Before You Begin
Purpose
In this tutorial, you create and build a Java
Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE) application
using Maven. You install, configure, build, and
create an executable Java Archive (JAR) file with
Maven.
Time to Complete
Approximately 90 minutes
Background
Maven is a build management tool that is central to project build tasks such as compilation, packaging, and artifact management. Maven uses a strict XML-based rule set to promote consistency while maintaining flexibility. Because most Java-centric continuous integration systems integrate well with Maven, it's a good choice for an underlying build system.The primary goal of Maven is to provide:
-
A project model that is reusable, maintainable, and easier to comprehend
-
Plug-ins or tools that interact with the declarative model
pom.xml file. The Project Object
Model (POM) is the fundamental unit of the entire
Maven system.Maven contains three types of repositories for storing JARs, plug-ins, and other project-related artifacts:
-
Local Repository: The location created on your machine when you run your first instance of a Maven command in your machine
-
Central Repository: The Maven community-owned repository that contains commonly used libraries
-
Remote Repository: A developer-owned custom repository that contains project-related libraries and JARs
What Do You Need?
- Download and install the latest Java SE Development Kit. For this tutorial, the available version is Java SE 8.
- Download the Apache Maven. For this tutorial, the available version is 3.2.2.
Setting Up the Maven Environment
In this section, you extract the downloaded archive
and install the latest Maven version to a directory
of your choice. You verify the Java installation,
set the Maven environment, and verify the Maven
installation.
- Verify the Java installation:
java -version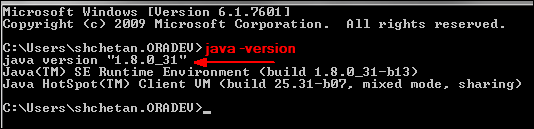
The output displays the Java version that you installed.
-
Extract the downloaded Maven x.x.x archive to a local directory.
The archive names are:
-
Windows OS: apache-maven-3.2.2-bin.zip
-
Linux OS: apache-maven-3.2.2-bin.tar.gz
-
Mac OS: apache-maven-3.2.2-bin.tar.gz
Note: This OBE shows you how to install and create a Java SE application using Maven in a Windows operating system.
-
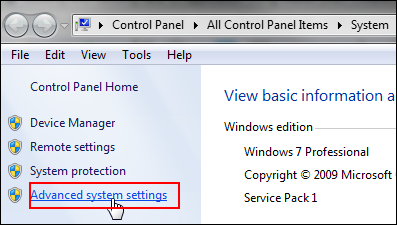
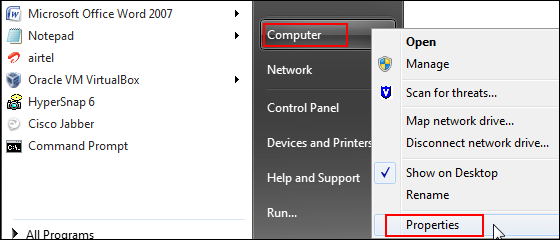
- Click Start, right-click Computer, and select Properties.
-
On the Control Panel home page, click Advanced system settings.
-
In the System Properties dialog box, click the Advanced tab, and then click Environment Variables.
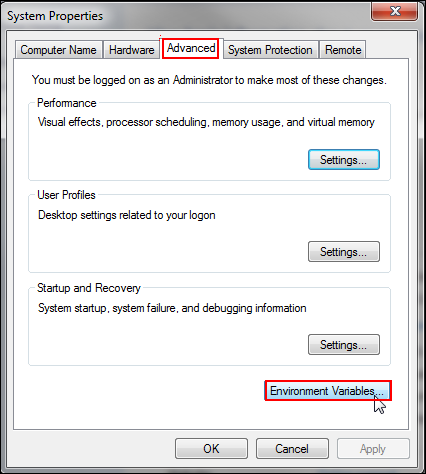
The Environment Variables dialog box is displayed.
-
Click New, add
M2, M2_HOME,andMAVEN_OPTSto the environment variables, and click OK.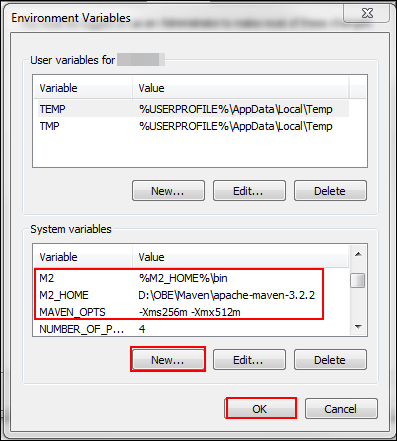
-
Under System variables, click New, enter the following values in the Edit System variable dialog box, and click OK:
-
Variable name:
Path -
Variable value:
%M2%(Enter the value afterbinin the system path)
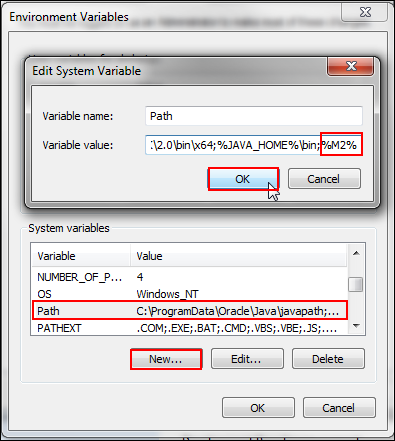
-
-
Verify the Maven installation:
mvn -version
The output displays the installed Maven version, the Java version, the Java home, the Default locale, and the OS name.
Creating a Java SE Project from a Maven Template
-
Open the command prompt, navigate to the directory where you installed Maven, and create
Maven_app,a Maven-based Java application folder:mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.example.bank
-DartifactId=OracleBanking
-DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart
-DinteractiveMode=falseAn archetype is an original pattern/model for creating similar projects. In Maven, an archetype is a template of a project that is combined with user input to produce a working Maven project. The following table describes what the template does:
Archetype ArtifactIds Description mvn archetype:generateCreates a project -DgroupId=com.example.bankCreates the com.example.bankdependency package structuremaven-archetype-quickstartCreates a Java project -DinteractiveMode=falseSets interactive mode to false
The Java project namedOracleBankingis created. The following table presents the project details:
Project Structure Description OracleBankingContains srcfolder andpom.xmlsrc/main/javaContains Java code files under the package structure
(com.example/bank)src/testContains test code files under the package structure
(com.example/bank)pom.xmlContains information about the project and details of various configurations used by Maven to build the project -
Open the
OracleBankingproject and verify the Java source file: -
Verify Java test file:
AppTest.java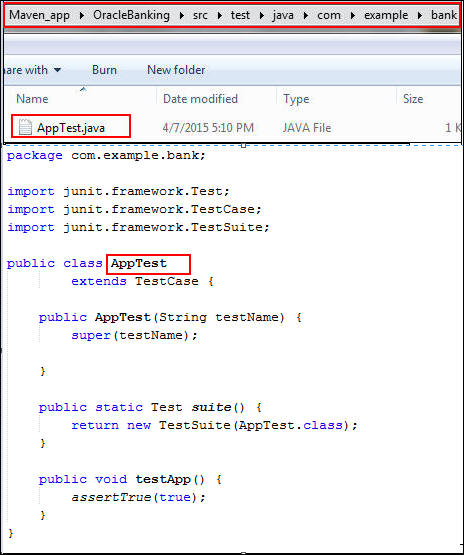
By default, Maven adds the
App.javasource file and theAppTest.javatest file to the default directory structure. -
Open the
pom.xmlfile and review the code.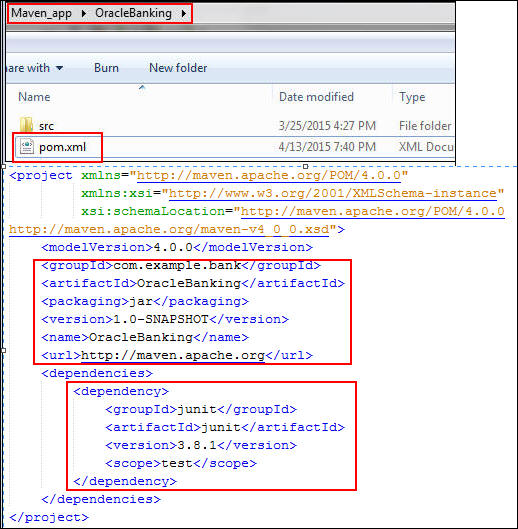
Each project has a single
pom.xmlfile, and eachpom.xmlfile has a project element and three mandatory fields:groupId, artifactId,andversion.Notice that Maven has already added JUnit as the test framework. The following table describes what each node does:Node Description projectTop-level element in all Maven pom.xmlfilesmodelVersionObject model version that this POM is using groupIdProject groupId (for example, com.example.bank)artifactIdProject ID (for example, OracleBanking)packagingProject files converted into a JAR file versionProject version used in the artifact's repository to separate each version (for example, 1.0-SNAPSHOT)nameProject display name urlLocation of the project site
App.java
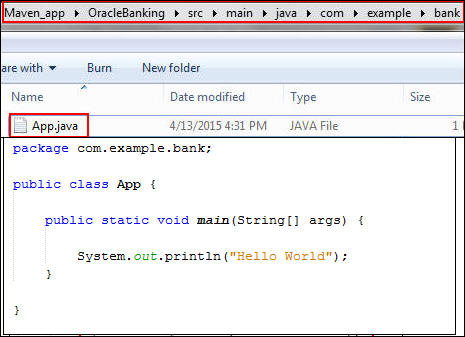
Creating and Modifying Java Source Files
In this section, you calculate simple interest by
creating the SimpleInterest.java
source file and modifying the App.java
source file.
-
Navigate to the directory where you created your Maven project, and then open the specified location:
\**\Maven_app\OracleBanking\src\main\java\com\example\bank -
Create a Java source file named
SimpleInterest.java.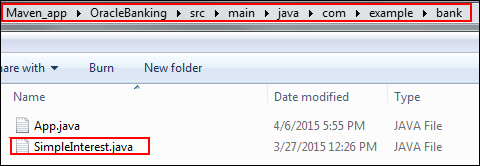
-
Edit the
SimpleInterest.javafile with the following code:package com.example.bank; public class SimpleInterest{ public static double calculateSimpleInterest(double amount, double years, double rate_of_interest) { double simple_interest; simple_interest = amount * years * rate_of_interest; return simple_interest; } }The
calculateSimpleInterestmethod calculates the interest rate on the loan amount, the tenure of the loan, and the rate of interest per annum. -
Press Ctrl+S and close the file.
-
Modify
App.javawith the following code:double result = SimpleInterest.calculateSimpleInterest(10000, 5, 7); System.out.println("The simple interest is:" + result); public static double calculateSimpleInterest(double amount, double years, double rate_of_interest) { double simple_interest; simple_interest = amount * years * rate_of_interest; return simple_interest; } -
Review the code. It should look like the following:
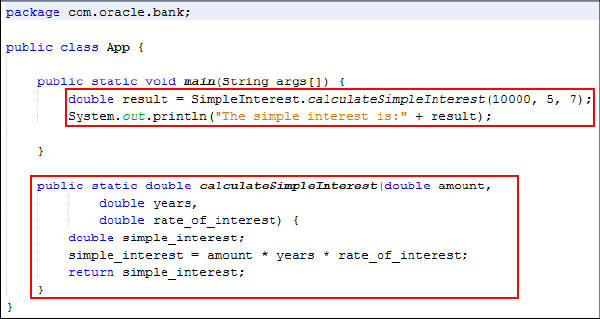
-
Press Ctrl+S and close the file.
Creating a Manifest with Maven
In this section, you learn how to use maven-jar-plugin
to create a manifest file and package it by adding
it to the JAR file.
- Defines the entry point of the project and
creates an executable JAR file.
- Adds the class path of the project
dependencies.
-
Edit the
pom.xmlfile:
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.4</version> <configuration> <archive> <manifest> <mainClass>com.example.bank.App</mainClass> </manifest> </archive> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>You defined
maven-jar-plugininpom.xml,and configured it within the configuration tag. -
Review the code. It should look like the following:

In the Maven project, you specify the main class details by updating the
pom.xmlfile. Thecom.example.bank.Appclass in the project is the main class that will be executed when you execute the JAR file. -
Press Ctrl+S and close the file.
You successfully updated your pom.xml
file.
Testing, Building, and Running the Application Using Maven
Testing the Application
In this section, you learn how to test your
application with AppTest.java
using the Maven command-line interface (CLI).
-
Import the package into
AppTest.java: -
Edit the
AppTestmethod:double result=App.calculateSimpleInterest(10000,5,7); Assert.assertEquals("Test failed. ",35000.0,result); -
Review the code. It should look like the following:
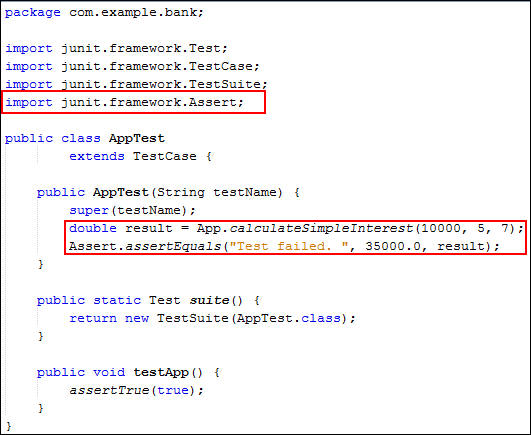
You modified the simple interest value, and then verified the value by using assert statements in the JUnit test case.
-
Press Ctrl+S and then run the test cases in
AppTest.javainside theOracleBankingproject.mvn test
-
Review the output.

The test case failed and the assert failed message is displayed.
- Modify
AppTest.java:
Assert.assertEquals("Test failed. ", 350000.0, result);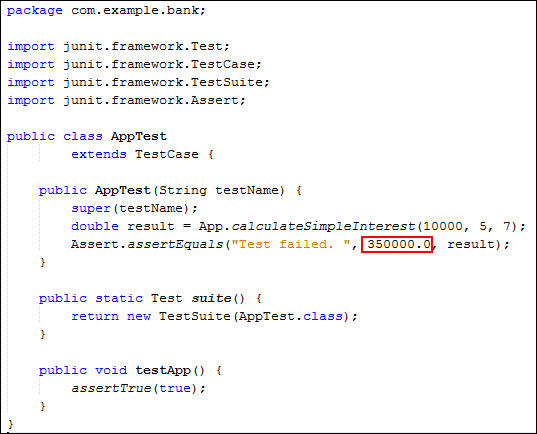
You modified the simple interest value, and then verified the value by using assert statements in the JUnit test case.
-
Press Ctrl+S and then run the test cases in
AppTest.java:mvn test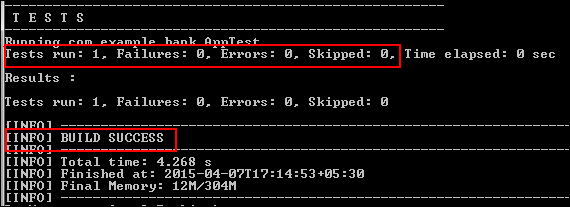
The test case executed successfully, and a build success message is displayed.
import junit.framework.Assert;Building the Application
In this section, you learn how to clean and build your application using the Maven CLI.
-
Clean and build your Maven project, and review the output:
mvn clean package
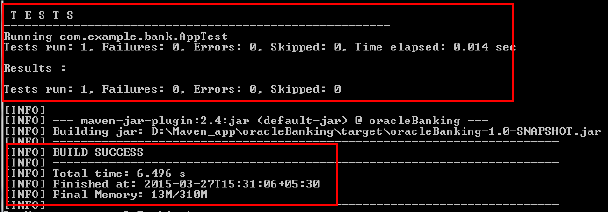
You successfully built the
OracleBankingJava SE application using Maven. -
Navigate to the directory where you created
OracleBankingand notice that atargetfolder was created.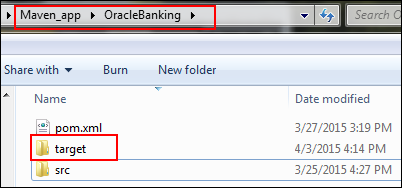
-
Open the
targetfolder, and review the folder structure.Folder name Description classesContains .classfiles of Java source filestest-classesContains .classfiles of Java test filesmaven-archiverContains the pom.propertiesfilesurefire-reportsContains the report of the application when mvncommand is executed.javaEmpty Java file OracleBanking-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jarContains all the project related details in a single zip file. This is the executable JAR file used to run the application
Packaging and Running
the Application
In this section, you learn how to package and run the Java SE project using the Maven CLI.
-
Navigate to the directory where you installed Maven, and open the
settings.xmlfile.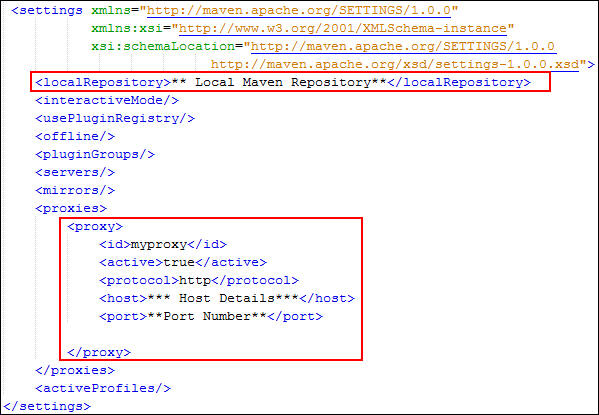
The
<localRepository>tag specifies the local repository location on your machine. By default, the local repository is created in the%USER_HOME%directory. You can specify another location by updating it in thesettings.xmlfile. If you need to set proxy details for the application, then update it in thesettings.xmlfile. -
Clean and package the files, plug-ins, and libraries before running the application:
mvn clean package -
Use the Maven Local repository to run your Java SE Maven application:
mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="com.example.bank.App" -s "*****location of settings.xml file.********"
-
Review the output.
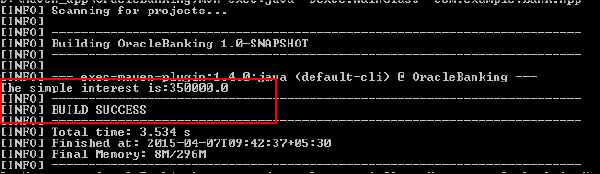
You successfully executed the Java SE application named
OracleBankingusing Maven. The simple interest is calculated and displayed in the Maven CLI. -
Execute the JAR file with following commands:
cd target
java -jar OracleBanking-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
-
Review the output.

You successfully executed the
OracleBankingJava SE application by using Maven. The simple interest is calculated and displayed in the Maven CLI.
Want to Learn More?
- Maven
Quick Guide
- Maven Getting Started Guide
- Installing and Configuring Maven for Build Automation and Dependency Management in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Applications Using Continuous Integration
Credits
To navigate this Oracle by Example tutorial, note
the following:
- Topic List:
- Click a topic to navigate to that section.
- Expand All Topics:
- Click the button to show or hide the details for
the sections. By default, all topics are
collapsed.
- Hide All Images:
- Click the button to show or hide the
screenshots. By default, all images are displayed.
- Print:
- Click the button to print the content. The
content that is currently displayed or hidden is
printed.
To navigate to a particular section in this
tutorial, select the topic from the list.