Creating and Deploying JSF/JPA Applications to Oracle Cloud
Overview
- Have an Oracle.com account.
- Have already completed the Oracle by Example tutorial titled Signing Up for a Java Cloud Service.
- Have already completed the Oracle by Example tutorial titled Configuring NetBeans for Oracle Cloud.
- Have access to or have installed the Oracle Express 11g, Release 2 (Oracle XE) database and unlocked the HR schema. (This example uses the HR schema included in Oracle Database 11g. The Oracle Sample Schemas installation guide is part of the Oracle Database 11g documentation set, and is also available online at http://otn.oracle.com.
- Have access to or have installed SQL Developer (version 3.2.2 or later).
- Have read the Oracle Database Cloud Service documentation
section titled Using
SQL Developer for Data Loading to configure your
SQL Developer instance for your Oracle Database Cloud Service.
- Download the Oracle thin driver, ojdbc6.jar
and save the file to a local directory; for example,
C:\Oracle\db\lib.
Purpose
This tutorial covers how to create and deploy a web
application that leverages JavaServer Faces (JSF) and Java
Persistence API (JPA) technology for Oracle Cloud by using
NetBeans..
Time to Complete
Approximately 1 hour
Introduction
Oracle Cloud is a public, enterprise, platform-as-a-service
(Paas) offering. Oracle Java Cloud Service provides support for
technologies associated with Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 5
(Java EE 5) and Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 6 (Java EE 6).
In this tutorial, you create and deploy an application that
leverages two Java EE 6 technologies, JSF 2.0 and JPA 2.0, which
are the latest versions introduced with Java EE 6. Oracle
WebLogic Server 11g (10.3.6) and Oracle Cloud provide
support for Java EE 5 and Java EE 6 technologies to enable Java
application developers to create a broad range of applications
that require sophisticated front-end user interfaces coupled
with persistent data storage.
Scenario
In this tutorial, you create a JSF 2.0/JPA 2.0 human resources
(HR) application by using wizards built into the NetBeans
integrated development environment (IDE). You develop, deploy,
and test the application locally in a WebLogic Server 11g
instance, and then deploy and test the application in Oracle
Cloud.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you should:
Creating a Connection to a Local Oracle XE database
Instance in NetBeans
In this section, you create a connection to a local instance of
Oracle XE.
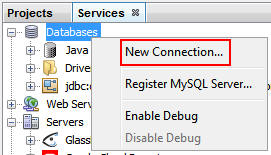
In NetBeans, in the Services window, right-click Databases
and select New Connection.
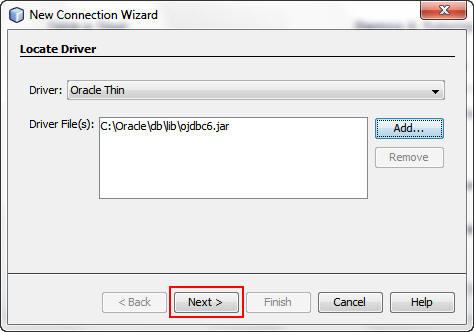
In the New Connection Wizard dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Select Oracle Thin from the Driver list.
b. Click Add.

Note: If you haven't downloaded the file yet, click the link in the dialog box.
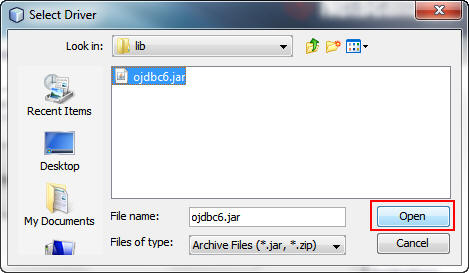
In the Select Driver dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Browse to the directory where you downloaded the ojdbc6.jar
file.
b. Select ojdbc6.jar.
c. Click Open.
Click Next.
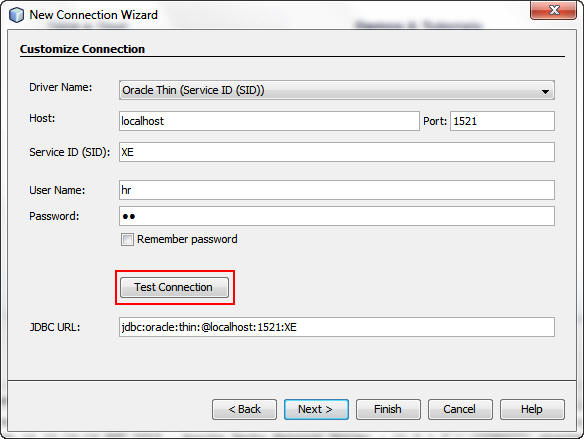
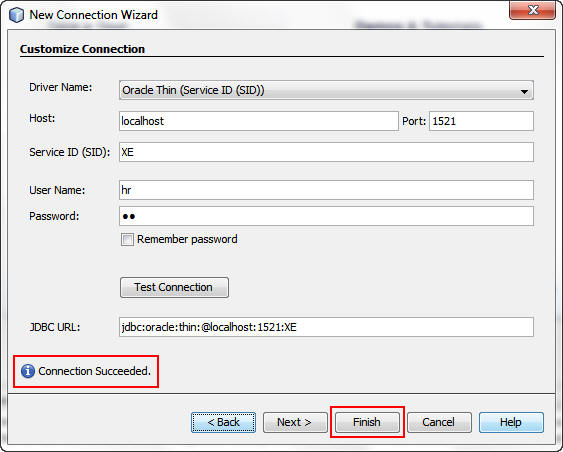
The Customize Connection dialog box displays prepopulated data for the HR database connection.
Click Test Connection to check that the connection
is working.
When the "Connection Succeeded" message appears, click Finish.
In the Services window, expand the new connection, then HR,
and then Tables.
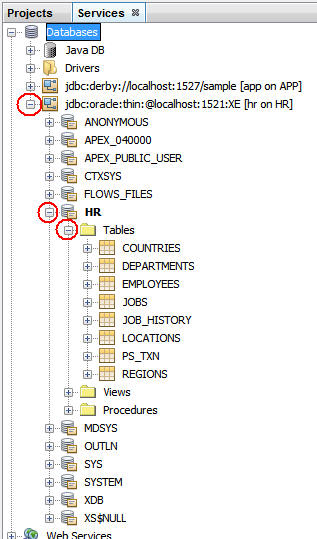
The tables are in the HR database.
Creating a Base JSF NetBeans Application Project
To build a JSF/JPA project, you start by creating a NetBeans
project application.
Select File > New Project.
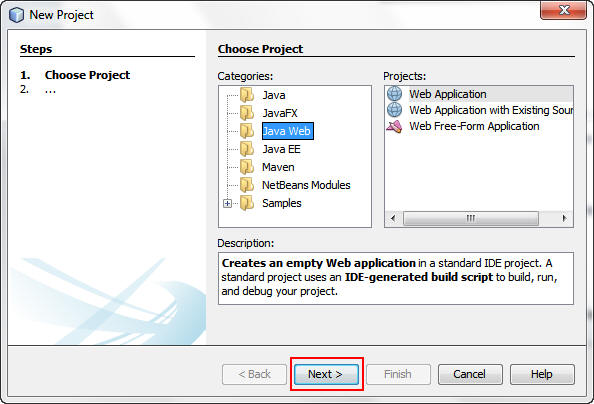
In the New Project dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Select Java Web from Categories.
b. Select Web Application from Projects.
c. Click Next.
In the New Web Application dialog box, enter TestJSFJPA
as the project name and click Next.
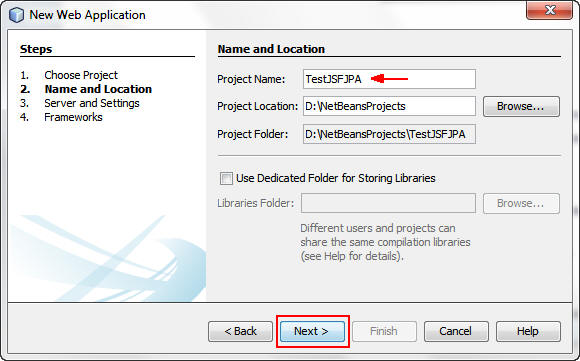
On the Server and Settings screen, perform the following steps:
a. Select Oracle Weblogic Server 10.3.6 from the list.
b. Deselect the Set Source Level to 1.5 check box.
c. Click Next.
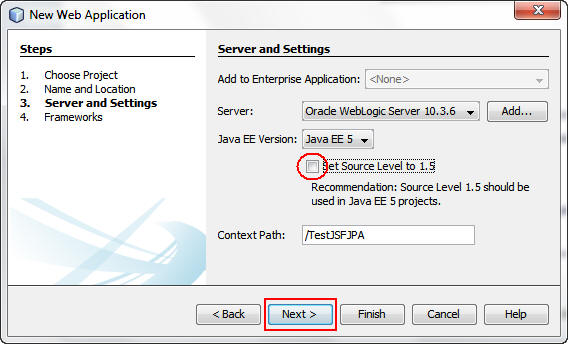
On the Frameworks screen, select JavaServer
Faces and click Finish.
Generating JPA Entities and JSF Pages
NetBeans provides a set of wizards that enables a developer to
quickly create a simple create, retrieve, update, and delete
(CRUD) application. A developer can generate JPA entities
directly from database tables, and then generate JSF pages to
support CRUD operations on those entities. The wizards make it
possible to quickly create an application to test end-to-end
support for JSF 2.0 and JPA 2.0 technologies.
Right-click TestJSFJPA in the Projects window and
select New > Other.
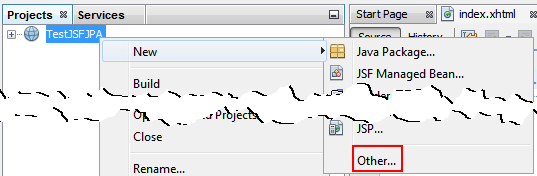
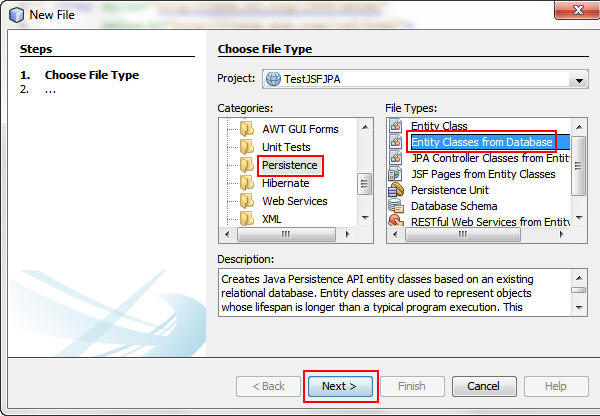
In the New File dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Select Persistence from Categories.
b. Select Entity Classes from Database from File Types.
c. Click Next.
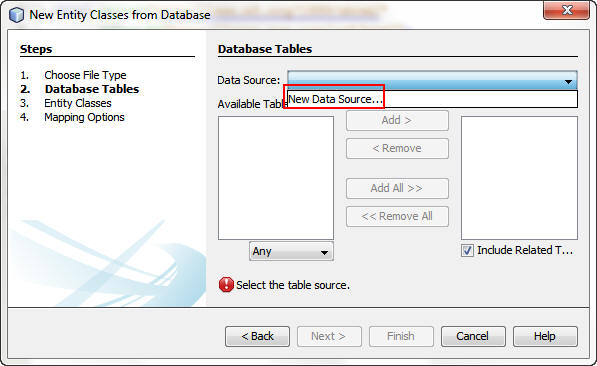
On the Database Tables screen, select New Data Source
from the Data Source list to display the Create Data Source
dialog box.
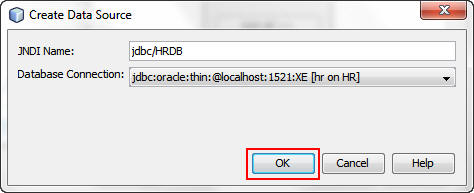
Perform the following steps:
a. Enter jdbc/HRDB as the Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) name.
b. Select the jdbc:oracle:thin JDBC connection.
c. Click OK.
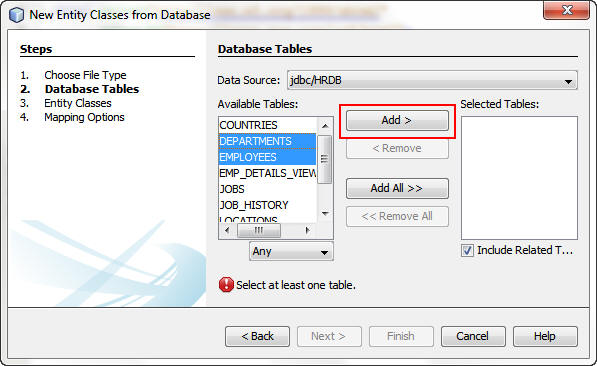
On the Database Tables screen, perform the following steps:
a. Press the Ctrl key and select DEPARTMENTS and EMPLOYEES from Available Tables.
b. Click Add.
The tables related to DEPARTMENTS and EMPLOYEES are also selected.
Click Next.
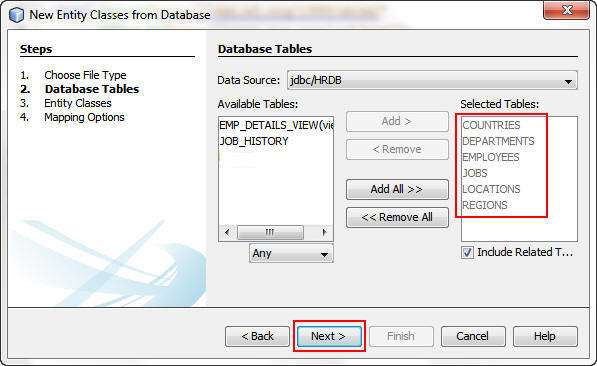
On the Entity Classes screen, enter example.entity
as the package name and click Finish.
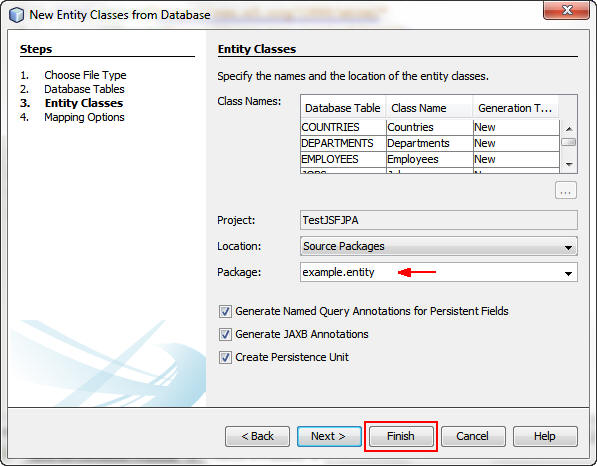
When the entity class generation is completed, expand the example.entity
package in the Projects window to see the entity classes.
Right-click TestJSFJPA and select New >
Other.
In the New File dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Select JavaServer Faces from Categories.
b. Select JSF Pages from Entity Classes from File Types.
c. Click Next.
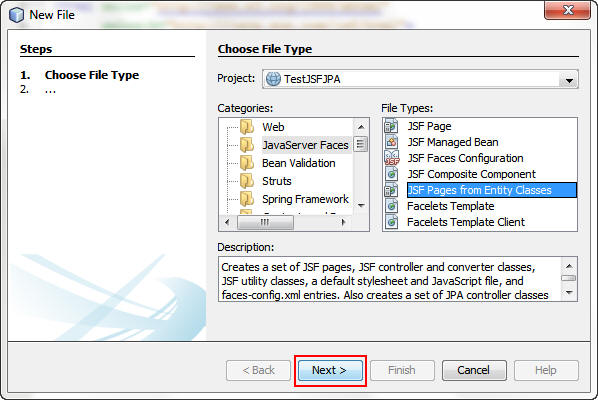
In the New JSF Pages from Entity Classes dialog box, click
Add All to move the Available Entity Classes list to
the Selected Entity Classes list.
Click Next.
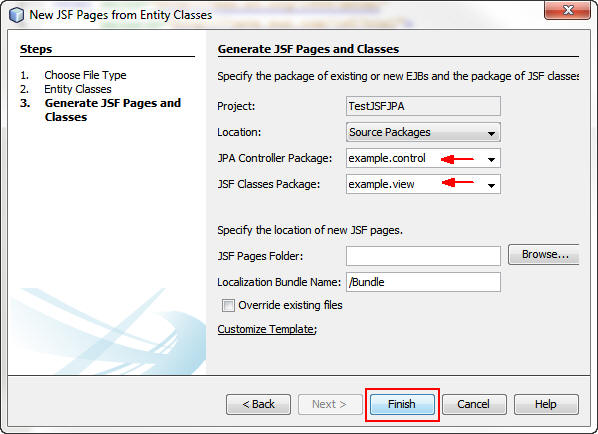
On the Generate JSF Pages and Classes screen, perform the following steps:
a. Enter example.control as the package name for
the JPA Controller Package.
b. Enter example.view as the package name for the JSF Classes Package.
c. Click Finish.
At this point, you have built a JSF/JPA application around the HR database tables. This application provides CRUD capabilities through a typical Model-View-Controller architecture.
Connecting to Your Oracle Database Cloud Service
In order to run the application that you created in Oracle
Cloud, you must first create the HR schema and data in your
Oracle Database Cloud Service. Oracle SQL Developer is a free
IDE that simplifies the development and management of Oracle
Database. You can use SQL Developer to copy the schema and
contents of a local Oracle database (such as Oracle XE) to your
Oracle Database Cloud Service instance.
In SQL Developer, right-click Connections and
select New Connection to create a connection to the
local Oracle XE database.
In the New / Select Database Connection dialog box, perform the following steps:
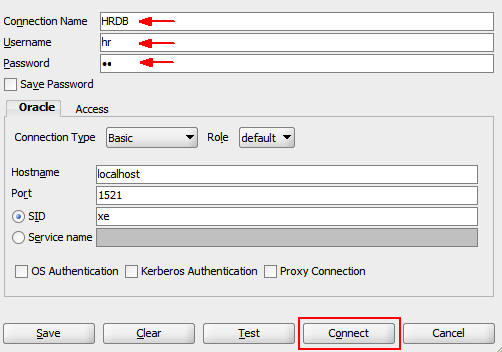
a. Enter HRDB in the Connection Name field.
b. Enter hr in the Username field.
c. Enter hr in the Password field.
d. Click Connect.
On the Connections tab, expand HRDB and Tables.
Collapse HRDB to make it easier to complete the
next steps.
In a browser, log in to your Oracle Cloud account, which
has two services.
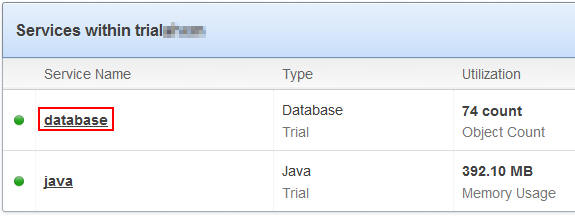
On the My Services page, select database to open
the Database Details page.
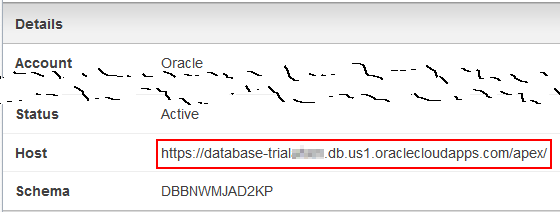
On the Database Details page, write down the host URL.
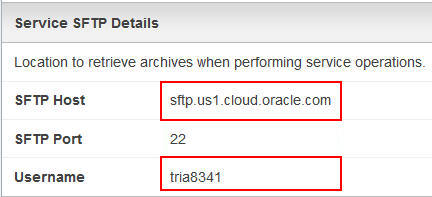
On the Service SFTP Details page, write down the SFTP host
and user name.
In SQL Developer, right-click Cloud Connections and
select New Cloud Connection to create a connection
to the Oracle Database Cloud Service instance.
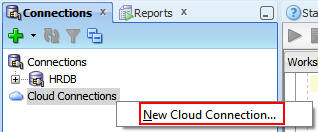
In the New Cloud Connection dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Enter CloudHRDB as the connection name.
b. Enter your Oracle Cloud user name.
c. Copy the Host URL from the Details section of your Oracle Database Cloud Service console to the URL.
d. Copy the SFTP user name to the Username field in the SFTP section.
e. Copy the SFTP host to the Hostname field.
f. Click OK.
Expand CloudHRDB.
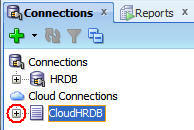
When you attempt to look at the contents of the connection, the Authentication dialog box is displayed, and you must authenticate with your Oracle Database Cloud Service.
Enter your Oracle Cloud password and click OK.
You are connected to your Oracle Database Cloud Service.
Expand Tables.
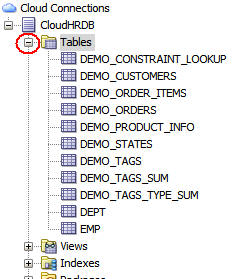
The default tables provided with the service are displayed.
Copying Database Schema and Data Between Oracle Database Instances
SQL Developer provides a tool with which you can copy a
database schema and data from one database to another. You will
use this capability to copy the HR database schema and data from
your local Oracle XE instance to your Oracle Database Cloud
Service instance.
Select View > Cart.
Expand HRDB and Tables.
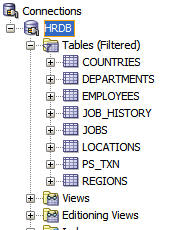
Press the Ctrl key and select COUNTRIES, DEPARTMENTS,
EMPLOYEES, JOBS, LOCATIONS, and
REGIONS.
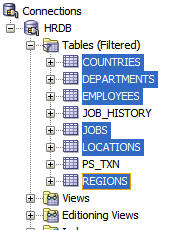
Drag the selected tables to the Cart window.
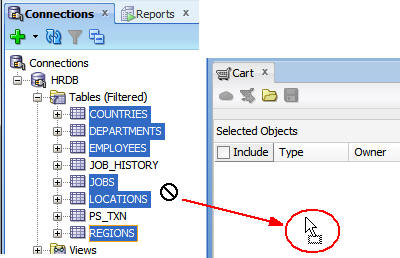
The cursor changes into a rectangle when you place it in the Cart window.
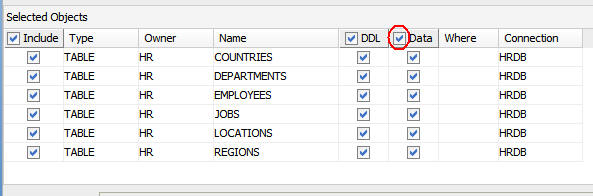
Select the Data check box so that the data is also
copied.
Click the Cloud button to deploy the selected HR
database entity objects to your Oracle Database Cloud
Service.
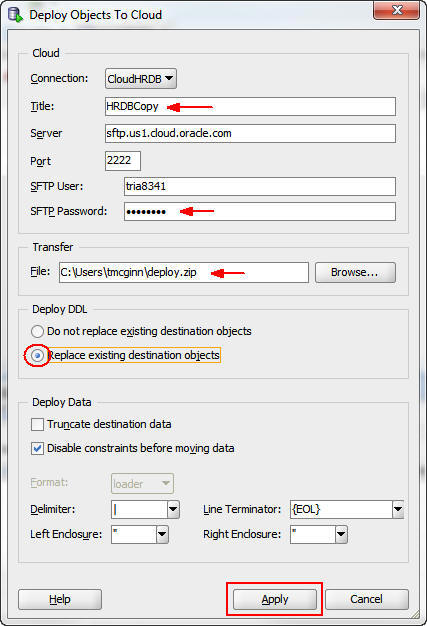
In the Deploy Objects to Cloud dialog box, perform the following steps:
a. Give the copy process a title; for example, HRDBCopy.
b. Enter the password for the SFTP user.
c. Enter the path and name to the file used to transfer the schema and data.
d. Select Replace existing destination objects.
e. Click Apply.
A progress bar displays the progress of the transfer.
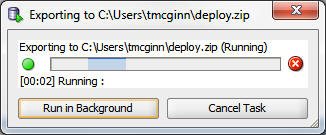
Collapse the HRDB connection and expand the CloudHRDB
connection.
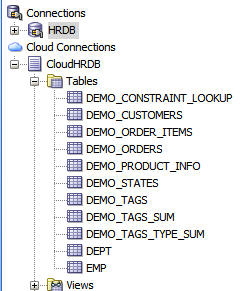
Perform the following steps:
a. Scroll down to Deployments.
b. Expand Deployments.
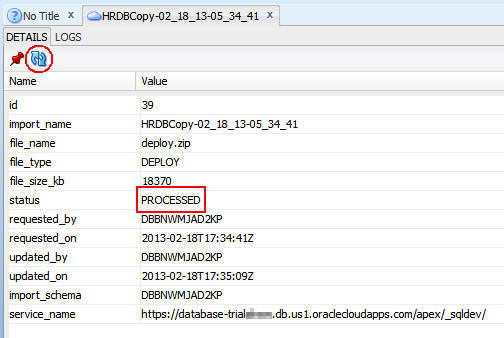
c. Double-click the HRDBCopy deployment.
The deployment log opens.
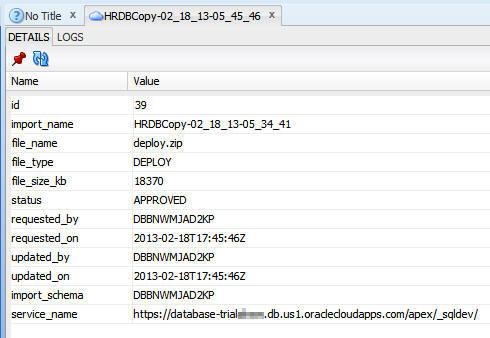
Click the Refresh button periodically until the
status changes to PROCESSED.
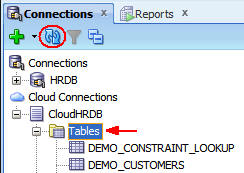
Perform the following steps:
a. Scroll up to CloudHRDB.
b. Select Tables.
c. Click Refresh.
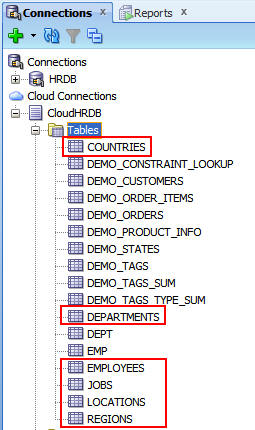
The tables that you copied from your Oracle XE instance
were successfully created in your Oracle Database Cloud
Service instance.
Deploying the JSF/JPA Application to Oracle Java Cloud
Service
After successfully copying the database to your Oracle Database
Cloud Service, you can deploy your JSF/JPA application to your
Oracle Java Cloud Service.
In NetBeans, right-click TestJSFJPA and select Properties.

In the Project Properties dialog box, select Run from
Categories.
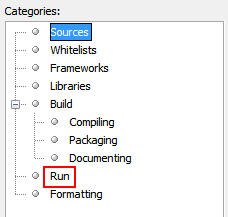
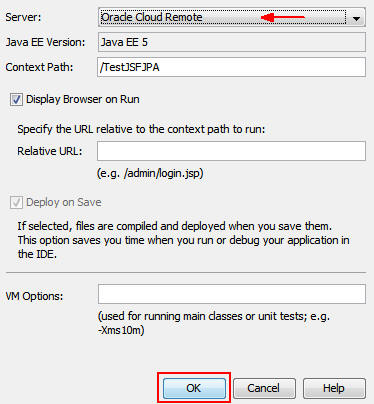
Select Oracle Cloud Remote from the Server list and
click OK.
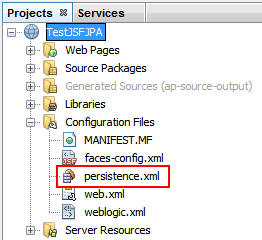
Expand Configuration Files and double-click persistence.xml
to open it in the editor.
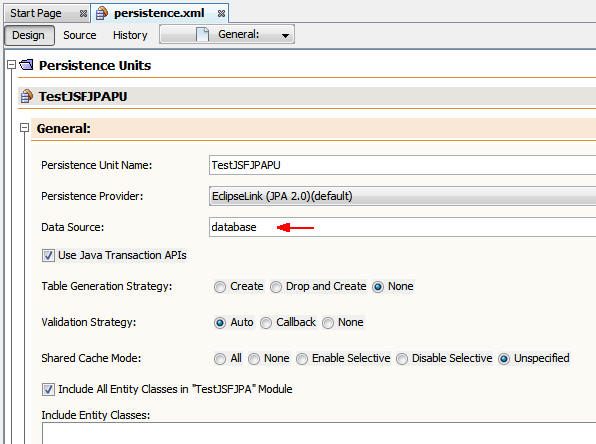
Enter database as the data source and save the
file.
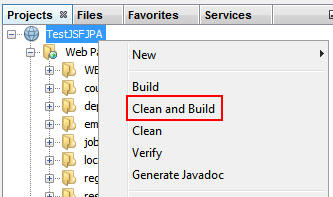
Right-click TestJSFJPA and select Clean and
Build.
Right-click TestJSFJPA and select Deploy.
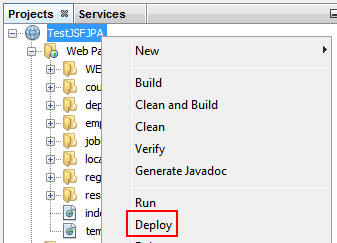
The following message is displayed in the Output window: Deployment was successful.
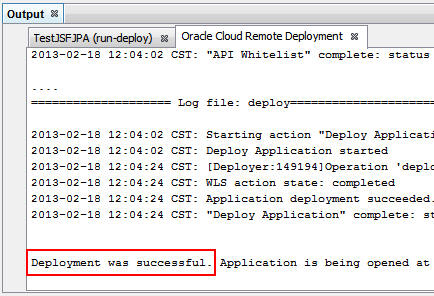
Running the JSF/JPA Application in Oracle Cloud
With the application successfully deployed to Oracle Cloud, you
can test the application.
In the Services window, expand Oracle Cloud Remote.
Right-click TestJSFJPA and select View to
open a browser window.
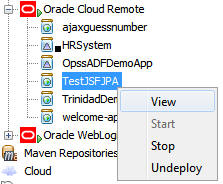
Log in to your Oracle Cloud account.
The application appears in the browser.
Click Show All Employee Items to display the
current employee list.
An employee table displays 10 employees at a time.
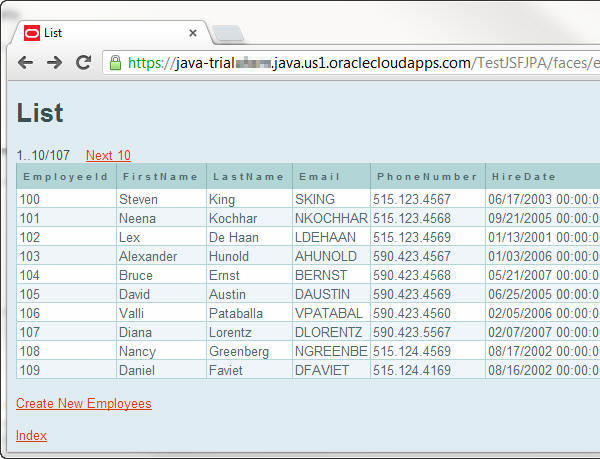
This table proves that the application is running in your
Oracle Java Cloud Service, and it is successfully retrieving
data from Oracle Database Cloud Service.
Summary
- Connect to a local Oracle XE database instance through NetBeans
- Create an application by using NetBeans wizards that use JPA entities and JSF pages
- Use SQL Developer to copy local HR database schema and data
to your Oracle Database Cloud Service
- Modify your JSF/JPA application and deploy it to Oracle Java Cloud Service
- Run your JSF/JPA application by using Oracle Cloud
- Oracle Cloud documentation
- NetBeans documentation
- Oracle WebLogic Server 11g documentation
- Oracle
SQL Developer documentation
- To learn more about Oracle
Cloud, refer to additional OBEs in the Oracle Learning Library
- Lead Curriculum Developer: Tom McGinn
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
Resources
Credits
To help navigate this Oracle by Example, note the following:
- Hiding Header Buttons:
- Click the Title to hide the buttons in the header. To show the buttons again, simply click the Title again.
- Topic List Button:
- A list of all the topics. Click one of the topics to navigate to that section.
- Expand/Collapse All Topics:
- To show/hide all the detail for all the sections. By default, all topics are collapsed
- Show/Hide All Images:
- To show/hide all the screenshots. By default, all images are displayed.
- Print:
- To print the content. The content currently displayed or hidden will be printed.
To navigate to a particular section in this tutorial, select the topic from the list.