Java EE 7: Applying JPA to Stored Procedures
Overview
Purpose
This tutorial demonstrates how to invoke a stored procedure residing in a database by using Java Persistence API 2.1 (JPA 2.1).
Time to Complete
Approximately 45 minutes
Introduction
Java Specification Request 238 (JSR 338) defines the specification of the Java API for the management of persistence and object/relational mapping with Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 7 (Java EE 7) and Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE). JPA 2.1 added support for the invocation of predefined and user-defined stored procedures residing in the database.
The StoredProcedureQuery interface supports
database-stored procedures. You can specify stored procedures with
the NamedStoredProcedureQuery annotation or you can
specify them dynamically.
- The
NamedStoredProcedureQueryannotation names a stored procedure residing in a database, specifies the parameter types for the stored procedure, and specifies mapping for the result sets. You use thecreateNamedStored-ProcedureQuerymethod to create an executableStoredProcedureQueryobject. - In a dynamically specified stored procedure, you must register
all parameters by using the
registerStoredProcedureParametermethod of theStoredProcedureQueryinterface. You can provide the result set mapping information with thecreateStoredProcedureQuerymethod.
In this tutorial, you use JPA 2.1 to invoke a stored procedure dynamically.
Scenario
This tutorial implements a simple scenario to demonstrate how to use JPA 2.1 to invoke an existing stored procedure in the Java database (Java DB) server.
You are provided with source files and scripts to create a stored
procedure in the sample database of the Java DB
server. The stored procedure, CUSTOMERCOUNT, returns
the count of customers whose credit limit is above a specific
value.
You modify a web application that contains the following:
- An Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) class with a method that
dynamically invokes the
CUSTOMERCOUNTstored procedure - A servlet that accepts user input for the credit limit, invokes the EJB method, and displays the count of customers whose credit limit is above the input value
Hardware and Software Requirements
The following is a list of hardware and software requirements:
- Java SE 7 (Java SE 7u11 recommended)
- NetBeans 7.3.1 IDE for Java EE 7
- Oracle GlassFish Server 4
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you should:
- Have some experience writing and deploying web applications.
- Have some experience using JPA 2.1 in a web application.
- Have installed NetBeans 7.3.1, Java EE 7, and GlassFish Server 4.
- Have started NetBeans.
- Have unzipped the
CustomerStoredProc.zipfile. - Have opened the
CustStoredProcproject in NetBeans. - Have unzipped the
JPAExampleApp.zipfile. - Have opened the
JPAExampleAppproject in NetBeans.
Creating a Stored Procedure in the Java DB Server
In this section, you create the CustomerStoredProc
stored procedure in the sample database of the Java
DB server.
-
On the Projects tab, expand
CustStoredProc > Source Packages > <default package>and then clickCustStoredProc.javato open it in the code editor window.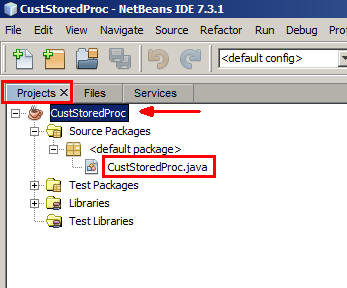
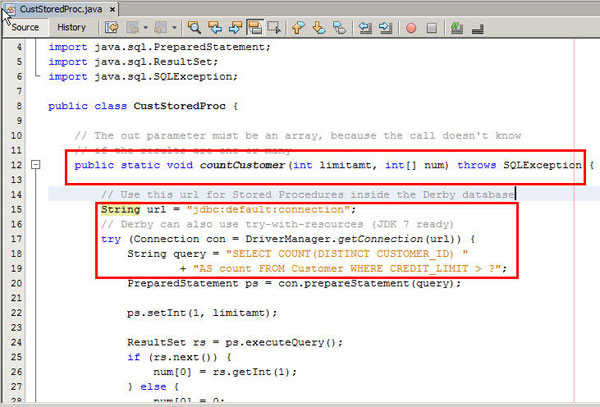
- Examine the
CusStoredProc.javafile and observe the content of theCountCustomermethod. Make a note of the method's arguments and data types.
-
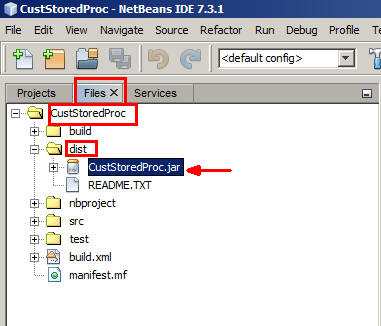
On the Projects tab, right-click
CustomerStoredProcand selectClean and Build. - On the Files tab, verify that
CustStoredproc.jaris located in thedistfolder.
- In Windows Explorer, copy
CustStoredproc.jarfrom theCustStoredProc > distfolder and paste it in theD:\drive of your system. -
On the NetBeans Services tab, perform the following steps:
- Expand Databases.
- Right-click
jdbc:derby://localhost:1527/sample [app on APP]. - Select Connect.
-
In the Connect dialog box, enter app for the password and click OK.

-
Complete the following steps to open a script file:
- Select Files > Open File.
- Browse to the
locationwhere you have extracted theCustomerStoredproc.zipfile. - Select
scripts.sqland click Open.
-
Complete the following steps to open a script file:
- In the Code Editor window, select
jdbc:derby://localhost:1527/sample [app on APP]from the Connection list. - Select the code snippet under SECTION 1, right-click, and select Run Selection.
- Select the code snippet under SECTION 2, right-click, and select Run Selection.
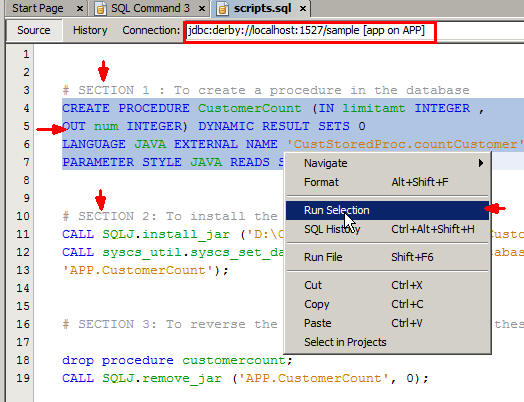
- In the Code Editor window, select
-
On the Services tab, expand
Databases > jdbc:derby://localhost:1527/sample [app on APP] > App > Proceduresand verify that theCUSTOMERCOUNT stored procedurewas created.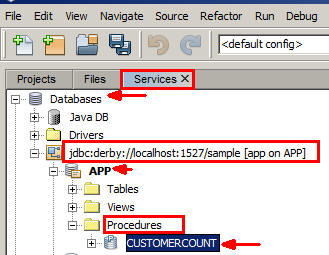
Reviewing the JPAExampleApp Web Application
In this section, you review the JPAExampleApp
web application in NetBeans.
-
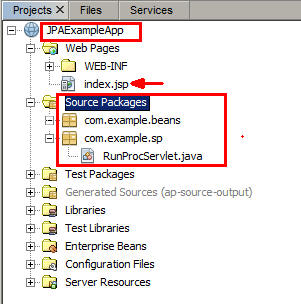
On the Projects tab, expand
JPAExampleAppand view the application structure. -
Expand
JPAExampleApp > Web Pagesand clickindex.jspto open it. -
Examine the code within the
<form>tags.
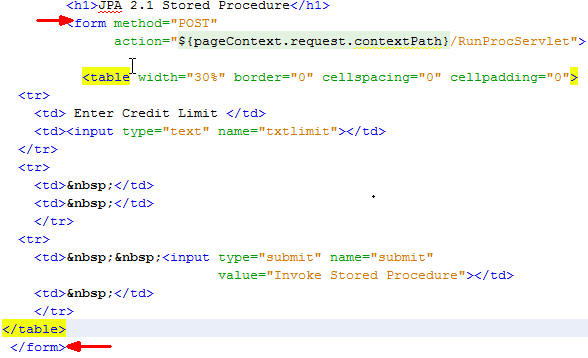
- On the Projects tab, expand
JPAExampleApp > Source Packages > com.example.spand ensure thatRunProcServlet.javais displayed.
Invoking the CUSTOMERCOUNT Stored Procedure in JPAExampleApp
In this section, you create a persistence unit and a stateless
session bean, CustEJB. You add a method to CustEJB
that invokes a stored procedure.
Creating the Persistence Unit
-
On the Projects tab, right-click
JPAExampleAppand select New > Persistence Unit. -
Perform the following steps in the New Persistence Unit dialog box:
- Select
jdbc/samplefor Data Source. - Select the Use Java Transaction APIs check box.
- Select None for Table Generation Strategy.
- Click Finish.
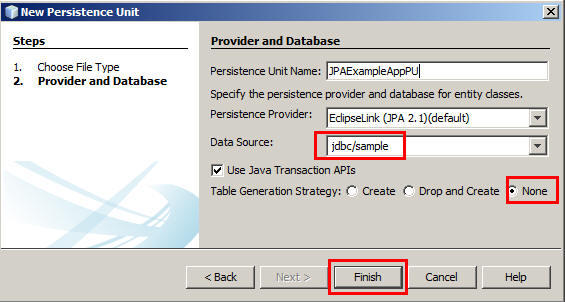
- Select
-
On the Projects tab, expand
JPAExampleApp > Configuration Filesand then perform the following steps:- Verify that
Persistence.xmlwas created. - Open
Persistence.xmland verify its configuration information.

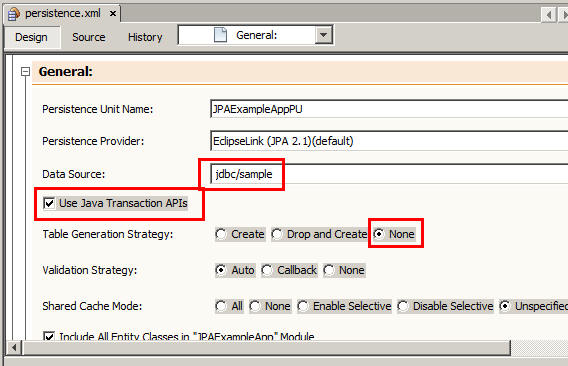
- Verify that
Developing the Session Bean
-
On the Projects tab, expand
JPAExampleApp > Source Packages.com.example.beansand then perform the following steps:- Right-click
com.example.beansand select New > Session Bean. - In the New Session Bean dialog box, provide the following information:
- EJB Name: Enter CustEJB.
- Package: Select
com.example.beans. - Session Type: Select Stateless.
- Click Finish.
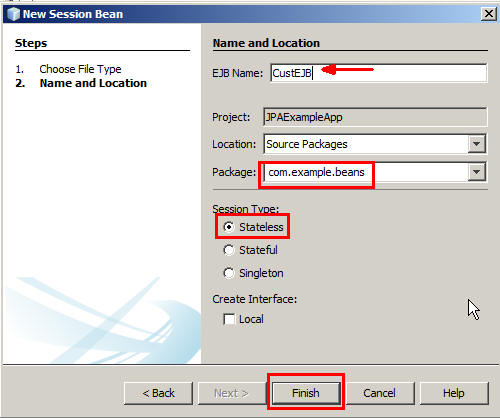
- Right-click
- Open
CustEJB.javaand modify it to add the following: - An
@LocalBeanannotation to the bean class - An instance of
EntityManagerwith an@PersistenceContextannotation - A method, with the following signature:
public Integer invokeStoredProcedure(String limit) - In the
invokeStoredProceduremethod, declare an instance ofStoredProcedureQueryto perform the following: - Invoke the
createStoredProcedureQuerymethod ofEntityManagerand store its return value in theStoredProcedureQuery instance. - Register the input and output parameters of the
CUSTOMERCOUNTstored procedure by using theregisterStoredProcedureParametermethod. - Set the values of the input parameter by using the
setParametermethod. - Execute the stored procedure by using the
executemethod. - All required import statements
package com.example.beans;
import javax.ejb.LocalBean;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.ParameterMode;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.persistence.StoredProcedureQuery;
@Stateless
@LocalBean
public class CustEJB {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager em;
public Integer invokeStoredProcedure(String limit) {
StoredProcedureQuery storedProcQuery = em.createStoredProcedureQuery("CustomerCount");
// Parameters can be numbered or named
// Derby stored procedures use numbers
storedProcQuery.registerStoredProcedureParameter(1, Integer.class, ParameterMode.IN);
storedProcQuery.registerStoredProcedureParameter(2, Integer.class, ParameterMode.OUT);
int limitamt=Integer.parseInt(limit);
storedProcQuery.setParameter(1,limitamt);
boolean result = storedProcQuery.execute();
return (Integer) storedProcQuery.getOutputParameterValue(2);
}
}Modifying the RunProcServlet Class
In this section, you modify the RunProcServlet
class to invoke the invokeProcedure method of the CustEJB
class.
-
On the Projects tab, expand
JPAExampleApp > Source Packages > com.example.sp. -
Open
RunProcServlet.javaand perform the following steps to modify it:- Declare an instance of
CustEJBwith an@EJBannotation. - Locate the
processRequestmethod. - Retrieve the value of the
txtlimitparameter from theRequestobject and store it in a string variable named limit. - Invoke the
invokeProceduremethod of theCustEJBclass and provide thelimitstring variable as its argument value. - Add the appropriate
catchstatement. - Import the required classes.
- Retain that the pre-exisitng methods in the class.
- Declare an instance of
-
On the Projects tab, expand
JPAExampleApp > Web Pagesand openindex.jsp.- Locate the starting
<Form>tag. - Ensure that the
<Form>tag has theactionattribute whose value points to theRunProcServletservlet.
<form method="POST" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/RunProcServlet"> - Locate the starting
package com.example.sp;
import com.example.beans.CustEJB;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.ejb.EJB;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet(name = "RunProcServlet", urlPatterns = {"/RunProcServlet"})
public class RunProcServlet extends HttpServlet {
@EJB
private CustEJB custejb;
protected void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
try (PrintWriter out = response.getWriter()) {
String limit = request.getParameter("txtlimit");
out.print("<h2>JPA 2.1 Stored Procedure Result </h2>");
out.print("<h4>Number of Customers with credit limit above " + limit + " = " + custejb.invokeStoredProcedure(request.getParameter("txtlimit")) + "</h4>");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("problem with return of proc " + e);
}
}
// per-exisiting methods go herePackaging, Deploying, and Testing the Web Application
-
Perform the following steps on the Projects tab:
- Right-click
JPAExampleAppand select Clean and Build. - Right-click
BatchExampleAppand select Run.
The home page opens in the web browser.
- Right-click
-
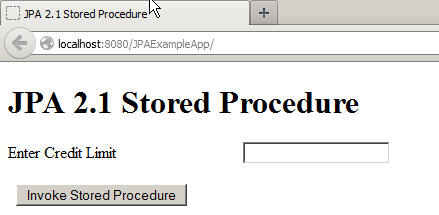
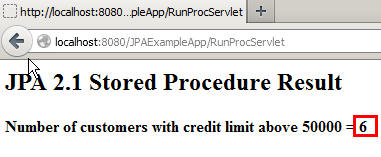
Enter 50000 in the Credit Limit text box and click Invoke Stored Procedure.
The result set of the
CUSTOMERCOUNTstored procedure is displayed. -
Repeat step 2 with credit limit values of 25000, 90000, and 70000, and verify that the number of customers changes.
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Create a stored procedure in the Java DB server
- Use JPA 2.1 to invoke the stored procedure dynamically in a web application:
- Declare the stored procedure
- Register the input and output parameters
- Provide the parameter values
- Execute the stored procedure and retrieve the result set
- Display the values from the result set
Resources
To learn more about Java EE 7 and the batch processing API, see the following resources:
- JSR 338: Java
Persistence API 2.1
- Java Persistence API 2.1: What’s New and What’s Coming
- Introduction to Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 7
- To learn more about Java EE 7, visit other OBE tutorials in the Oracle Learning Library.
Credits
- Lead Curriculum Developer: Paromita Dutta
- Contributor: Tom McGinn
- QA: Diganta Choudhury
- Editor: Susan Moxley
To navigate this Oracle by Example tutorial, note the following:
- Topic List:
- Click a topic to navigate to that section.
- Expand All Topics:
- Click the button to show or hide the details for the sections.
By default, all topics are collapsed.
- Hide All Images:
- Click the button to show or hide the screenshots. By default,
all images are displayed.
- Print:
- Click the button to print the content. The content that is
currently displayed or hidden is printed.
To navigate to a particular section in this tutorial, select the
topic from the list.