- Revision History
- Overview
- Feature Summary
-
- Customer
- Customer Information
- Start, Stop, and Transfer Service
-
- Agent Contact Scripting for Start/Service/Transfer Service Request Process Flows
- Start/Stop/Transfer Service Request Process Flows - Paperless Billing
- Start Service Request Process Flow Cancellation - Auto Person/Account Clean Up
- Start/Stop/Transfer Service Request Process Flows – Custom Panel Elements
- Service Agreements to Start Determination
- Service Agreements to Start for a Service Point Derivation
- "Add All SA Type When None Are Initial" Feature Configuration Option Type
- Contextual Insights
-
- Contextual Insights - Financially Responsible Person
- Contextual Insights - Highlight In Progress Start/Stop/Transfer Requests
- Contextual Insights - Highlight Premise Service Information
- Contextual Insights - Pending Start/Stop Service Agreements
- Contextual Insights - Person and Premise Life Support/Sensitive Load
- Contextual Insights - Insight Classes
- Payment Processing
- Web Services
- Meter Solution
- Analytics Visualization
- Cloud Service Foundation
- Utilities Application Framework
- Product Usability
- Implementation Tools
- Web Services
-
- Additional Metadata to Support API Publishing
- Description Added to Inbound Web Service Operation
- HTTP Method Available to Internal Service Script
- Inbound Web Service Maintenance (REST)
- New Published APIs
- Outbound OAuth Client Credentials Grant Type
- Rootless Request and Response Schemas (JSON)
- Support for an External-facing Schema
- Access Utilities Cloud Service REST APIs with OAuth Credentials
- Miscellaneous
- Utilities Testing Accelerator
- System Wide
- Customer
- IMPORTANT Actions and Considerations
This document will continue to evolve as existing sections change and new information is added. All updates appear in the following table:
| Date | Product | Feature | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 02 AUG 2021 | Created initial document. |
Oracle Utilities Customer Cloud Service is a customer care, service order, metering, billing, and credit and collections solution. The solution is designed to cater for utilities of all sizes, supports one to many utility service types, and handles the complexities associated with a utility's processes.
This guide outlines the information you need to know about new or improved functionality in this update, and describes any tasks you might need to perform for the update. Each section includes a brief description of the feature, the steps you need to take to enable or begin using the feature, any tips or considerations that you should keep in mind, and the resources available to help you.
Column Definitions:
Report = New or modified, Oracle-delivered, ready to run reports.
UI or Process-Based: Small Scale = These UI or process-based features are typically comprised of minor field, validation, or program changes. Therefore, the potential impact to users is minimal.
UI or Process-Based: Larger Scale* = These UI or process-based features have more complex designs. Therefore, the potential impact to users is higher.
Features Delivered Disabled = Action is needed BEFORE these features can be used by END USERS. These features are delivered disabled and you choose if and when to enable them. For example, a) new or expanded BI subject areas need to first be incorporated into reports, b) Integration is required to utilize new web services, or c) features must be assigned to user roles before they can be accessed.
| Ready for Use by End Users Reports plus Small Scale UI or Process-Based new features will have minimal user impact after an update. Therefore, customer acceptance testing should focus on the Larger Scale UI or Process-Based* new features. |
Customer Must Take Action before Use by End Users Not disruptive as action is required to make these features ready to use. As you selectively choose to leverage, you set your test and roll out timing. |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature |
Report |
UI or |
UI or |
|
||
Agent Contact Scripting for Start/Service/Transfer Service Request Process Flows |
||||||
Start/Stop/Transfer Service Request Process Flows - Paperless Billing |
||||||
Start Service Request Process Flow Cancellation - Auto Person/Account Clean Up |
||||||
Start/Stop/Transfer Service Request Process Flows – Custom Panel Elements |
||||||
"Add All SA Type When None Are Initial" Feature Configuration Option Type |
||||||
Contextual Insights - Highlight In Progress Start/Stop/Transfer Requests |
||||||
Contextual Insights - Person and Premise Life Support/Sensitive Load |
||||||
Access Utilities Cloud Service REST APIs with OAuth Credentials |
||||||
The Customer Activity History zone and Financial Details zone tabs of the Customer 360 portal provide an enriched view of a customer with the following updates:
- Enhanced Customer Activity History Zone:
- The zone displays a Filter By drop-down list (previously labeled as Filter by) that lists the applicable activity categories for the account, which has been expanded to include Service Order, Payment Arrangement, and Device Event activities. The expanded list also includes Cash-only and Credit Rating histories.
- The Display Icon Override Configuration master configuration's Service Agreement maintenance object option includes a Service Agreement Type for overriding the Service Agreement maintenance object icon (for example, for assigning a custom icon for payment arrangement service agreement). The master configuration also provides a new Service Agreement Relationship option for overriding the SA Relationship maintenance object icon.
- Enhanced Financial Details Zone Tabs:
- Enhanced Usage and Billing tab:
- An Hourly View time scale for viewing a customer's hourly usage details on a specific day.
- The Billing and Usage Display Configuration master configuration now provides color previews when configuring the Usage and Billing tab.
- Enhanced Payment Agreements tab:
- Support for payment arrangement for bills.
- New Credit & Collection tab:
- Displays the latest information for these processes in Tree view:
- Collection and Severance: Shows active collection processes or collection processes associated with active severance processes for the account. If there are no active collection processes or collection processes associated with active severance processes, the system may display the most recent inactive collection process by debt class.
- Overdue and Cut: Shows active overdue processes or overdue processes associated with active cut processes for the account. If there are no active overdue processes or overdue processes associated with active cut processes, the system may display the most recent inactive overdue processes.
- Write Off: Shows active write processes linked to the account. If there are no active write off processes, the system may display the most recent inactive write off process by write off debt class.
- You can use the tree to view high-level information and transfer to the maintenance page of the record.
- Displays the latest information for these processes in Tree view:
- Enhanced Usage and Billing tab:
The Customer 360 portal enhancements provide a fuller view of your customer's activity history and financial details, resulting in better handling of account maintenance requests and most common inquiries.
Steps to Enable
Refer to the Defining Customer 360 Options section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
The Customer and Premise Tree zones of the Dashboard portal provide a more intuitive user experience with the following additions or enhancements:
- Customer Zone
- The Person's alternative name is displayed if available.
- The Account drop-down does not appear for a Person with multiple accounts. The Customer Insights zone of the Customer 360 portal ma be configured with an insight for this situation.
- Premise Tree Zone
- The Status string of smart meters at a service point are shorter and indicate if the meters are "Connected," "Disconnected," or "Removed." Previously, the text included the commissioning status.
- The Device information string is shorter and only includes the Device ID and Device Type description.
You can more accurately interact with your customers using the important customer-related information displayed by the Dashboard portal zones.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Key Resources
- Refer to the Defining Customer 360 Options section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Start, Stop, and Transfer Service
Agent Contact Scripting for Start/Service/Transfer Service Request Process Flows
The Customer Service Request Type enables you to define contact scripting for call center agents. Your agents can use the contact scripting as they work through a Start, Stop or Transfer Service Request process flow for a customer who is on the phone. The agents can also read the contact script to the customer to handle requests for customer data or for information-only notices.
You can specify the contact script text to display in predefined locations or script points related to the following in start service request process flows:
- For the type of person linked to the start service request process flow (Person or Business):
- New Customer Identification Introduction
- Identification Request
- Date of Birth Explanation
- Life Support/Sensitive Load
- Phone Number Advisory
- Email Address Advisory
- For the Customer Class for the account linked to the start service request process flow:
- Other Persons on Account
- Paperless Billing Advisory
You can specify the contact script text to display in predefined locations or script points related to the following in stop service request process flows:
- For the type of person linked to the stop service request process flow (Person or Business):
- Life Support/Sensitive Load
- Phone Number Advisory
- Email Address Advisory
- For the Customer Class for the account linked to the stop service request process flow:
- Other Persons on Account
- Paperless Billing Advisory
You can specify the contact script text to display in predefined locations or script points related to the following in transfer service request process flows:
- For the type of person linked to the transfer service request process flow (Person or Business):
- Life Support/Sensitive Load
- Phone Number Advisory
- Email Address Advisory
- For the Customer Class for the account linked to the transfer service request process flow:
- Other Persons on Account
- Paperless Billing Advisory
You can use this feature to provide specific instructions to call center agents or specific information to customers about how their collected information (such as, identifiers or email) is used.
Steps to Enable
Refer to Adding Custom Text to the Start, Stop, and Transfer Processes in the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Tips And Considerations
If your implementation has added custom elements through data area extensions, the extensions can reference custom script points. To implement custom script points, ensure your map fragment’s class attribute is set to “contact-script-point” and the scriptPoint attribute is set to the CM script point extendable lookup value. For example, <div class="contact-script-point" scriptPoint="CM-NewScriptPoint"/>.
Start/Stop/Transfer Service Request Process Flows - Paperless Billing
The system automatically notifies you when the Paperless Billing option is selected and the customer does not have an active email address.
This ensures that customers with paperless billing provide an active email addresses before the system initiates email interactions.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Start Service Request Process Flow Cancellation - Auto Person/Account Clean Up
Canceling (deleting) a Start Service Request will automatically delete the Person and/or Account record created by that process flow.
Auto Person/Account Clean Up reduces the number of Person and/or Account records to maintain for customers you do not have an immediate ongoing relationship with.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Start/Stop/Transfer Service Request Process Flows – Custom Panel Elements
Extension-related data areas enable you to add custom elements at the bottom of panels for the Start Service Request, Stop Service Request, and Transfer Service Request process flows. The panels to which you can insert implementation-specific elements and user interface hints or fragments are as follows:
- Start Service Request
- Move To Premise Address
- Customer Identification
- Services To Start
- Person and Account Details
- Stop Service Request
- Services To Stop
- Person and Account Details
- Transfer Service Request
- Move To Premise Address
- Services to Start
- Services to Stop
- Person and Account Details
Similarly, Customer Service Request business objects related to these process flows now have their own corresponding extension-related data areas. Your extended data areas must match the corresponding extensions in the process flow panels. The processing associated with each process flow will pass the implementation-specific elements to the applicable Customer Service Request-related records.
Extension-related data areas reduce your implementation-specific extensions by leveraging and extending application-owned process flows to include custom panel elements.
Steps to Enable
Refer to Capturing Custom Elements in the Start, Stop, and Transfer Processes in the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Service Agreements to Start Determination
The system determines the Service Agreement Types for new service agreements based on the previous services, regardless of status, when the previous services are on the same account. The Start SA switch on the service agreements to start reflects the services that are currently switched on or off. When all services are switched off, the service agreements are defaulted to start.
Previously, when previous services have different statuses such as an active electric service and a stopped water service, the new electric service was based on the active electric service and the water service was based on the initial Service Agreement Types defined for the service point's Service Point Type. If Service Agreement Types were not configured as initial for the Service Point Type, service agreements for the service point were not shown and prevented the start service on the service point via the Start/Stop function.
This Start/Stop Service Agreement enhancement streamlines the processes associated with Start Service requests.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Service Agreements to Start for a Service Point Derivation
The system only includes the service agreement to start based on the Service Agreement Type from the current or recent service for the service point. Additionally, the system automatically notifies you when starting the service to indicate that the Service Agreement Type is not the default for the service point's Service Point Type.
Previously, the system included the Service Agreement Type matching the current or recent service (defaulted to start) and the initial Service Agreement Type for the service point's Service Point Type (defaulted not to start), thus more than one service agreement could be unintentionally started for the service point.
This Start/Stop Service Agreement enhancement streamlines the processes associated with Start Service requests.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
"Add All SA Type When None Are Initial" Feature Configuration Option Type
The "Add All SA Type When None Are Initial" option type, for the Customer Information Options feature configuration type, provides control over the behavior when you are starting service for the first time at a service point and initial Service Agreement Types have not been configured as initial service agreement types on the service point's Service Point Type.
This new Option Type streamlines the processes associated with Start Service requests and is useful when more than the Service Agreement Type is needed for the service point's Service Point Type but your implementation's rules preclude any initial service agreement.
Steps to Enable
To enable this feature, configure the "Add All SA Type When None Are Initial" option type on the applicable Customer Information Options feature configuration type.
-
If the feature option type is set, an entry for each Service Agreement Type for the service point's Service Point Type is created in lieu of a single row without a service agreement type. All entries default to not starting and you must select the service(s) to start from the collection.
-
If the feature option type is not set, a single entry is added to the service agreement collection to be started and linked to the service point. The added service agreement allows you to select the Service Agreement Type for the service agreement to start.
Contextual Insights - Financially Responsible Person
The C1-FINPER-BADGE (Financially Responsible Person) insight type enables you to surface focused alerts about the Person's financial role (Main Person, Financially Responsible Person, or Third Party Guarantor) on an account.
This contextual insight can help you can elevate your customer service interactions by increasing your knowledge about the customer in the most appropriate screens.
Steps to Enable
Configure the insight type on the appropriate Insight Groups.
Key Resources
-
Refer to the Insight Groups section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Contextual Insights - Highlight In Progress Start/Stop/Transfer Requests
The C1-CSRQSST-LIST (Highlight In Progress Start/Stop/Transfer Requests) insight type allows you to surface focused alerts about the following process flows for the customer or premise in context:
- Start Service Request
- Stop Service Request
- Transfer Service Request
You can elevate your customer service interactions by providing contextual insights about in-progress start service, stop service, and transfer service requests in the most appropriate screens.
Steps to Enable
Configure the insight type on the appropriate Insight Groups.
Key Resources
-
Refer to the Insight Groups section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Contextual Insights - Highlight Premise Service Information
The C1CSRTPREMSI (Highlight Premise Service Information) algorithm type can surface additional service point and device details that can be used on contextual insights. The Control Central Alert algorithm type is used by the C1-PREMSVC-LIST (Highlight Premise Service Info - List) insight type.
You can elevate your customer service interactions by providing Premise service contextual insights on the most applicable screens.
Steps to Enable
Configure the insight type on the appropriate Insight Groups.
Key Resources
-
Refer to the Insight Groups section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Contextual Insights - Pending Start/Stop Service Agreements
These Insight Types enables you to surface focused intelligence about pending Start/Stop service agreement information:
- C1-PNDSTR-BADGE (Highlight Pending Start) - Badge insight for pending Start service agreements
- C1-PNDSTR-LIST (Highlight Pending Start) - List insight for pending Start service agreements
- C1-PNDSTP-LIST (Highlight Pending Stop) - List insight for pending Stop service agreements
You can elevate your customer service interactions by providing pending Start/Stop badge and/or list contextual insights on the most applicable screens.
Steps to Enable
Configure the insight type on the appropriate Insight Groups.
Key Resources
-
Refer to the Insight Groups section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Contextual Insights - Person and Premise Life Support/Sensitive Load
The following Control Central Alert algorithm-based Insight Types allows you to surface focused alerts, for Premises and Persons with life support or sensitive load information, on applicable screens:
- C1-PERLSSL-BADGE (Highlight Person Life Support/Sensitive Load)
- C1-PRMLSSL-BADGE (Highlight Premise Life Support/Sensitive Load)
You can use these alerts to more effectively interact with customers within the context of the current business process.
Steps to Enable
Configure the insight type on the appropriate Insight Groups.
Key Resources
- Refer to the Insight Groups section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Contextual Insights - Insight Classes
Additional Insight Classes were added to designated areas within corresponding UI Maps for specific zones, which enables you to configure new Insight Types with defined valid visual structures and render these in the designated areas. Insight Classes serve as placeholders within specific zones for rendering contextual insights.
You can elevate your customer service interactions by providing quick access to key information from the most appropriate zones.
Steps to Enable
Refer to the Customer 360 - Contextual Insights section of the Administrative User Guide for more information.
Support for NACHA’s Web Debit Account Validation Rule
Automated Clearing House (ACH) originators of web debits, are required to validate a customer's checking or savings account prior to using the account for the first time for an electronic payment. This release enhances several business objects, entities, and batch controls to provide support for the web debit account validation rule.
BUSINESS OBJECTS (associated with Inbound Web Services (IWS))
- WX-AutoPayTask (Automatic Payment Setup Task)
- The CXAutoPaySetUp (Auto Pay Setup) and WXAutoPaySetup (Auto Pay Setup) IWS create an automatic payment self-service task for setting up the customer's account with auto-pay details.
- The WX-AutoPayTask business object includes the "Account Validation" lifecycle state that provides:
- A Business Object: Enter algorithm that calls the Web Debit Account Validation plugin spot when the service task's Web Debit Account Validation flag is set to "Yes" and the account number is not referenced on the account's existing Auto Pay options or Person Self-Service Options.
- A Business Object: Monitor algorithm checks the status of the account validation process and transitions the self-service task to the next appropriate state such as Process Auto Pay Set Up, Account Validation Error, or Rejected.
- The WX-AutoPayTask business object also includes the "Account Validation Error" state that provides:
- A Business Object – Enter algorithm that creates a To Do Entry error.
- A Business Object – Monitor algorithm for retry processing.
- A Business Object – Monitor algorithm for wait timeout processing that checks if the service task has been in the current state for too long, based on the Wait Timeout Threshold configured on the service task type. If the threshold is exceeded, the algorithm creates a To Do Entry using the To Do Type or To Do Role configured on the service task type and transitions the service task to the Discarded state.
- The related WX-AutoPayTaskType (Automatic Payment Setup Task Type) business object provides an attribute to indicate whether or not the account (first time to be used for an electronic payment) requires web debit account validation.
- The Main tab of the Automatic Payment Setup self-service task includes an Account Validation Details section with the following fields:
- Web Debit Account Validation Status - Specifies the validation status of the account.
- Error Wait Timeout Date/Time - Automatically populated if the service task in in the Account Validation Error state.
- WX-OneTimePayTask (One Time Payment Task)
- The CXMakePayment (Make One Time Payment) and WXMakePayment (Make One Time Payment) IWS create a One Time Payment Task self-service task for managing an immediate or scheduled one-time payment. The created task is based on the WX-OneTimePayTask (One Time Payment Task) business object.
- The WX-OneTimePayTask business object includes the "Account Validation" lifecycle state that provides:
- A Business Object – Enter algorithm that calls the Web Debit Account Validation plugin spot when the service task's Web Debit Account Validation flag is set to "Yes" and the account number is not referenced on the account's existing Auto Pay options or Person Self-Service Options.
- A Business Object – Monitor algorithm checks the status of the account validation process and transitions the self-service task to the next appropriate state such as Process Auto Pay Set Up, Account Validation Error, or Rejected.
- The WX-AutoPayTask business object also includes the "Account Validation Error" state that provides:
- A Business Object – Enter algorithm that creates a To Do Entry error.
- A Business Object – Monitor algorithm for retry processing.
- A Business Object – Monitor algorithm for wait timeout processing that checks if the service task has been in the current state for too long, based on the Wait Timeout Threshold configured on the service task type. If the threshold is exceeded, the algorithm creates a To Do Entry using the To Do Type or To Do Role configured on the service task type and transitions the service task to the Discarded state.
- The related WX-OneTimePayTaskType (One Time Payment Task Type) business object provides an attribute to indicate whether or not the account (first time to be used for an electronic payment) requires web debit account validation.
- The Main tab of the One Time Payment Task self-service task includes a Web Debit Account Validation Details section with the following fields:
- Web Debit Account Validation Status - Specifies the validation status of the account.
- Error Wait Timeout Date/Time - Automatically populated if the service task in in the Account Validation Error state.
ENTITIES
The Auto Pay Clearing Staging Record provides a Prenote switch. The base-provided algorithm for Web Debit Account Validation that performs ACH prenotification sets the switch to "True" when the prenotification auto pay staging record is created.
The following entities provide a plugin spot for the Web Debit Account Validation algorithm:
- Auto Pay Route Type
- CIS Division in the Auto Pay Route Type Override Controls
You can use the plugin spots to validate the checking or savings account to be used for the first time for web-initiated one-time payments or recurring bill auto pay enrollments. In addition, the base product provides an algorithm for one type of prenotification method for account validation. The Web Debit Account Validation algorithm creates a pre-notification auto pay staging record (request) with a zero payment amount and the rest of the auto pay information that includes the new account number.
BATCH CONTROLS
The following batch controls can populate the Entry Details section of an ACH extract record with the 28 (Check Debit Prenote) or 38 (Savings Debit Prenote) Transaction Code if the related Auto Pay staging record is a pre-notification:
- APAYACH (Auto Pay Extract – ACH)
- C1-APACH (Auto Pay Extract – ACH (with offset days parameters))
In addition, these batch controls use the Prenote switch to stamp the specific transaction code on the checking or savings debit prenotification.
These enhancements reduce the need for implementation-specific extensions to support NACHA's web debit account validation rule.
Steps to Enable
ACCOUNT VALIDATION ERROR STATE
The Business Object – Enter algorithm for creating a To Do Entry error is an instance of the F1-TDCREATE algorithm type (Oracle Utilities Application Framework), which specifies the new C1-AVETD To Do Type as soft parameter. To use the Retry Account Validation monitor algorithm (instance of F1-TODORETRY algorithm type) plugged in to the Account Validation Error state, add an algorithm parameter instance that also specifies the Retry Frequency (parameter 11).
The Business Object – Monitor algorithm for retry processing is an instance of TODORETRY algorithm type (Oracle Utilities Application Framework). To use this Account Validation Error state algorithm, add an algorithm parameter instance that specifies the Maximum Retry (parameter 1).
ENTITIES
If your implementation will not use the base package supplied Web Debit Account Validation algorithm, plug in your custom algorithm for initiating that validation process.
The following REST API Inbound Web Services expose various customer-related data and provide the capability to view and/or manage that stored data:
- C1-CXPerson (Person Primary Information Synchronization)
- C1-AccountPersonCommunication (Account Person Communication)
- C1-PersonContext (Accounts for Person)
- C1-CustomerActivityHistory (Customer Activity History)
- C1-Adjustment (Adjustment)
- C1-WebUser (Web User)
- C1-WebUserAccount (Web User Account)
- C1-SelfServiceServiceTask (Self Service Task)
Decrease project costs and project timelines using new REST Inbound Web Services to view and/or manage various customer-related data.
Steps to Enable
Review the REST service definition in the REST API guides, once available from the Oracle Help Center > your utilities application service area of interest > REST API. If you are new to Oracle Utilities REST services, you may want to begin with the Quick Start section.
Device Characteristics provide projects or multi-commodity utilities with the capability to define valid and required characteristics, configure the characteristics' defaults, and assign the characteristics to be used on a device. For example, the characteristics for a water meter can vary from an electric meter.
Configure and define characteristics for devices using new Device Characteristics zones to reduce project costs.
Steps to Enable
Refer to the Characteristic Types and Defining Characteristic Types sections of the Oracle Utilities Meter Solution Cloud Service Administrative User Guide for more information.
Tips And Considerations
You can configure the characteristics for your projects on the device types.
Dynamic Aggregation Totalization
The Dynamic Aggregation Engine now uses the same totalization rules as that of the Billing Determinant Engine. The aggregation process considers the Measuring Component rules and the Usage Subscription-Service Point rules when totaling usage. For example:
- Measuring Component Rules
- How to Use: Valid values are Additive, Check, Peak, and Subtractive
- Usage Subscription-Service Point Rules
- How to Use: Add, Check, Subtract
- Use Percent: Percentage in whole numbers, for example 50 = 50%
This ensures that billing processes are consistent with the aggregation processes.
Steps to Enable
To enable this feature on the Measurement from US Service Points and Measurements from US Direct Links data sources, you should set the Apply Usage Subscription Multiplier to "Yes."
The D1-GAGRR (Generate Aggregation Group Run for Re-Aggregation) batch control allows downstream processes to perform multiple dynamic aggregation on the same business day by generating a new aggregation group for each batch control run. You can schedule multiple runs of the batch control, which is helpful for complex customer billing that need to re-aggregate before running the billing processes.
This feature enables aggregation to be run as many times as is necessary for a given business day according to the requirements for billing processes.
Steps to Enable
You can schedule a D1-GAGRR batch job at each point of the day that requires re-aggregation. Optionally, you can provide an Aggregation Group Code to limit the re-aggregations into a single aggregation group.
You can use rich prebuilt analytical data models, metrics, and key performance indicators in Analytics Visualization. You can use Analytics Visualization to create your own calculations, visualizations, and filters to analyze the data exposed by the prebuilt data models.
Master Data Analytics Visualization
The Meter Master Data Tables allow you to identify the service point types used, meters not receiving measurements or providing erroneous reads, installed meters without billing setups, and disconnected service points and devices. The tables also enable you to verify data counts after conversion and track the number of AMI devices replacing scalar meters during AMI rollouts.
You can verify data counts after conversion, track the number of Scalar meters replaced by AMI devices, identify the service point types used, and more.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
Refer to the Demo Data for examples on setting up the Master Data Set and building Map Visuals.
Key Resources
OAuth-based Client Credentials Authorization
OAuth-based Client Credentials Authorization supports Inbound Web Services, enhancing the reliability and security of the Oracle Utilities Cloud Service REST APIs. In addition, client credentials authorization simplifies the integration of on premises and cloud Oracle products with non-Oracle products.
OAuth-based Client Credentials Authorization provides industry-standard integration mechanism for Utilities Cloud Services REST APIs.
Steps to Enable
To enable this feature, perform these steps:
- Submit a service request to create or manage the integration of the OAuth client with your Identity Cloud Service tenancy.
- Retrieve the client credentials from the Oracle Identity Cloud Service administration console.
- Complete the integration configuration in the Oracle Utility Cloud Service application.
For detailed instructions, refer to the Setting Up an Integration OAuth Client for REST Web Services section of the Oracle Utilities Cloud Service Administration Guide.
Utilities Application Framework
Oracle's Redwood user experience introduces a new compact page header that takes up less vertical space to allow more page content to be displayed, as well as new portal tabs, buttons, background colors, borders, and fonts all updated to match the overall Redwood user experience found in other Oracle applications.
Oracle Redwood provides a consistent user interface experience across Oracle's latest solutions.
Steps to Enable
To enable the Redwood user experience, add the redwood=true parameter to your application or environment URL.
Key Resources
- Refer to the Redwood Look and Feel section of the Business User Guide for more information.
Oracle's Redwood user experience provides a single search box to quickly retrieve customer, account, and meter information such as customer name, premise address, account ID, badge/serial number, and more (where applicable). For more complex queries, you can use the link provided to navigate to a pre-configured advanced search portal. You can also search for Oracle Utilities application menu items using the same single search box.
Unified Search allows you to quickly find customer, account, and meter information without leaving the current page.
Steps to Enable
To enable the Redwood user experience, add the redwood=true parameter to your application or environment URL.
Key Resources
- Refer to the Unified Search section of the Business User Guide for more information.
Batch Day Dashboard and Batch Run Threads Portals
The Batch Day Dashboard portal provides a high level summary of the batch jobs that ran for a given business date. It provides analysis by job status and job category using analytic charts. The batch jobs summary provides links to the Batch Run Threads portal and the Batch Run Tree for a selected batch run.
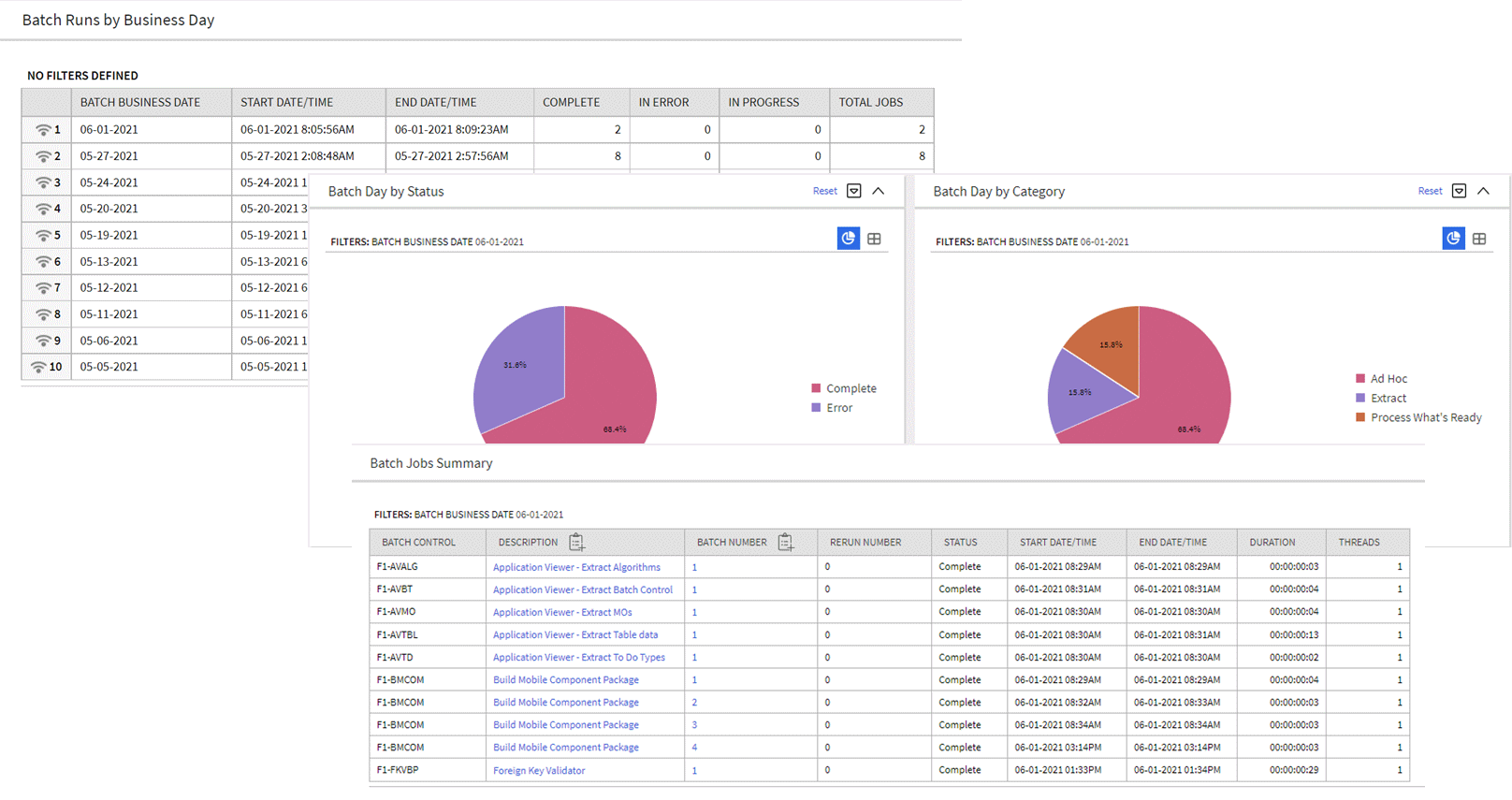
Batch Day Dashboard Portal
The Batch Run Threads portal provides a high level summary of the threads for a given batch run. It provides analysis by various criteria using analytic charts. The portal is accessed via a link from the batch jobs summary zone on the Batch Day Dashboard portal.
An implementation may introduce additional zones to these portals as needed.
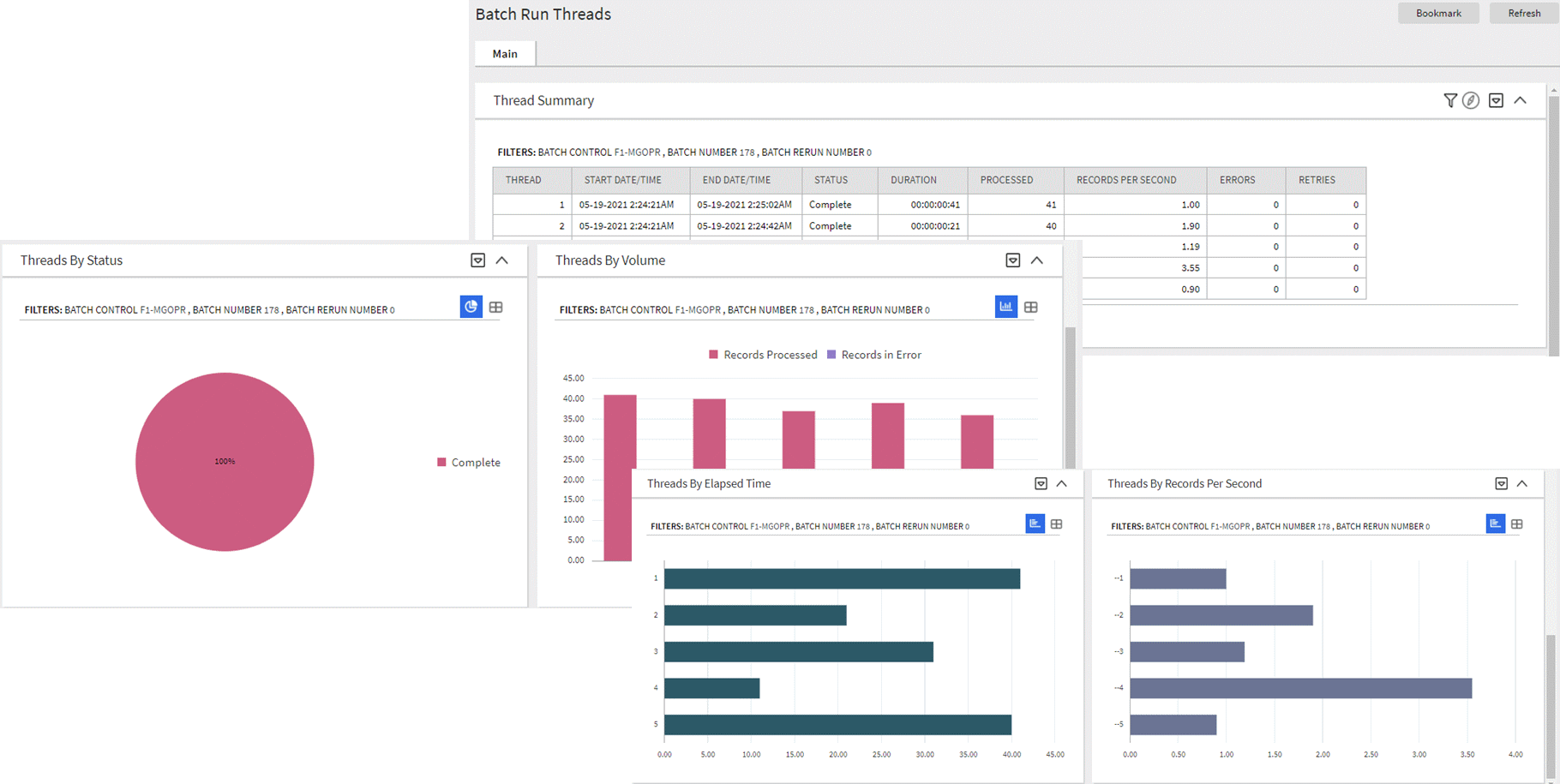
Batch Run Threads Portal
The introduction of the Business Day Dashboard allows you to quickly determine the state and performance information of your batch workloads using the Business Date as a key dimension. The portal contains zones to provide details about state and individual thread performance to assist in detecting data and performance issues with individual batch workloads.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
This table lists the new application services for the portals.
| Object | New Application Service |
|---|---|
| Batch Day Dashboard | F1BTCHDY |
| Batch Run Threads Portal | F1BTCHTH |
Key Resources
Dashboard Portal Controls - User Preferences
Oracle's Redwood user experience enables you to set the following Dashboard portal control options according to your preferences:
-
Collapsed/Expanded Portal: The system retains the collapsed Dashboard portal after your logged out and start a new session. Previously, when you ended your session with your Dashboard portal collapsed, the system displays an expanded Dashboard portal the next time you logged in to the application.
-
Portal Width: You can resize or adjust the width of the Dashboard portal by using a slider and the system retains your preferred width even after logging out of the application. Previously, your needed to navigate to User Preferences to adjust the width of the Dashboard portal.
-
Vertical Position: You can position the Dashboard portal on the left or right side of the screen. Previously, the portal's position is fixed on the right side of the screen.
User Preferences allow you to select and retain a layout that is tailored to your needs.
Steps to Enable
To enable the Redwood user experience, add the redwood=true parameter to your application or environment URL.
Tips And Considerations
Refer to the User Preferences section of the Administrative User Guide for more information on defining the portal's location.
Display Domain Name in Toolbar
The system supports defining a Domain name using an installation message. When using the Redwood user experience view, the text entered in the Installation Message Text for domain name is displayed in the title bar.
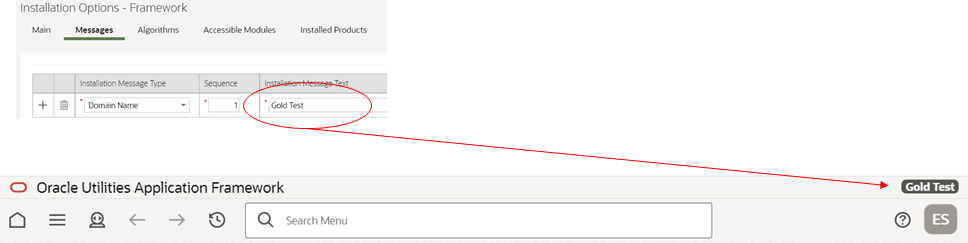
Display Domain Name in Toolbar - Installation Option
Implementations with multiple environments for development, testing, production, and others can easily identify their current environment using this name.
NOTE: This feature is only supported under the Redwood user experience view. Refer to online documentation for more information on Redwood user experience view.
Steps to Enable
To enable the Redwood user experience, add the redwood=true parameter to your application or environment URL.
The enhanced button web component (ou-button) provides a number of button formats:
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Icon buttons show only an image, such as the search and filter icons. This was previously the only button format supported. |
 |
Text buttons show text within a shape or outline. |
 |
Text + Icon buttons show text aligned with an icon. |
 |
Menu buttons show text and a down caret. |
 |
Icon Menu buttons show an icon and a down caret. |
In addition, the ou_button component supports the use of a Display Icon Reference instead of a direct reference to the image file and the ability to reference edge application owned images, including SVGs.
The enhanced button web component expands the available features to include new button types, support for product-specific images, and more granular security options. This standardizes the use of buttons on the user interface.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
New Base Display Icon Images Provided
Several additional SVG icons are provided for use in contextual insights and trees, and other user interface features that support SVG icons.
| Icon | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| F1ARRCL |
Left Arrow - Circled |
 |
| F1ARRCR |
Right Arrow - Circled |
 |
| F1BLDING |
Building |
 |
| F1BOOK |
Book |
 |
| F1CHK |
Check |
 |
| F1CLOSE |
Close |
 |
| F1CLOSEC |
Close - Circled |
 |
| F1EVT |
Event |
 |
| F1EVTN |
Event Note |
 |
| F1KMBOOK |
Knowledge Management |
 |
| F1NOIMG |
Image Not Found |
 |
| F1REFNCE |
Reference |
 |
Additional icons allow for richer user experience for displayed information.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
A new zone type is introduced that allows a single zone to display different panels of information using tabs.
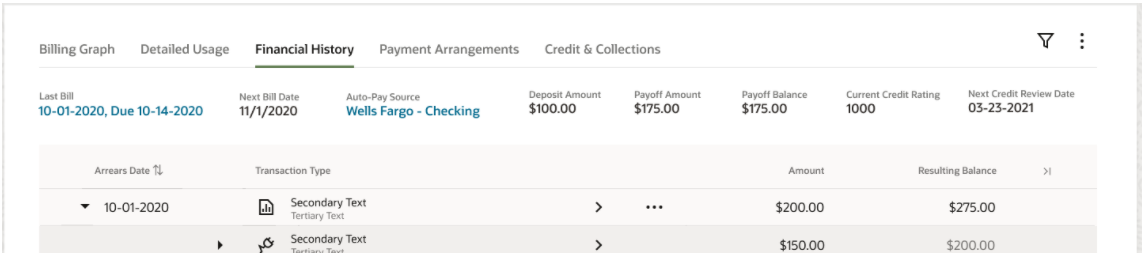
Zone Tabs
The zone supports up to 50 zones as tabs with overflow support when the tab display exceeds the screen resolution available.

Zone Tabs - Overflow Support
The Tab Display zone supports the display of complex of information using tabs within a single zone. This allows you to stay within a context of a zone, but it allows for flexibility in the information available in that zone to reduce your time and costs.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Support Additional Zone Layout Options
Additional zone width options, zone height options, and layout options are now available. This allows portal designers to have finer-grained control over how the zones are laid out in a portal to optimize layout and reduce whitespace. Additional configuration options added include:
- Row Start Layout: You can start a new row containing one, two or three zones displayed vertically. In past releases, a row included a single zone in each column.
- Increased Width Options: In past releases, zones may be full or half width. You can add additional widths to take advantage of flexible row layouts.
- Flexible Height Options: You can configure additional options for the zone height to optimize the display of the zone.
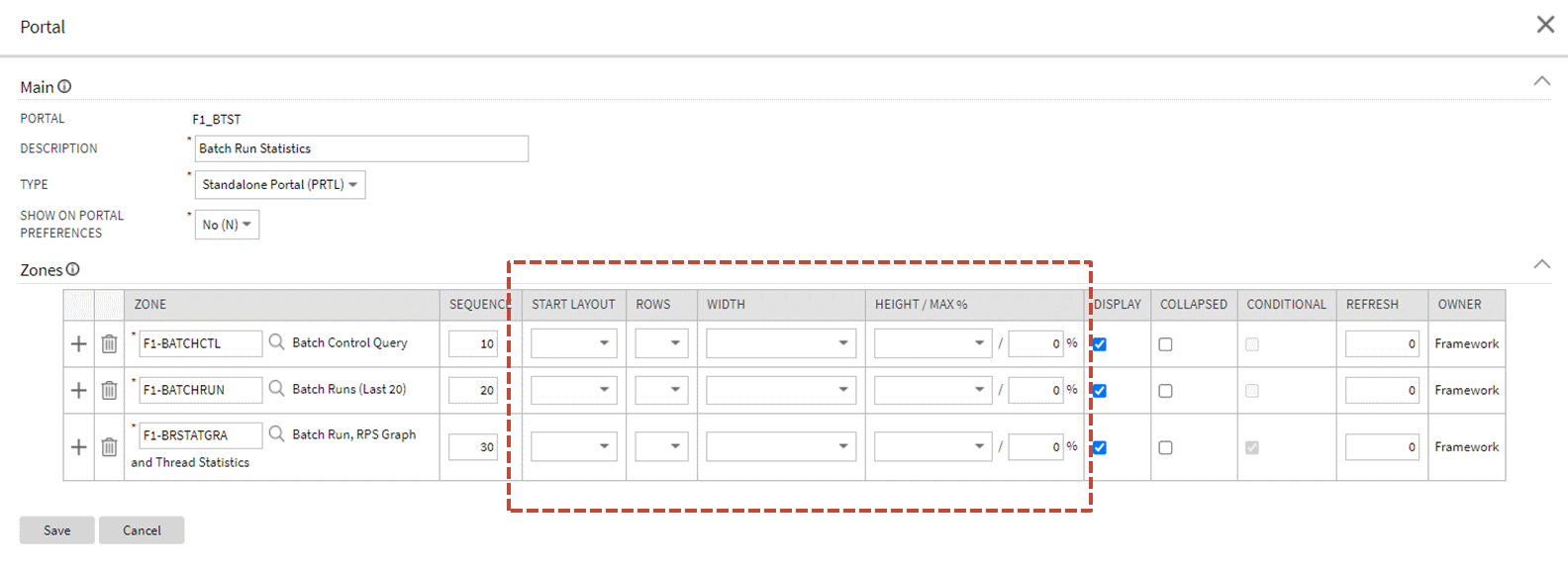
Additional Zone Layout Options
NOTE: These options are only supported under the Redwood user experience view. Refer to online documentation for more information on Redwood user experience view.
The additional zone configuration options allow for more specialized design of portals to ensure that information is presented in the optimal way for the user. They also give designers more control of the configuration for better organization of zones in portals.
Steps to Enable
To enable the Redwood user experience, add the redwood=true parameter to your application or environment URL.
Support for Defining Links and List Standards in Schemas
Standards for published APIs related to standard REST operations can be defined in the API's operation schema. In some cases, the published API includes elements that are different from the internal schema or additional features on top of the internal schema. In this release, with the introduction of the external facing schema (IWS operation schema), syntax has been added to configure these features directly in the operation schema, allowing the internal schema to remain unaffected. Note that not all published REST APIs follow the standards below. Refer to the online help for more information about the types of APIs that follow the below standards.
DYNAMIC LINKS
There are use cases where the published API will include a "_self" element that includes the endpoint URL of the Get operation related to the data returned in the response. Additionally, these same response payloads may include foreign keys and for those entities, the response includes a "_link" element that includes the endpoint URL of the GET operation for that entity (if it exists).
In this release, syntax is provided in the REST IWS operation schema to support building the runtime endpoint URL for the _self and _link. Besides dynamically building the static portion of the URL based on the current environment details, it also builds the dynamic portion of the URL, substituting the URL components for the operation and substituting the path parameters. The syntax allows you to define a specific IWS Operation or allows you to reference a maintenance object and at runtime for a REST call, and the system determines the appropriate IWS operation and builds the URL for this REST service.
Example of the syntax: <_self getOperation="mo:'TO DO ENTRY';pk1:toDoEntryId;"/>
The following is the information returned for the above syntax when performing a Get operation for a To Do Entry with ID 17798129050729. The system determined the Inbound Web Service 'get' operation for To Do Entry and built the URL components for that operation.
"_self": "/rest/apis/common/toDos/toDoEntries/17798129050729"
To support dynamically determining the Get Operation for a maintenance object, the following metadata is introduced:
-
IWS Operation is enhanced to reference a Maintenance Object code. This field may only be populated on GET operations for REST IWS.
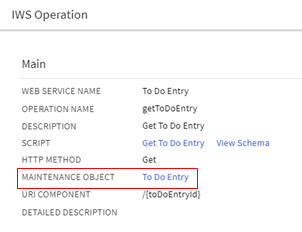
Maintenance Object Reference
-
A new Maintenance Object (MO) Option type is added. It supports defining the IWS, operation name for the GET operation. This option allows for an implementation to override the default GET operation for an object, if needed.
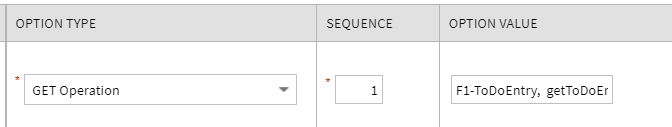
Maintenance Object Option Type - GET Operation
-
A new Business Object (BO) Option type is added. The syntax is the same as the maintenance object option. This is useful for maintenance objects that support diverse business objects that may warrant specialized REST APIs.
When you use the "mo" syntax for the GET operation at runtime, the system takes the key of the entity and determines its business object. If it finds a specific GET operation as a BO option, that is used. Otherwise, if it finds a GET Operation configured as an MO option, that is used. Otherwise if it finds an IWS operation that references this MO as a foreign key, that is used. Finally, if it cannot determine a GET operation, it builds the text "Not available".
FOREIGN KEY GROUP
As mentioned above, when this type of published API includes a foreign key in the response, besides returning the value of the foreign key, we should also return a "_link" with the endpoint URL of that object's 'Get' REST operation. To support that, the standard is that foreign keys are returned in a group.
Example:
<user>
<user/>
<_link/>
</user>
With the new features, the internal schema includes only the element for the data and the external schema includes configuration to build the group.
| Internal schema | Operation schema syntax |
|---|---|
| ... <user/> ... |
... <user role="FKGP"> <user/> <_link getOperation="mo:'USER';pk1:user;"/> </user> ... |
COLLECTION LISTS OF DATA
When this type of published API returns a list of information, the standard is to use the element "_data" for the list grouping tag.
Example:
<drillKeys>
<_data>
<sequence/>
<keyValue/>
<description/>
<version/>
</_data>
</drillKeys>
With the new features, the internal schema includes the list as defined internally (which does not include the _data element). Syntax in the operation schema allows you to define the list using the _data element.
| Internal schema | Operation schema text |
|---|---|
| <drillKeys type="list"> <sequence/> <keyValue/> <description/> <version/> </drillKeys> |
<drillKeys role="COLL"> <_data mapTo="drillKeys"> <sequence/> <keyValue/> <description/> <version/> </_data> </drillKeys> |
Supporting syntax in the REST IWS operation schema for some standard features in our published APIs moves the burden of configuration to the object that needs the feature. The internal schema can therefore remain devoid of this configuration that is not applicable to the internal service. This is in the style of the Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State (HATEOAS) standard.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
To take advantage of this feature, service scripts used for REST operations should include the F1-WebServiceControl data area. This includes the HTTP method element and allows for future enhancements. Once added, the service script logic can be enhanced to check the value of the HTTP Method and perform different steps based on the value.
Explicit Imports in Groovy Scripts
Any scripts that include Groovy code should explicitly declare the Groovy classes to import using the Groovy Imports step type. The system includes a new com.oracle.ouaf.groovy.skip.defaultImports=true setting in the Properties file. If this is configured and the system detects that there are classes referenced in the script that are not explicitly defined when saving a script, it issues a warning and automatically adds import statements for the classes.
Previously, the system did not require explicit imports and had logic to import all callable classes available to Groovy at run time. Two issues were found with this practice.
-
It was possible that the referenced class had the same name as a class in a different package and at runtime, the system would use a different class than what was intended. The non-unique name may not have been visible when writing the code, but rather would be found in a subsequent release (after a new class was introduced) or would be found in a different product layer.
-
As the number of classes grew, the compilation time for Groovy scripts continued to increase.
To accommodate scripts written previously, the system compiles the Groovy script at runtime without the automatic import logic. If the script compiles, the system continues and runs the script. If the script does not compile, the system then performs the auto import of all callable classes.
This helps to eliminate ambiguous class references and improves compilation time.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
It is recommended that implementations review their existing custom Groovy scripts and proactively update the scripts to explicitly declare the imports.
The attributes for Oracle Utilities Application Framework web components have been amended to make them easier to read and more similar to HTML This will impact any existing ou-tree or ou-insight web component reference. The definition has been changed as follows:
-
Supported value types are XPath and context.
-
XPath references must explicitly say "x[..]". For example, <ou-insights insightType="x[insightType]" mode="preview"></ou-insights>. Previously, XPath was the default and did not need any mnemonic. For example, <ou-insights insightType="insightType" mode="'preview'"></ou-insights>.
-
The change applies to all XPath references. For example in the context values, <ou-insights insightType="F1-RELATED-TODO" context="TD_ENTRY_ID:x[toDoEntryId];"></ou-insights>. Previously, the context values appear as <ou-insights insightType="'F1-RELATED-TODO'" context="'TD_ENTRY_ID':toDoEntryId;"></ou-insights>.
-
Note that in addition to the changes above, literals no longer need to be surrounded by single quotes. Single quotes will continue to be supported but will not be necessary. Refer to F1-RELATED-TODO and TD_ENTRY_ID in the examples.
This enhancement standardizes the interface using industry standard syntax and amends the default rules for the attributes passed into a web component to facilitate enhanced web component features.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Additional Metadata to Support API Publishing
The following internal fields have been added to support publishing product-delivered APIs in the product catalog:
- Detailed description for a REST IWS operation. This new field allows for the product to provide information visible in the catalogue of published APIs.
- Help text is provided for individual elements in a given published API.
- Sample request and response documents may be defined using a new IWS Operation Options collection.
- Operations may be associated with a sequence number that controls the order in which they appear in the Open API Specification.
Previously, the above text was added later in a separate documentation process. The new fields streamline the internal publishing process. Note that this text is visible to implementations in the IWS user interface pages. The information may be added for custom owned IWS, but it will not be used by any product processes. Note that this text is not translated as the published catalogue documentation is in English language only.
New Metadata for API Publishing
This provides the ability to include a detailed description of a REST IWS operation and to support help text for individual elements to better describe the published API. This increases the usability of the API's provided for integration and interfaces to help reduce integration costs.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Description Added to Inbound Web Service Operation
A language table has been added to the IWS operation and a description has been added. This description is included in the Open API Specification and may be included in the published API catalogue for published services. Previously, the operation description was taken from the internal service script, business service or business object. The internal description is not always relevant when publishing the service as an API. The new description allows the system to use an internal description for the internal service and use the operation description for a description specific to the published API.
The description captured on a REST IWS operation allows for a description specific to the operation as compared to the internal service description. This increases the usability of the API's provided for integration and interfaces to help reduce integration costs.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
HTTP Method Available to Internal Service Script
When delivering REST operations for a given object, the logic to perform the operation is handled by a service script. In this release, the REST servlet populates the HTTP Method into a variable available to the invoked service script. This allows the product team and implementations the ability to use one service script to handle more than one HTTP method for an entity.
This encourages reuse and isolation of change to reduce implementation costs.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
To take advantage of this feature, service scripts used for REST operations should include the F1-WebServiceControl data area. This includes the HTTP method element and allows for future enhancements. Once added, the service script logic can be enhanced to check the value of the HTTP Method and perform different steps based on the value.
Inbound Web Service Maintenance (REST)
The definition of a REST IWS was enriched to include an external-facing schema and documentation options for each operation.
The following enhancements were made to streamline the maintenance of the additional information:
-
A standalone Inbound Web Service Operation portal is provided for providing additional information about an operation.
-
Operations are displayed in a separate zone on the Inbound Web Service portal. The zone lists operations in the order they appear in the Open API Specification and supports navigation to the new operation portal.
-
Help text information to be shared across all operations of a web service is maintained on a new zone on the Inbound Web Service portal.
The enhanced user interface for maintaining a REST IWS definition optimizes the maintenance of services to reduce implementation costs.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
Upgrade scripts ensure that users with access to the existing application service will have access to the new application service associated with the new portal. This table lists the existing and new application services.
| Object | New Application Service | Access Added to any User Groups with this Application Service |
|---|---|---|
| Inbound Web Service Operation Portal | F1IWSOPR | F1IWSSVCP (Inbound Web Service Portal) |
| Inbound Web Service Operation Maintenance Object | F1IWSSVCOPR | F1IWSSVC (Inbound Web Service Maintenance Object) |
The following new APIs are provided:
- F1-ToDoEntry: A REST IWS for the To Do Entry object. In this release, GET operations are provided for To Do Entry and for To Do Entry Logs.
- F1-ExtendableLookup: A REST IWS for the Extendable Lookup object. In this release, a GET operation is provided.
Both REST services take advantage of the new external facing schema features.
New published APIs for To Do Entry and Extendable Lookup expand the catalogue of options provided for implementations.
Steps to Enable
Make the feature accessible by assigning or updating privileges and/or job roles. Details are provided in the Role section below.
Role Information
Users must be granted access to the following new application services in order to use this functionality.
| REST IWS | Application Service | Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
| F1-ToDoEntry |
F1-INTG-SUITE-API |
F1EX |
| F1-ExtendableLookup |
F1LEXTLKUP |
F1EX |
Outbound OAuth Client Credentials Grant Type
OAuth is an open standard token-exchange technology for verifying a client’s identity across multiple systems and domains without risking the exposure of a password. The OAuth specification methods for acquiring an access token are known as grant types. This release adds support for outbound integration with REST APIs that are secured by the Client Credentials grant type.
The configuration of a message sender is extended to capture the following OAuth related context options:
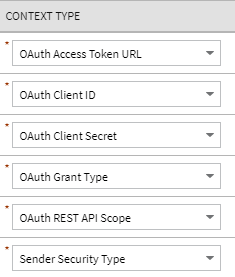
OAuth Context Types
You can use "OAUTH" for the Sender Security type and "client_credentials" for the grant type. You can configure the rest of these options based on the client information provided by the external system. Note that the Client Secret value is encrypted.
This supports outbound REST API integrations that are based on OAuth “Client Credentials” grant type and increases support within OAuth domains such as the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and other external OAuth domains.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Rootless Request and Response Schemas (JSON)
The configuration of an outbound message type on the External System page is enhanced to include a new JSON Conversion Method option, "Rootless JSON Conversion," that converts the internal XML-based request and response schemas to and from rootless documents. Previously, exchanging messages with an external system in JSON format required the request and response elements to be enclosed in a root node which is not a typical structure for REST service calls. This release also supports rootless JSON request and response schemas.
This supports standard message exchange with an external system in JSON format where the request and response schemas are rootless structures. It also reduces implementation costs by natively supporting rootless structures where interfaces require them.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Support for an External-facing Schema
You can define a schema for a REST IWS operation. This allows a user to adjust the schema for an external-facing consumer. Previously, the schema of the underlying service (for example, service script) was also the schema for the REST IWS operation. The new IWS operation schema also supports some special configuration that allows additional features to be defined only for the IWS operation schema.
All references to the internal service below reference service script, but the same comments apply to business services and business objects, if that is what is referenced by the IWS operation:
-
An element may reference a usage attribute, with values of Request Only, Response Only, Exclude and Both (the default). Previously, all elements in the service script schema were visible in both the request schema and the response schema (for HTTP methods that have both a request and response schema). This sometimes caused confusion or required additional documentation to clarify when the element is applicable.
-
A different element name may be defined in the IWS operation schema, overriding the name in the service script. This allows the internal service script element name to more closely align to internal references to the element, if needed. The externa- facing element name can be different allowing for a more readable schema.
The external schema for REST operations allows for more configuration to benefit the published API and helps reduce costs in integration. This increases the usability of the API's provided for integration and interfaces to help reduce integration costs.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
If you have existing REST IWS operations, there is no requirement to take advantage of this feature. It is useful if you have elements that you would like to suppress or if there are elements you would like to appear in only the Request or only the Response.
Access Utilities Cloud Service REST APIs with OAuth Credentials
OAuth-based Client Credentials Authorization supports Inbound Web Services, enhancing the reliability and security of the Oracle Utilities Cloud Service REST APIs. In addition, client credentials authorization simplifies the integration of on premises and cloud Oracle products with non-Oracle products.
OAuth-based Client Credentials Authorization provides industry-standard integration mechanism for Utilities Cloud Services REST APIs.
Steps to Enable
To enable this feature, perform these steps:
- Submit a service request to create or manage the integration of the OAuth client with your Identity Cloud Service tenancy.
- Retrieve the client credentials from the Oracle Identity Cloud Service administration console.
- Complete the integration configuration in the Oracle Utility Cloud Service application.
For detailed instructions, refer to the Setting Up an OAuth Client for REST/SOAP Web Services section of the Oracle Utilities Cloud Service Administration Guide.
Conversion Tool Support for Generic Foreign Key References
The conversion step of inserting records to the production schema is enhanced to also resolve foreign key references that are captured in a generic set of fields that include the entity's maintenance object (MAINT_OBJ_CD) and its prime key values (PK_VALUE1-5). Tables with more than one set of fields are not supported and all referenced maintenance objects on the table should be convertible.
The enhancement improves the support for complex conversion processes by providing the ability to convert tables with generic foreign key references.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Conversion Tool Support for Long Running Batch Processes
The Override SQL Timeout batch parameter has been added to all conversion batch processes allowing them to set a different timeout limit than the default setting in the cloud. The parameter is set to three hours by default but can be supplied with a different time limit as needed when submitting the conversion batch process.
This provides the ability to extend the time limit set in the cloud for long running conversion batch processes.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Return Additional Details in DBMS Get Job Details Service
More supporting information is provided about the steps related to DBMS job runs when calling the F1-DBMSGetJobs (DBMS Scheduler Job List) business service. The following information is now provided for steps in the job run, where the information is applicable for that step:
- Batch Code
- Batch Number
- Batch Rerun Number
- Error Details (if applicable)
In addition, adjustments were made to what is considered an "In Progress" job run and what is considered a "Completed" job run. Previously, if a step in the DBMS job failed, it was returned for both an In Progress job run request and a Completed job run request. This could become confusing because a job with a failed step was not ever going to continue unless manual intervention occurred, so it is not "in progress." The system now uses the following criteria (from top down) for considering a job run In Progress or Completed:
- If a DBMS Job run has at least one step that is Running, the job is considered In Progress.
- If at least one step is Failed, it is considered Completed.
- If at least one step is Not Started (and no steps are Failed), it is considered In Progress.
- If none of the above is true (all steps are Completed), it is considered Completed.
This feature provides additional batch run information for each step in a DBMS job run to facilitate easy navigation and access to batch run tree, and any error information for each step in a DBMS job run. The additional information improves integration with the Cloud Service Foundation.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Service to Maintain the Sequence Table
A new business service (F1-DocumentSequenceAddUpd) has been provided to add or maintain records in the Sequence table (CI_SEQ). This service includes various actions to add, retrieve, update or delete a sequence which may be used for any business use case that requires a sequential number to be maintained (such as sequential document numbers in Oracle Utilities Work and Asset Management Cloud Service).
The new business service provides the ability for product teams and implementation teams to maintain records in the Sequence table (CI_SEQ) through configuration tools processes.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Service Order Management Data in Local Time
The following portals now use and display the time in the Service Point or Installation Event time zone:
- Activities - SOM
- Activities - Command
- Appointment Booking
Previously, Service Order Management did not include a time zone component at the Activity Type level and used the application's default Installation Option time zone, which did not match the time zone of the local service point.
Service point's local time allows customer service representatives to more easily communicate service times with customers.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Update Customer Release Version Details
You can update the Customer Release row in the Installed Products collection, allowing implementations to set a version, build, and patch level. This feature is useful for implementations that would like to use this information to manage their own release of customizable code or configuration.
There is a F1CustRelM (Customer Release Maintenance) BPA script that you may use when in a given environment to update the Customer Release information. The script could be linked to a menu entry or configured by appropriate users as a 'favorite script.' Implementation teams may wish to expose this as a REST- or SOAP-based service for integration into Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) tools.
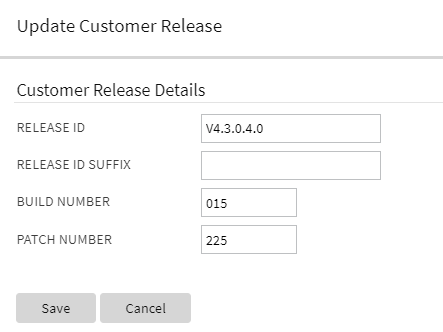
Customer Release - Extended Details
This provides the ability for continuous integration and either continuous delivery or continuous deployment (CI/CD) tools and processes to update the customer release version number for reporting and audit purposes.
Steps to Enable
Make the feature accessible by assigning or updating privileges and/or job roles. Details are provided in the Role section below.
Role Information
Users must have the Execute access mode for the Installation Options application service (CILTINSP).
Test Planning brings all your test assets together to simplify the test automation process and helps identify the test flows to use to meet testing objectives (positive and negative test or assertions). You define a test plan by using Flow Sets that run the specified set of Flows with the prescribed Environment and Credentials, on demand. You may need to execute tests multiple times to meet a given objective. For example, you may may need to create a test plan with the objective of successfully generating bills for a customer that includes some automated test flows. Users may run this test plan n number of times (for example, during sprints in an Agile environment), and log bugs and issues during each iterative execution of the test plan. When the test plan is complete, it provides a consolidated summary report of the status of the test plan run.
Test Planning organizes automated test flows or test flow sets into a single test plan, eliminating the need to run each test flow or test flow set and manually consolidate the results.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Global Variables for Mapping Component Response Elements
Mapping to a component response element enables you to move test data from the response of one component to the input field of another component by selecting the component data fields and mapping the corresponding values. You can access this feature by clicking the Search icon beside the Flow Test Data input fields.
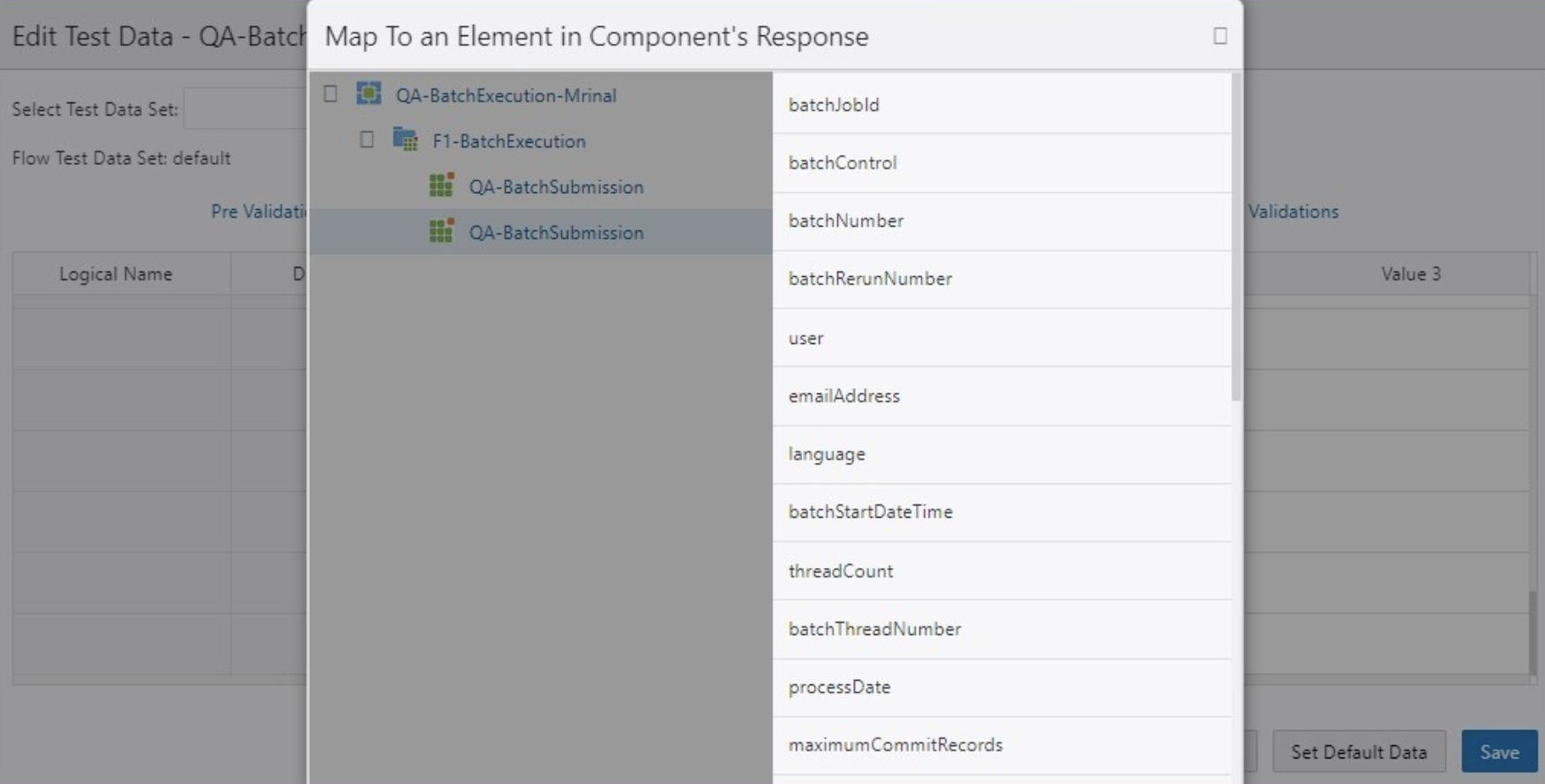
Mapping the elements of a component response removes the need to capture required values into variables and using these variables as inputs to other component test data. This reduces the steps required in test flow development and the effort to map the test data elements.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Key Resources
-
Refer to the Using Global Variables section of the Oracle Utilities Testing Accelerator User's Guide for more information.
See a preview of the database changes coming for 21B in the Oracle Utilities Cloud Services Database Changes Guide.
This includes information about databases changes to tables, indexes, views, columns, and more.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
IMPORTANT Actions and Considerations
REPLACED OR REMOVED FEATURES
From time to time, Oracle replaces existing cloud services with new features, or removes existing features. Replaced features may be put on a path to removal. As a best practice, you should use the newer version of a replaced feature as soon as a newer version is available.
This section identifies the features in this Cloud service that have been replaced or removed.
| Product | Removed Feature | Target Removal | Replacement Feature | Replaced In | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle Utilities Application Framework | LDAP Import Metadata (legacy feature) |
21B | Not applicable | Not applicable | Service Programs: CILTLDIP, CILTLDIL, CILTLDIS Application Service: CILTLDIP Fields: F1_LDAP_SUMM, F1_LDAPGROUPSEARCHDATA_SUMM, F1_LDAPUSERSEARCHDATA_SUMM, IMP_GRP_LBL, LDAP_ENTITY_FLG, LDAP_IMP_JNDI_LBL, LDAP_PASSWORD, LDAP_PASSWORD_ENC, LDAP_USER, RTRV_LDAP_ENT_LBL, SEARCH_4_LD_GRP_LB, SEARCH_4_LD_USR_LB, SEARCH_BY_LDAP_GRP Navigation options: CI0000000956, ldapImportTabMenu Navigation keys: ldapGroupSearchData, ldapGroupSearchPage, ldapImportGrid, ldapImportPage, ldapImportTabMenu, ldapUserSearchData Records in the UI metadata program component tables related to the above navigation keys. NOTE: Implementations may continue to use the F1-LDAP batch job to perform external LDAP integration, if required. NOTE: Customers using Oracle Identity Cloud Service are not affected by this removal as a native adapter is used for that integration. |
| Oracle Utilities Application Framework | Miscellaneous Metadata Removed |
21B | Not applicable | Not applicable | Script: F1-BundleInf, F1-GENPRINFO, F1-MgPlnInf Zone: F1-MGRREQDSP |
| Oracle Utilities Application Framework | Metadata no longer supported in base (owner flag set to CM) |
21B | Not applicable | Not applicable | Implementations should review and remove if not in use. Lookup value: CHAR_ENTITY_FLG / F1SE Algorithms: F1-LDAPIMPRT, F1-LDAPPREPR Algorithm Types: F1-LDAPIMPRT, F1-LDAPPREPR Maintenance Object: ENV REF Business Object: F1-EnvironmentRefPhysicalBO To Do Type: F1-SYNRQ Zone: F1-IWSSCHS, F1-IWSSCHS1, F1-IWSSCHS2, F1-IWSSCHS3 |
| Oracle Utilities Application Framework | Characteristic Type legacy page metadata |
21B | Portal-based user interface | 20C | Navigation keys: charTypeMenu, charValuesPage, charValuesPage_H, charValuesGrid, charEntitiesPage, charEntitiesPage_H, charEntityGrid Records in the UI metadata program component tables related to the above navigation keys. |
| Oracle Utilities Application Framework | Access Group legacy page metadata |
21B | Portal-based user interface | 20C | Navigation keys: accessGroupMainPage_H, accessGroupDARGrid, accessGroupMainPage. accessGroupMaint, accessGroupTabMenu Records in the UI metadata program component tables related to the above navigation keys. |
| Oracle Utilities Application Framework | Application Service legacy page metadata |
21B | Portal-based user interface | 20C | Navigation keys: applicationServiceMainPage_H, applicationServiceMaintNew, applicationServiceTabMenu, applicationServiceMainPage, appSvcAccessModeGrid Records in the UI metadata program component tables related to the above navigation keys. |
Unless otherwise specified below, these notes are for informational purposes and no action is required.
PLANNED REMOVAL
Plan to Remove Custom Groovy Function Support from Oracle Utilities Testing Accelerator
Support for defining custom functions with Groovy script will be deprecated in a future release.

 or
or 