for much larger Essbase outlines, typically supporting many more (and larger) dimensions.
For some projects, combining the calculation strengths of BSO with the aggregation strengths of ASO offers the best fit for your Essbase analytical needs. An ASO reporting cube, combining BSO and ASO cubes, is one example.
Scenario
The Hyptek corporation, manufacturer of hard disk drives, uses Essbase BSO cube Fcst_BSO for top-down sales forecasting. Forecasts are input at a high level, then pushed down to the lowest level using a series of sophisticated calculation scripts. Actual (historical) and budget sales data reside in Essbase ASO cube, AcBu_ASO.
Hyptek management would like you to create a combined BSO/ASO solution that enables Hyptek analysts to view forecast data in comparison to the actual and budget data that is already stored in AcBu_ASO. You do this by creating an ASO reporting cube called Rptg_ASO that utilizes transparent partitions to access forecast data from Fcst_BSO and actual and budget data from AcBu_ASO.
Software and Hardware Requirements
The following is a list of software requirements:
- Oracle® Essbase 11.1.2
Prerequisites
None
Creating an Application and Database for Reporting
You begin by creating an Essbase ASO application and database, using the AcBu_ASO (actual and budget data) cube as a template, since it contains the level of detail required for reporting.
[Note: In this tutorial, the terms "database" and "cube" have the same meaning; that is, "Essbase multidimensional database." The term "database" is displayed within the user interface, Administration Services Console.]
. |
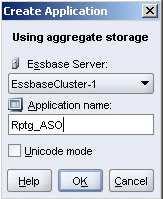
In Administration Services Console, right-click Applications, then select Create application, and then select Using aggregate storage.
|
|---|---|
. |
For Application name, enter Rptg_ASO, and then click OK.
|
. |
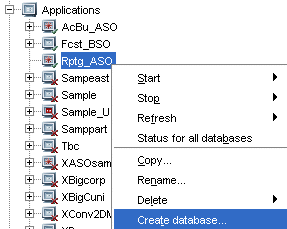
Right-click application node Rptg_ASO and select Create database.
|
. |
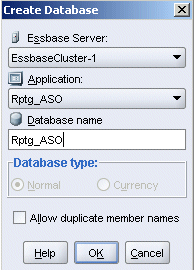
For the database name, enter Rptg_ASO, then click OK.
|
Creating the Reporting Cube Outline
The outline for the newly created reporting cube Rptg_ASO is empty. But you can use database outline AcBu_ASO as a starting point and save it as the reporting cube outline.
. |
Expand database node AcBu_ASO, then right-click Outline and select Edit.
|
|---|---|
. |
Select File, then Save As.
|
. |
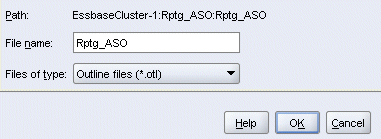
In the Save As dialog box, select the Essbase Server tab, and then navigate to database Rptg_ASO.
|
. |
Double-click the row corresponding to database Rptg_ASO (to populate the File name), then click OK.
|
. |
A confirmation message is displayed. Click Yes.
|
. |
An Outline Editor message is displayed. Click Yes.
|
. |
Examine the reporting cube outline.
Keep the Rptg_ASO outline open in Outline Editor for the next topic. |
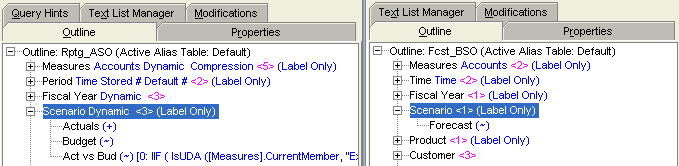
Comparing Outlines
The reporting cube (Rptg_ASO) will be a partitioned application, with data sourced from the cube containing actual and budget data (AcBu_ASO) and the cube containing forecast data (Fcst_BSO). You need to compare the reporting cube and forecast cube outlines to understand how to partition the two cubes.
. |
Expand database node Fcst_BSO, then right-click Outline and select Edit.
|
|---|---|
. |
In Administration Services Console, close all open objects except for the two outlines. Then select Organize, and then Tile Vertical to view the outlines side by side.
|
. |
Expand Scenario in both outlines.
|
Adding a Forecast Scenario to the Reporting Cube
. |
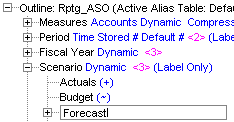
In the Rptg_ASO outline, right-click Budget and select Add sibling.
|
|---|---|
. |
Enter Forecast, and then press Enter.
|
. |
Another text entry box is displayed.
|
. |
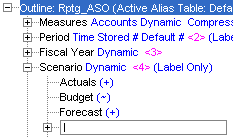
Press Enter to exit text entry mode.
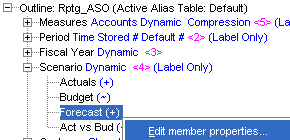
The Forecast entry is added. It needs to be a non-consolidated member of the Scenario dimension. |
. |
Right-click Forecast and select Edit member properties.
|
. |
In the Information tab in the consolidation drop-down list, select (~) Ignore, and then click OK.
|
. |
Click Save to preserve your changes to the Rptg_ASO outline.
|
. |
Close both outlines.
|
Creating a Partition for the Forecast (BSO) Database
To provide forecast data to the reporting cube, you define a transparent partition between the source cube (Fcst_BSO) and the target cube (Rptg_ASO).
. |
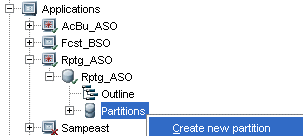
In the navigation panel, expand the Rptg_ASO database node, then right-click the Partitions node, and then select Create new partition.
|
|---|---|
. |
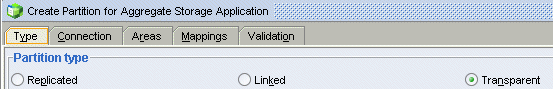
In the Type tab for Partition Type, select Transparent (the default).
|
. |
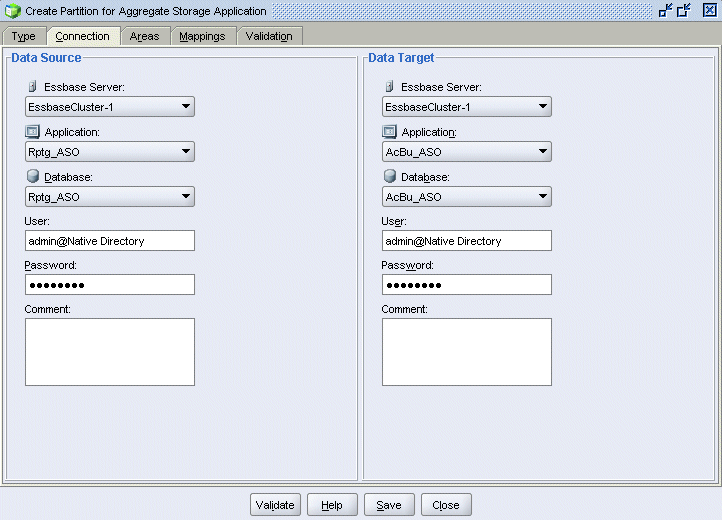
Select the Connection tab.
|
. |
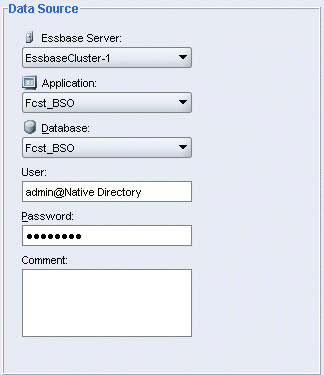
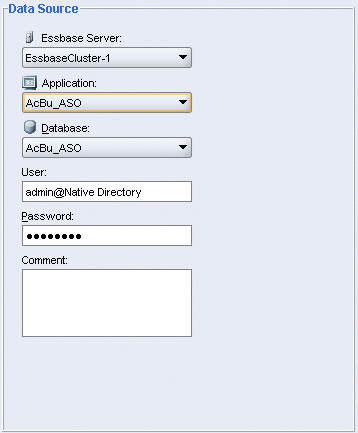
Under Data Source, make the following selections:
|
. |
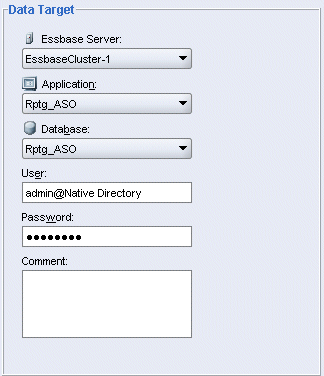
Under Data Target, make the following selections:
|
Defining the Source Partition Area
To enable the reporting cube to draw data from the forecast cube, you define the outline members involved in the flow between the source cube (Fcst_BSO) and the target cube (Rptg_ASO). In this section, you define the source partition area.
. |
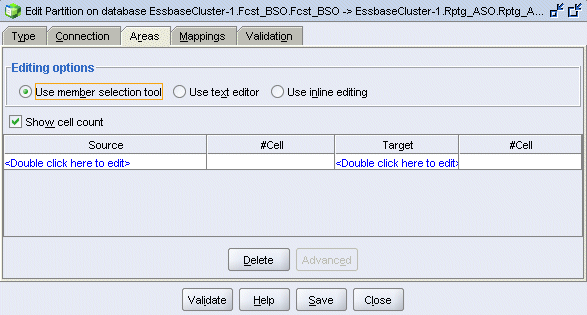
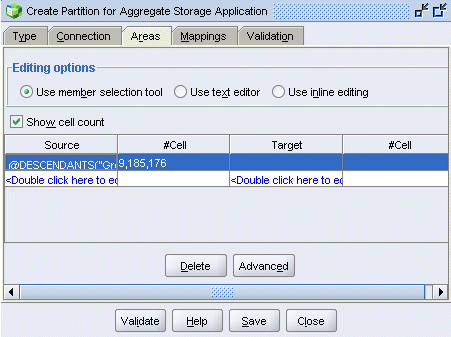
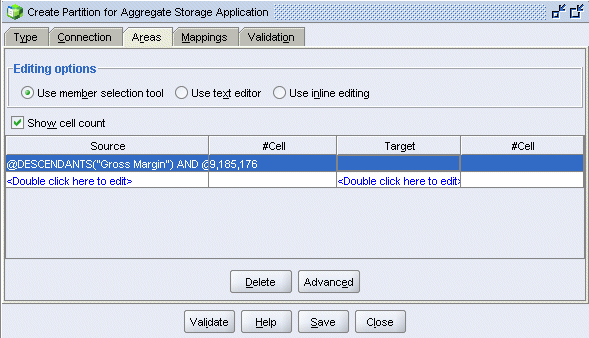
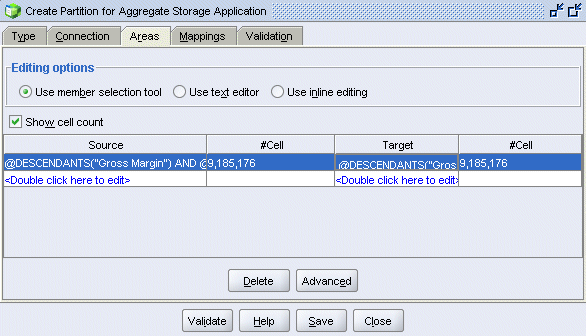
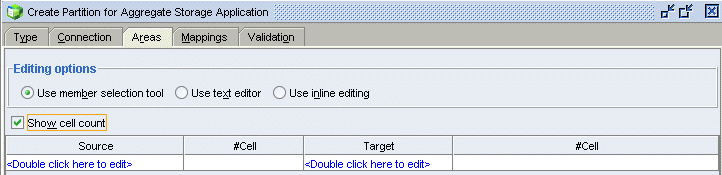
Select the Areas tab, and then select Show cell count.
|
|---|---|
. |
In the Source column, double-click <double-click here to edit>.
|
. |
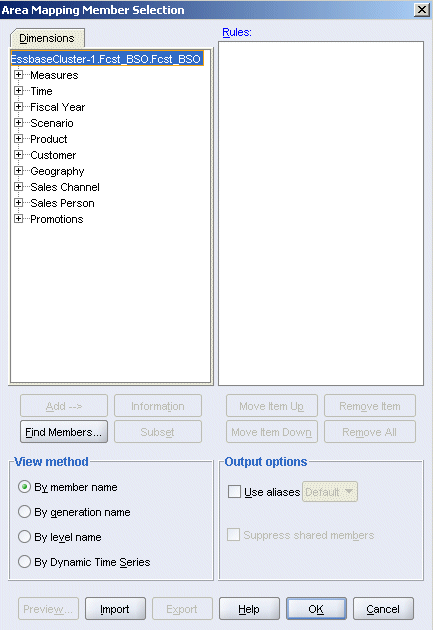
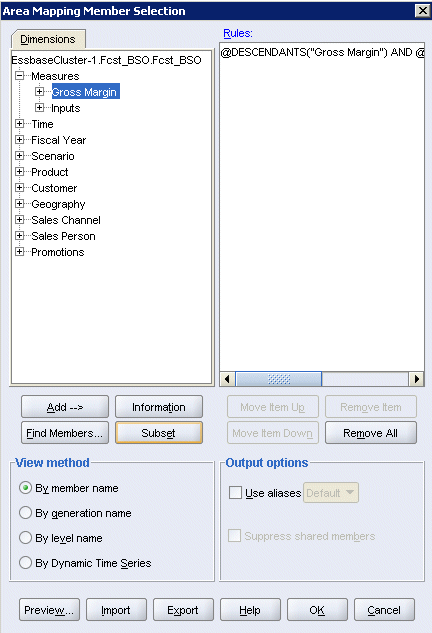
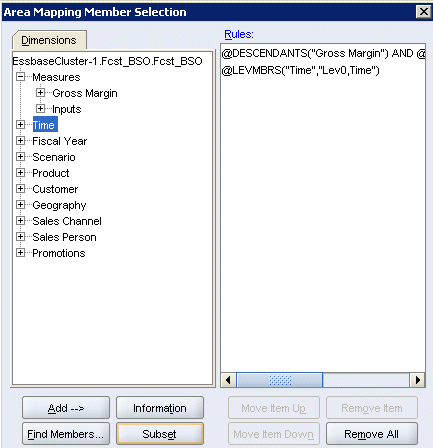
The Measures dimensions in the Rptg_ASO and Fcst_BSO outlines are different, except for member Gross Margin and its descendants, which are identical. ASO targets can be partitioned only along level 0 members. So, to define the source area to match the target (defined in the next topic), you select Measures to include the level 0 members of Gross Margin.
|
. |
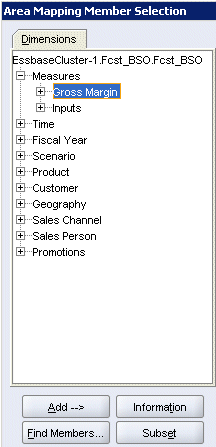
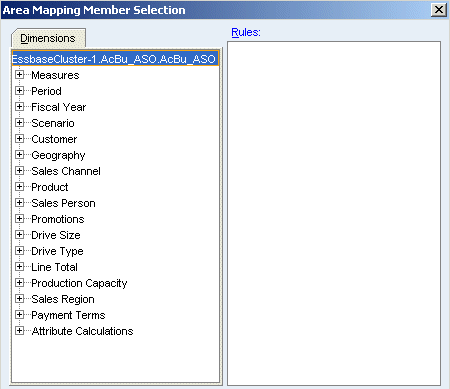
In the Area Mapping Member Selection dialog box, expand the Measures dimension, and select Gross Margin.
|
. |
Click Subset.
|
. |
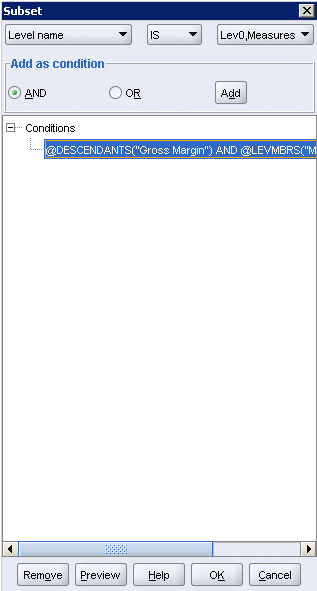
In the first drop-down list, select Level name, and in the third drop-down list, select Lev0,Measures, and then click Add.
|
. |
Click OK.
|
. |
A comparison of the outlines shows that the Periods dimension in Rptg_ASO corresponds to the Time dimension in Fcst_BSO. Although the upper-level members in the Fcst_BSO Time dimension differ from the upper-level members in the Rptg_ASO Periods dimension, the level 0 members in both dimensions are the same and can be included in the partition definition.
|
. |
Repeat steps 5 through 8 to select the subset for the level 0 descendants of Time.
|
. |
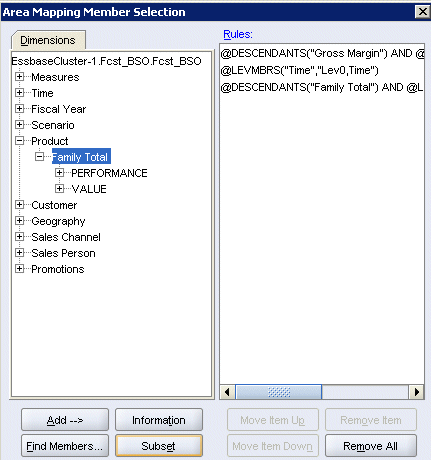
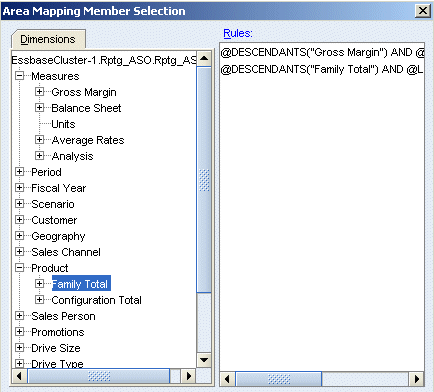
A comparison of the outlines shows that the Fcst_BSO Product dimension includes the Family Total rollup, but not the Configuration Total
rollup found in Rptg_ASO.
|
. |
Repeat steps 5 through 8 to select the subset for the level 0 descendants of Family Total.
|
. |
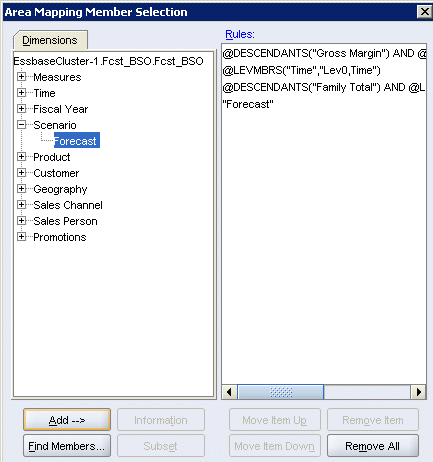
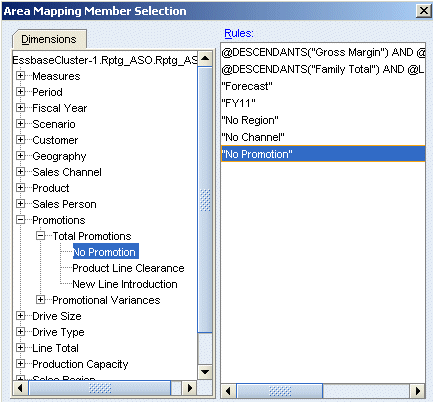
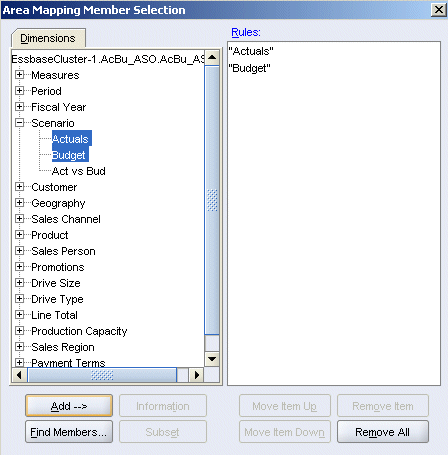
A comparison of the outlines shows that Fcst_BSO has only one member in the Scenario dimension. To enable Rptg_ASO to source forecast data from Fcst_BSO, expand the Scenario dimension, then select Forecast, and then click Add.
|
. |
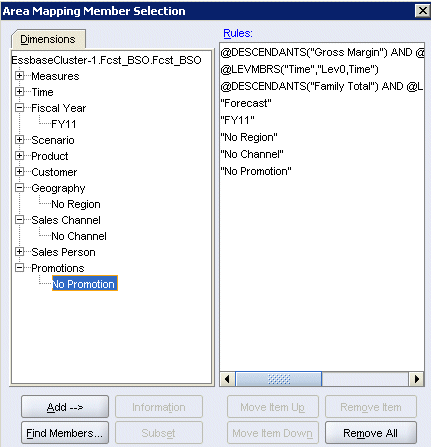
A comparison of the outlines shows that Fcst_BSO has one member in not only the Scenario dimension, but also the Fiscal Year, Geography, Sales Channel, and Promotions dimensions.
|
. |
Repeat step 13 to select each of the following single members:
|
. |
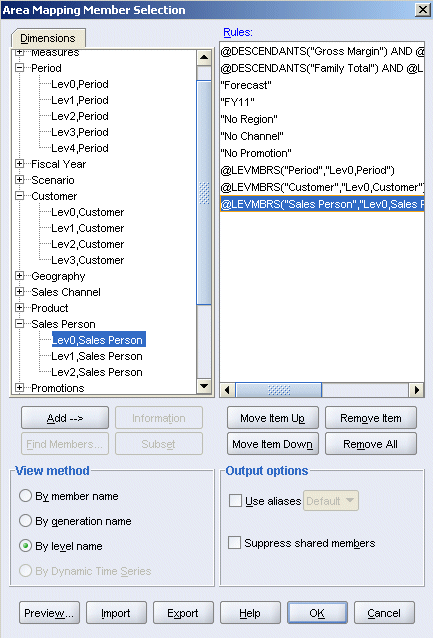
A comparison of the outlines shows that Customer dimension in Fcst_BSO matches the Customer dimension in Rptg_ASO. All of the level 0 source members can be added for Customer.
|
. |
To select the level 0 members for the Customer dimension, under View Method, select By level name.
|
. |
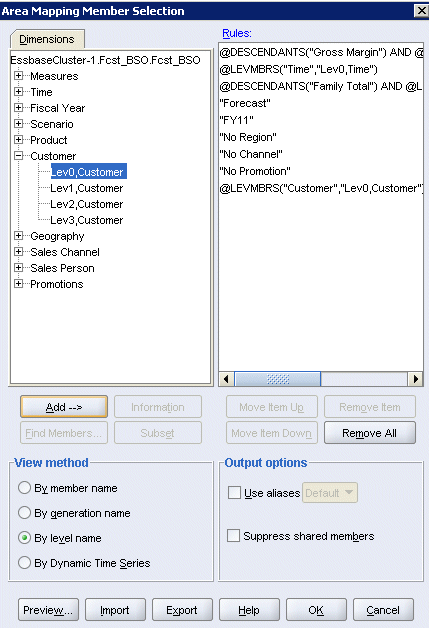
Expand Customer, and select Lev0,Customer, and then click Add.
|
. |
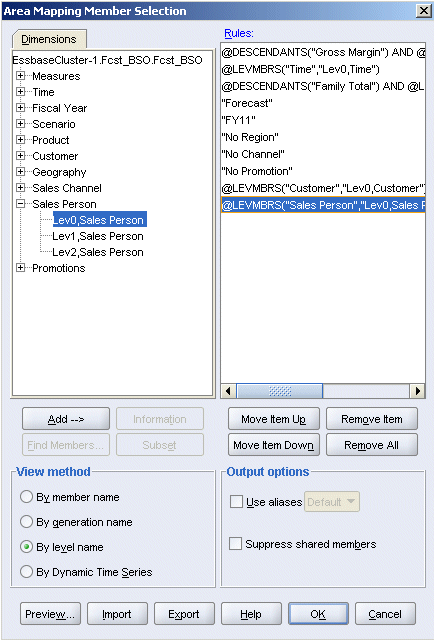
A comparison of the outlines also shows a corresponding match between the Sales Person dimensions. All of the level 0 source members can be added for Sales Person.
|
. |
Repeat step 18 to select level 0 Sales Person members.
|
. |
Click OK.
|
. |
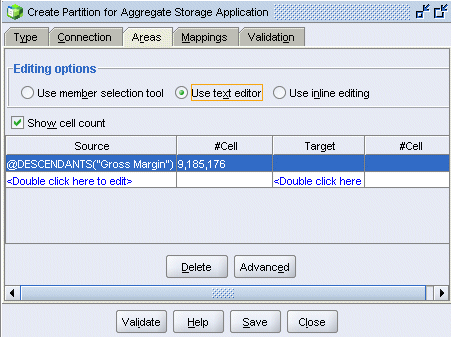
Select editing option Use text editor, then double-click the first row in the Areas table.
|
. |
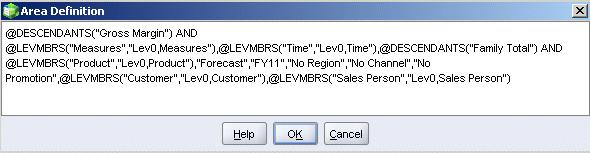
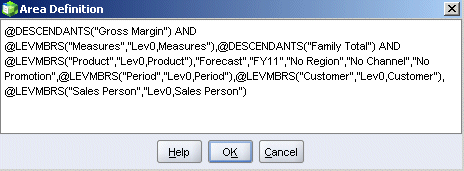
Resize the Area Definition text box and review the area definition. When finished, click OK.
|
Defining the Target Partition Area
The other half of the partition definition between the reporting cube and the forecast cube is the target cube (Rptg_ASO). In this section, you define the target partition area.
. |
Ensure that you are in the Create Partition for Aggregate Storage Application window, with the Areas tab selected.
|
|---|---|
. |
In the Target column, double-click the first row (the same row as your source area definition).
|
. |
Using the same techniques described in the topic entitled "Defining the Source Partition Area," select the following dimension subsets:
|
. |
Using the same techniques described in the topic entitled "Defining the Source Partition Area", select the following single members:
|
. |
Using the same techniques described in the topic entitled "Defining the Source Partition Area", select all level 0 members of the following dimensions:
|
. |
Click OK.
|
. |
Using the same technique described in the topic entitled "Defining the Source Partition Area", review the area definition for the target partition area. When finished, click OK.
|
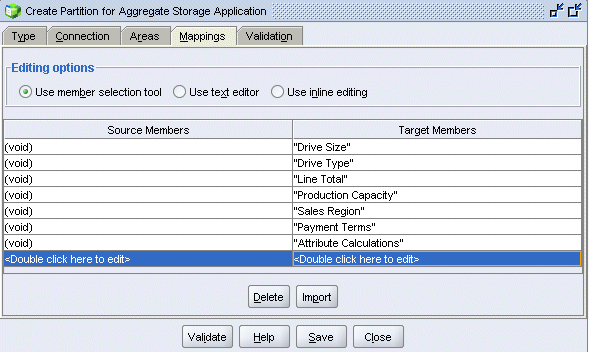
Mapping Member Names
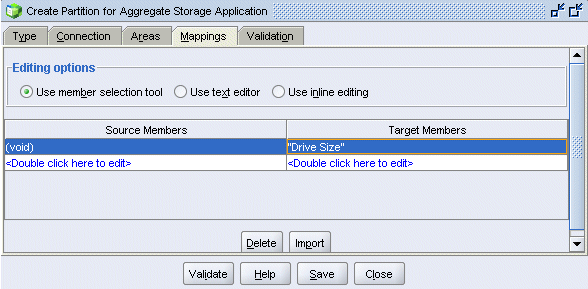
While the area definitions define the members that are common to both outlines, the reporting cube outline has six attribute dimensions that are not represented in the forecast cube outline. In this section, you eliminate the attribute dimensions from the partition definition by mapping the missing dimensions ( "void") in the source cube to each attribute dimension in the target cube.
. |
Select the Mappings tab.
|
|---|---|
. |
In the Target Members column, double-click <double-click here to edit>.
|
. |
Select Drive Size.
|
. |
Click OK.
|
. |
Repeat the previous three steps to map the following attribute dimensions (and the attribute calculations dimension) to void:
|
Validating and Saving the Partition
. |
Click Validate.
|
|---|---|
. |
Click OK, then click Save.
|
. |
The partition is saved under Source Databases in the Partitions node for database Rptg_ASO.
|
Creating a Partition for the Actual-Budget (ASO) Database
Creating a partition for the actual-budget database (AcBu_ASO) is straightforward, since the reporting cube was created as a copy of that database outline. You just need to specify the appropriate Fiscal Year (FY11, to match the forecast database) and Scenarios (Actuals, Budget) required for reporting.
. |
In the navigation panel, expand the Rptg_ASO database node, then right-click the Partitions node, and then select Create new partition.
|
|---|---|
. |
In the Type tab for Partition Type, select Transparent (the default).
|
. |
Select the Connection tab.
|
. |
Under Data Source, make the following selections:
|
. |
Under Data Target, make the following selections:
|
Defining the Source Partition Area
. |
Select the Areas tab, and then select Show cell count.
|
|---|---|
. |
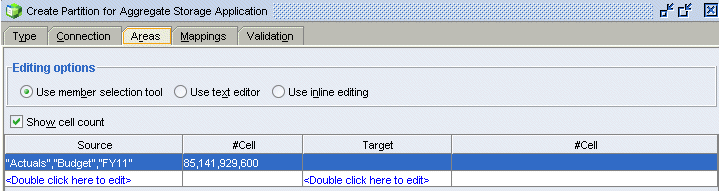
In the Source column, double-click <double-click here to edit>.
|
. |
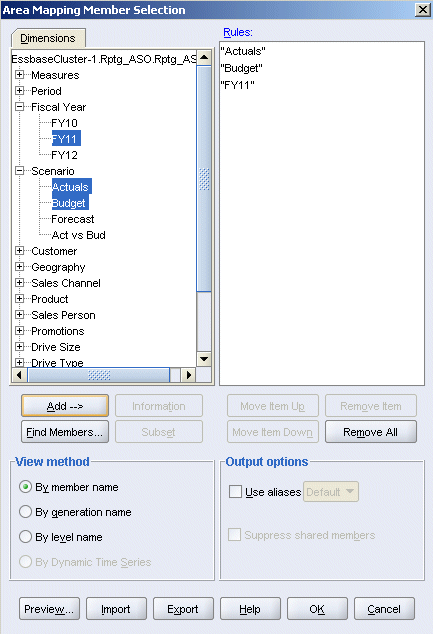
In the Area Mapping Member Selection dialog box, expand the Scenario dimension, then multiple select Actuals and Budget, and then click Add.
|
. |
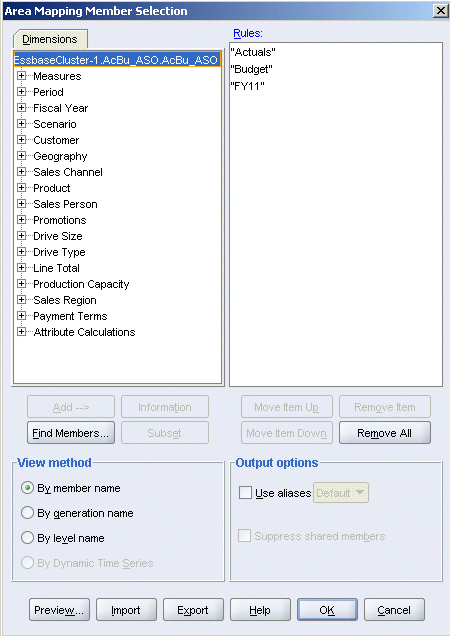
Repeat the previous step to select FY11 from the Fiscal Year dimension.
|
. |
Click OK.
|
Defining the Target Partition Area
In this section, you define the target partition area.
. |
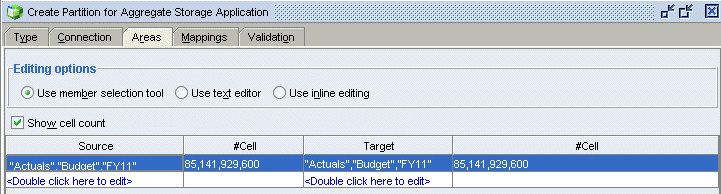
In the Target column, double-click the first row (the same row as your source area definition).
|
|---|---|
. |
Expand Scenario and Fiscal Year, then multiple select Actuals, Budget, and FY11, and then click Add.
|
. |
Click OK.
|
Validating and Saving the Partition
. |
Click Validate.
|
|---|---|
. |
Click OK, then click Save.
|
. |
The partition is saved under Source Databases in the Partitions node for database Rptg_ASO.
|
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to create an aggregate storage reporting cube for a combined aggregate storage/block storage analytical solution.
Resources
- To learn more about aggregate storage applications, refer to the Oracle Essbase Release 11.1.2 Database Administrator's Guide.
- For a list of available online tutorials regarding aggregate storage, search "aggregate storage" on the Oracle Learning Library Web site.
- For Oracle University training on aggregate storage applications, including partitioning ASO databases, search "deploy aggregate storage databases" on the Oracle University Web site.
![]()
|
|
About
Oracle | Oracle and Sun | |