Deploying ADF Applications to Oracle Cloud by Using JDeveloper, Part
1
Overview
- Have experience developing applications with Oracle JDeveloper and ADF.
- Have an Oracle.com account.
- Have already completed the Oracle by Example tutorial titled Signing Up for a Java Cloud Service.
- Have access to or have installed Oracle JDeveloper 11g (version 11.1.1.6.0 required).
- Have access to or have installed the Oracle
Express 11g Release 2 (Oracle XE) database and unlocked
the HR schema.
- This example uses the HR schema included in the Oracle 11g Database. The Oracle Sample Schemas installation guide is part of the Oracle 11g Database documentation set, and is also available online at: http://otn.oracle.com.
Purpose
This tutorial covers how to create a database in the Oracle
Database Cloud Service by using Oracle JDeveloper and the human
resources (HR) database schema that ships with Oracle databases.
This tutorial is the first part of a two-part tutorial that
shows how you can use JDeveloper with Oracle Cloud services,
Oracle Java Cloud Service, and Oracle Database Cloud Service.
Oracle JDeveloper 11g,
version 11.1.1.6.0, nicely integrates with Oracle Cloud and can
be configured out-of-the-box to work with Oracle Database Cloud
Service and Oracle Java Cloud Service.
Time to Complete
Approximately 30 minutes
Introduction
Oracle Cloud is a public, enterprise, platform-as-a-service (Paas) offering. Two services provided by Oracle Cloud are particularly interesting to Java applications developers: Oracle Java Cloud Service and Oracle Database Cloud Service. You can configure these services through a web interface, a command-line tool, or an integrated development environment (IDE) such as JDeveloper.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you should:
Creating a Local Connection by Using the Database
Navigator
Oracle JDeveloper includes the Database Navigator tool to open
and manipulate database tables. Start by creating a connection
to the local Oracle XE database instance.
Select View > Database > Database Navigator
to open the tool.

Right-click IDE Connections and select New
Connection.
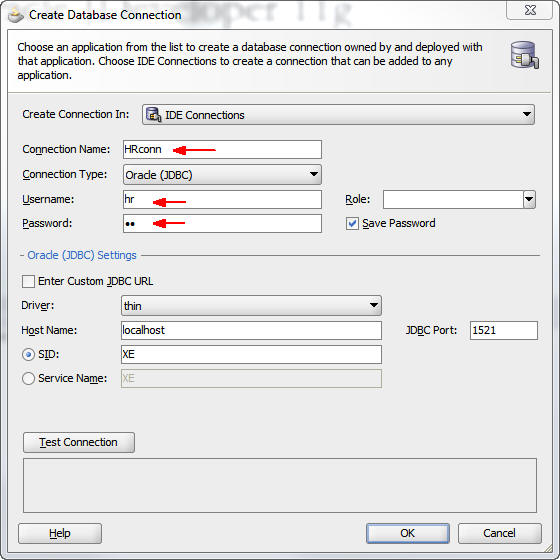
Enter the following information in the Create Database Connection dialog box:
Connection Name: HRconn
User Name: hr
Password: hr
Click Test Connection to ensure that you entered the data correctly and that you have a running local instance of a database.
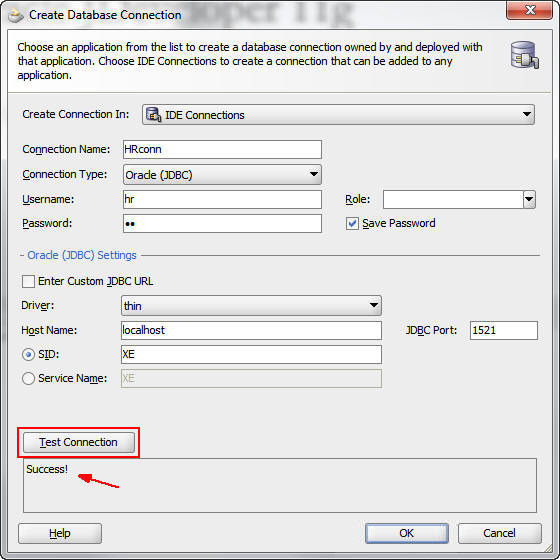
The word "Success" appears in the frame beneath the button.
Click the OK button.
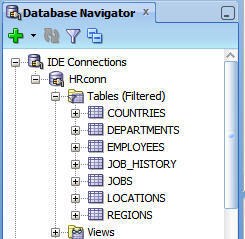
Expand HRconn and then expand Tables to see the HR tables in the database.
Configuring Your Oracle Database Cloud Service
Oracle Cloud provides a database service instance as a part of
a Java service. The database service has one connection for
reading the database and another connection for changing the
contents of the database. You need to create a user that
JDeveloper can use to access the database service instance to
read the database. You also need to modify the user account used
to modify the database.
Sign in to your Oracle Cloud account. Note: You will supply the identity domain provided to you in your confirmation email. For more details, see the Oracle by Example tutorial titled Signing Up for a Java Cloud Service.
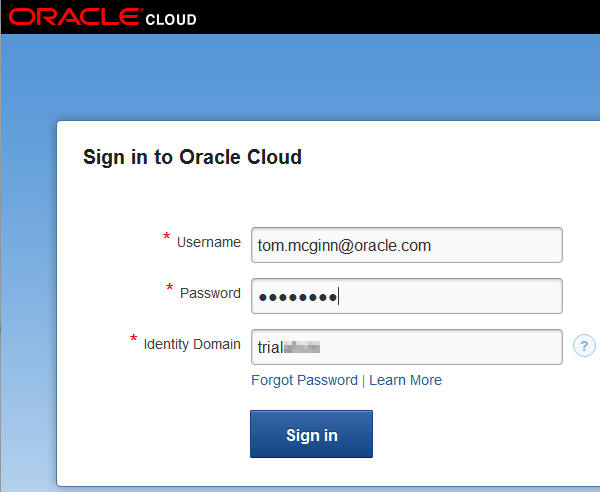
The services for the identity domain of your account appear on the screen.
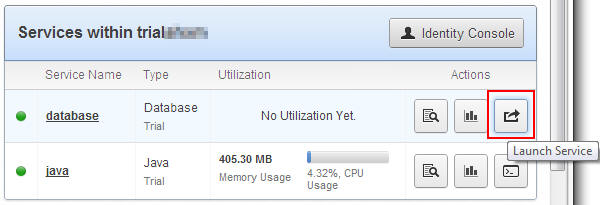
On the My Services page, click the Launch Service
button for the database service.
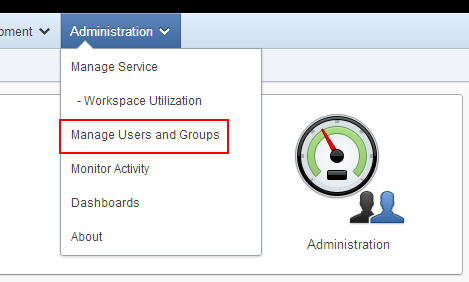
On the Oracle Application Express screen, select Administration
> Manage Users and Groups.
On the Manage Users page, click Create User.
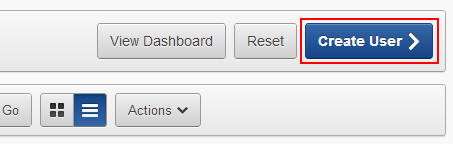
Enter CloudHRDB as the user name and then enter
your email address. The other fields are optional.
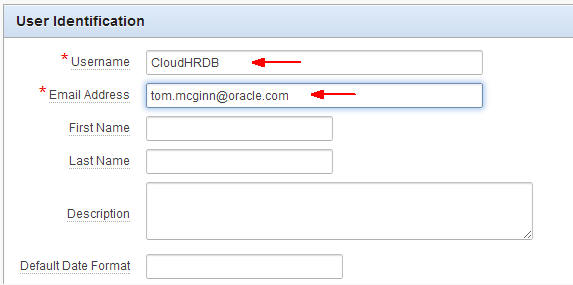
Scroll down to the Password section and enter the same
password in both fields.
Note: To avoid an error, do not make the password too simple.
In the User Groups section, select SQL Developer.
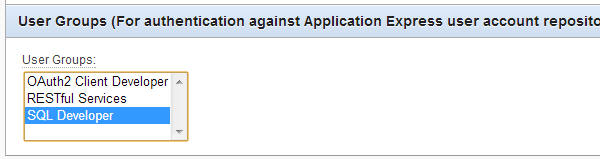
Scroll to the top and click Create User.
A message at the top of the page indicates that the user was created.
Take note of the URL in the browser window (up to and
including "/apex"):

On the My Services page, click the database service
link to see the details for the service.
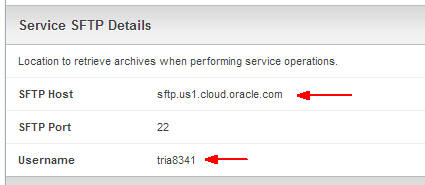
Scroll down to the Service SFTP Details section and take note of the SFTP host and user name.
Scroll to the top of the page and click Identity Console.
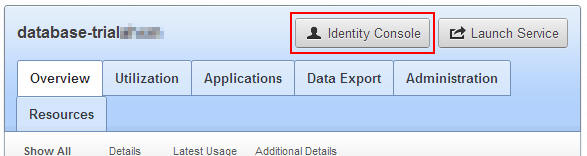
On the Identity Console page, select Manage Users.
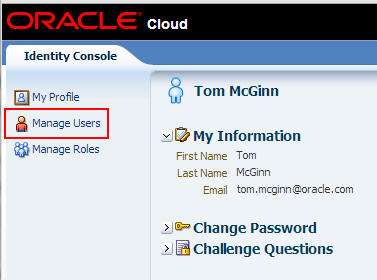
In the Search Users panel, enter * (asterisk) in the search window and click Search to return a list of all users.
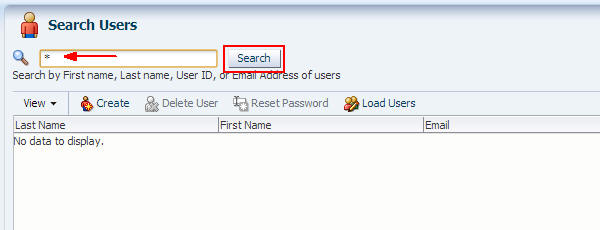
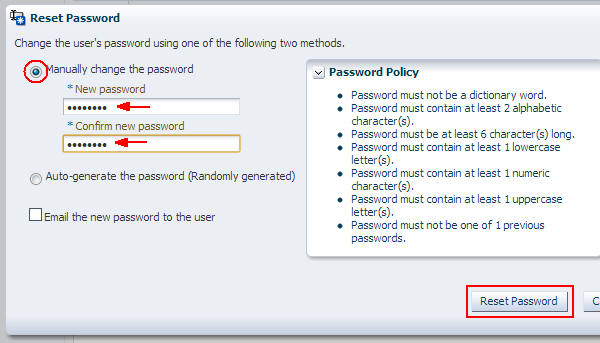
Select the SFTP user (from step 11) and click Reset Password.
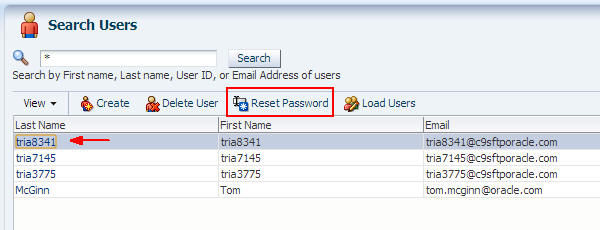
Select Manually change the password, enter a new
password twice, and then click Reset Password.
Click OK to close the Confirmation dialog box.
(Optional) Configuring Oracle JDeveloper to Use a Proxy
If you are using JDeveloper within a corporate network or
behind a firewall, you need to configure it to use a proxy to
connect to the Oracle Cloud services.
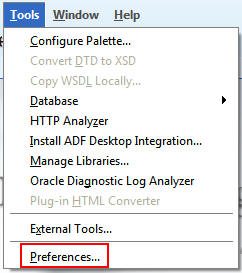
Select Tools >
Preferences.
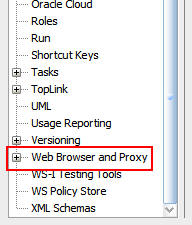
In the Preferences dialog box, scroll to the bottom of the
left panel and select Web
Browser and Proxy.
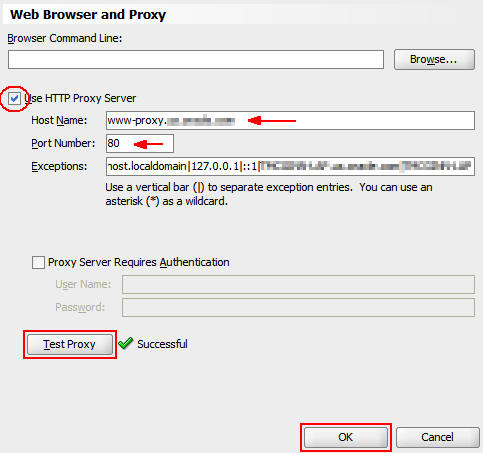
In the Web Browser and Proxy panel, perform the following steps:
a. Select the Use HTTP Proxy Server check box.
b. Enter the host name of your proxy.
c. Enter the port number of your proxy.
d. Click Test Proxy to test the configuration.
e. Click OK to
close the dialog box.
Creating a Connection to the Oracle Database Cloud Service
With the Oracle Database Cloud Service instance configured, you
can now create a connection to it from JDeveloper.
Scroll down the Database Navigator window until Cloud
Connections appears at the bottom of the window.
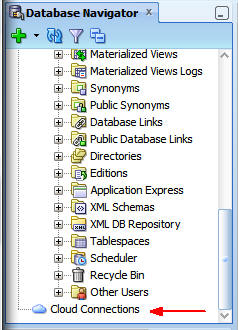
Right-click Cloud Connections and select New
Cloud Connection.
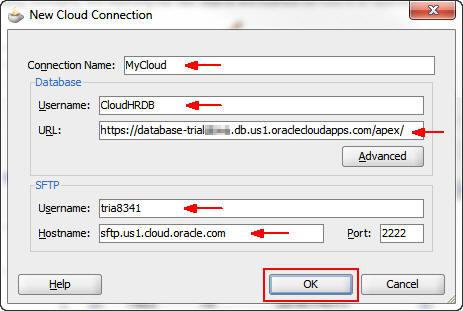
In the Edit Cloud Connection dialog box, enter the
following information and click OK:
Connection Name: MyCloud
Database Username: CloudHRDB
Database URL: Enter the URL that you copied from the Create User page.
SFTP Username: Enter the user name from the SFTP Details section.
SFTP Hostname: Enter the host URL from the SFTP Details section.
In the Database Navigator window, expand the MyCloud
connection that you just created:
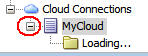
An authentication dialog box appears.
Enter the password for the database user that you created
and click OK.
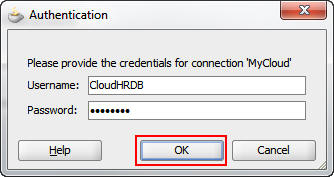
The MyCloud cloud connection is now connected to the Oracle Database Cloud Service instance.
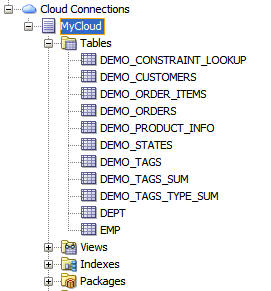
Expand Tables to see the database tables provided
in the default instance.
Copying the HR Database Schema and Data to the Oracle
Database Cloud Service
JDeveloper provides the Database Cart tool for copying database
tables from one data source to another. You will use this tool
to create a copy of the definition of the HR database schema and
copy it to the database instance in Oracle Cloud.
To configure the Database Cart, select Tools >
Preferences.
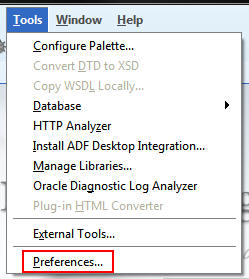
To access the preferences for the Database Cart deployment,
perform the following steps in the Preferences dialog box:
a. Scroll down to Database.
b. Expand Database.
c. Expand Utilities.
d. Expand Cart.
e. Select Cart Deploy.
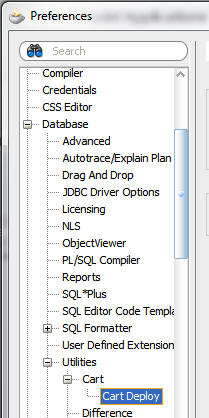
Enter or browse to a path where the deployment zip files
will be created and click OK.
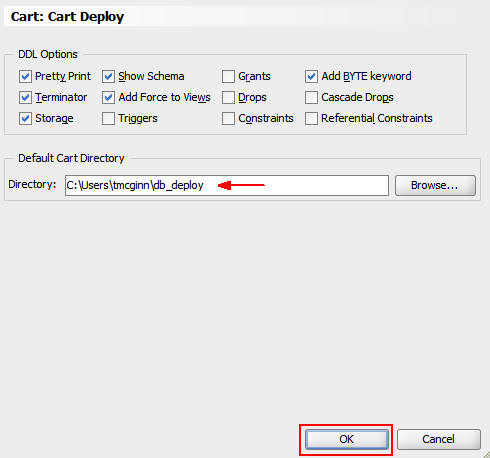
Select View > Database > Database
Cart.
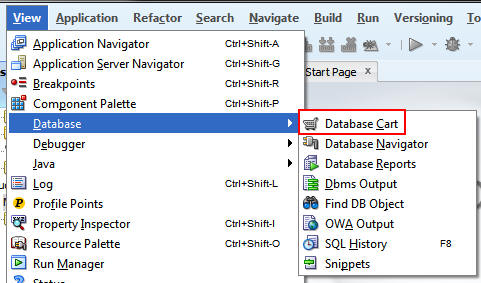
Click in the space to the right of the Database Cart tab
and drag it to the center of the screen to detach and float
the window.
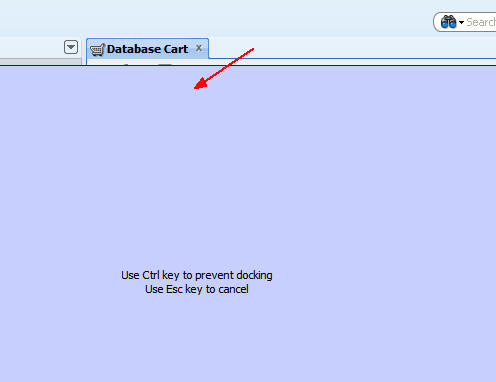
In the Database Navigator, scroll up to the HRconn
connection, expand Tables, and select COUNTRIES,
DEPARTMENTS, EMPLOYEES, JOBS, LOCATIONS,
and REGIONS. Note: Press the Ctrl key
to select the tables.
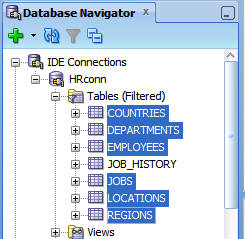
Drag the selected tables to the Database Cart tab.
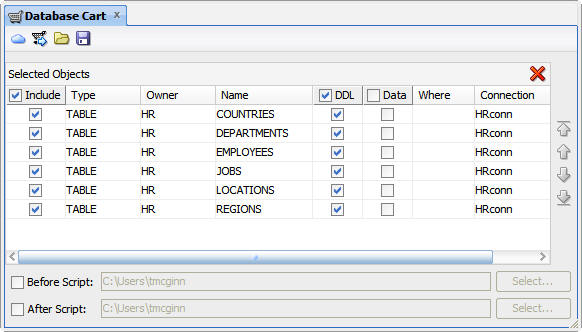
When you release the mouse, the tables appear on the Database Cart tab.
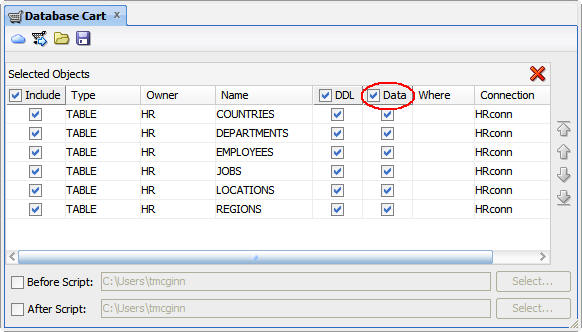
Select the Data check box to include the data from
the tables in the transfer.
Click the cloud icon.
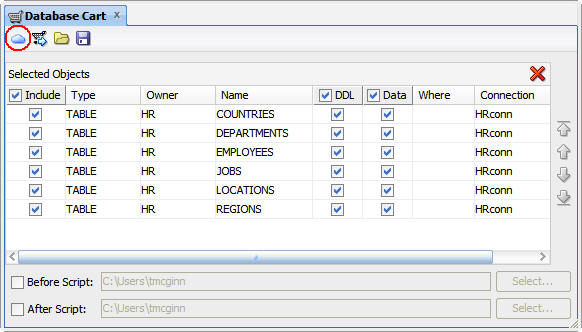
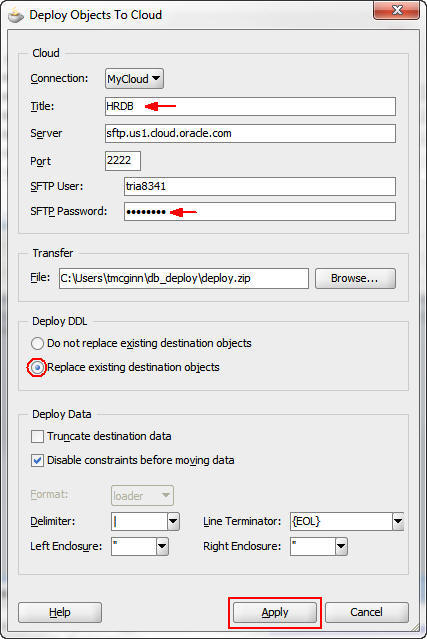
In the Deploy Objects to Cloud dialog box, perform the
following steps:
a. Enter HRDB as the title.
b. Enter the SFTP password that you created for the SFTP user.
c. Select Replace existing destination objects.
d. Click Apply.
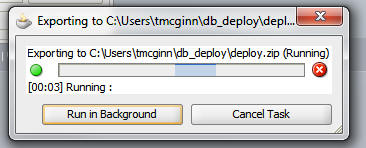
A dialog box indicates the progress of the data transfer.
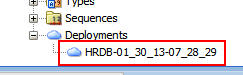
After the dialog box closes, scroll to the bottom of the
list in the Database Navigator and expand Deployments
to see the deployment to the cloud. (The deployment name
begins with HRDB.)
Double-click the deployment name to open the deployment
status.
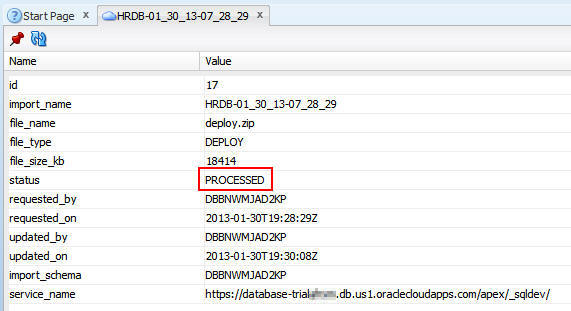
You may see the status listed as APPROVED. After a few seconds, double-click again to refresh the status. When the status changes to PROCESSED, the tables and their data were successfully moved to the cloud.
Refresh the local view of the cloud tables by performing
the following steps:
a. Select Tables below the MyCloud connection.
b. Click the Refresh icon at the top of the
Database Navigator panel.
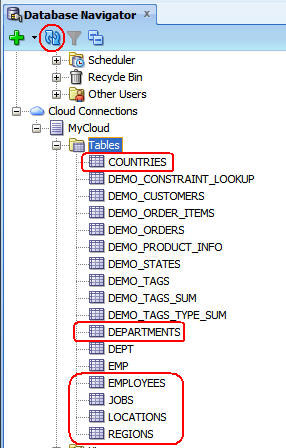
The tables from the HR database were created in the Oracle Database Cloud Service instance.
To confirm that the data also transferred to the cloud,
perform the following steps:
a. Double-click the EMPLOYEES table.
b. At the bottom of the EMPLOYEES panel, select the Data
tab to see the data in the table.
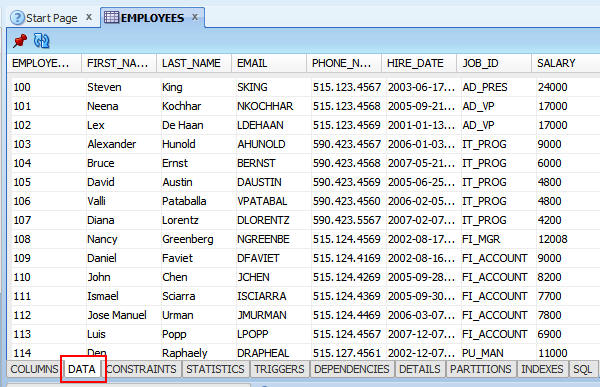
Summary
- Create a connection to a local database instance with the JDeveloper Database Navigator
- Configure an Oracle Database Cloud Service instance for read and write access from JDeveloper
- Create a connection to an Oracle Database Cloud Service
instance with JDeveloper
- Copy the schema and data from a set of database tables in a
local Oracle XE instance to an Oracle Database Cloud Service
instance
- Shay Shmeltzer's Blog: Deploying
Oracle ADF Applications on the Oracle Java/Database Cloud
- Oracle Cloud Documentation
- Oracle
XE Documentation
- To learn more about Oracle
Cloud refer to additional OBEs in the Oracle Learning Library
- Lead Curriculum Developer: Tom McGinn
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
Resources
Credits
To help navigate this Oracle by Example, note the following:
- Hiding Header Buttons:
- Click the Title to hide the buttons in the header. To show the buttons again, simply click the Title again.
- Topic List Button:
- A list of all the topics. Click one of the topics to navigate to that section.
- Expand/Collapse All Topics:
- To show/hide all the detail for all the sections. By default, all topics are collapsed
- Show/Hide All Images:
- To show/hide all the screenshots. By default, all images are displayed.
- Print:
- To print the content. The content currently displayed or hidden will be printed.
To navigate to a particular section in this tutorial, select the topic from the list.