Open topic with navigation
Parsing Concept Guide
Why parsing is needed
An important aspect of data being fit for purpose is the structure it
is found in. Often, the structure itself is not suitable for the needs
of the data. For example:
- The data capture system does not have fields for
each distinct piece of information with a distinct use, leading to user
workarounds, such as entering many distinct pieces of information into a
single free text field, or using the wrong fields for information which
has no obvious place (for example, placing company information in individual contact fields).
- The data needs to be moved to a new system, with
a different data structure.
- Duplicates need to be removed from the data, and
it is difficult to identify and remove duplicates due to the data structure
(for example, key address identifiers such as the Premise Number are not separated
from the remainder of the address).
Alternatively, the structure of the data may be sound, but the use of
it insufficiently controlled, or subject to error. For example:
- Users are not trained to gather all the required
information, causing issues such as entering contacts with ‘data cheats’ rather than real
names in the name fields
- The application displays fields in an illogical
order, leading to users entering data in the wrong fields
- Users enter duplicate records in ways that are
hard to detect, such as entering inaccurate data in multiple records representing the same
entity, or entering the accurate data, but in the wrong fields.
These issues all lead to poor data quality, which may in many cases
be costly to the business. It is therefore important for businesses to
be able to analyze data for these problems, and to resolve them where
necessary.
The OEDQ Parser
The OEDQ Parse processor is designed to be used by developers
of data quality processes to create packaged parsers for the understanding
and transformation of specific types of data - for example Names data,
Address data, or Product Descriptions. However, it is a generic parser
that has no default rules that are specific to any type of data. Data-specific
rules can be created by analyzing the data itself, and setting the Parse
configuration.
Terminology
Parsing is a frequently used term both in the realm of data quality,
and in computing in general. It can mean anything from simply 'breaking
up data' to full Natural Language Parsing (NLP), which uses sophisticated
artificial intelligence to allow computers to 'understand' human language.
A number of other terms are also frequently used related to parsing. Again,
these can have slightly different meanings in different contexts. It is
therefore important to define what we mean by parsing, and its associated
terms, in OEDQ.
Please note the following terms and definitions:
|
Term
|
Definition
|
|
Parsing
|
In OEDQ, Parsing is defined as the application of user-specified
business rules and artificial intelligence in order to understand and
validate any type of data en masse, and, if required, improve its structure
in order to make it fit for purpose.
|
|
Token
|
A token is a piece of data that is recognized as a unit by the Parse
processor using rules. A given data value may consist of one or many tokens.
A token may be recognized using either syntactic or semantic analysis
of the data.
|
|
Tokenization
|
The initial syntactic analysis of data, in order to split it into its
smallest units (base tokens) using rules. Each base token is given a tag,
such as <A>, which is used to represent unbroken sequences of alphabetic characters.
|
|
Base Token
|
An initial token, as recognized by Tokenization. A sequence of Base
Tokens may later be combined to form a new Token, in Classification or
Reclassification.
|
|
Classification
|
Semantic analysis of data, in order to assign meaning to base tokens,
or sequences of base tokens. Each classification has a tag, such as 'Building',
and a classification level (Valid or Possible) that is used when selecting
the best understanding of ambiguous data.
|
|
Token Check
|
A set of classification rules that is applied against an attribute in
order to check for a specific type of token.
|
|
Reclassification
|
An optional additional classification step which allows sequences of
classified tokens and unclassified (base) tokens to be reclassified as
a single new token.
|
|
Token Pattern
|
An explanation of a String of data using a pattern of token tags, either
in a single attribute, or across a number of attributes.
A String of data may be represented using a number of different token
patterns.
|
|
Selection
|
The process by which the Parse processor attempts to select the 'best'
explanation of the data using a tuneable algorithm, where a record has
many possible explanations (or token patterns).
|
|
Resolution
|
The categorization of records with a given selected explanation (token
pattern) with a Result (Pass, Review or Fail), and an optional Comment.
Resolution may also resolve records into a new output structure using
rules based on the selected token pattern.
|
Summary of the OEDQ Parse processor
The following diagram shows a summary of the way the OEDQ Parse
processor works:
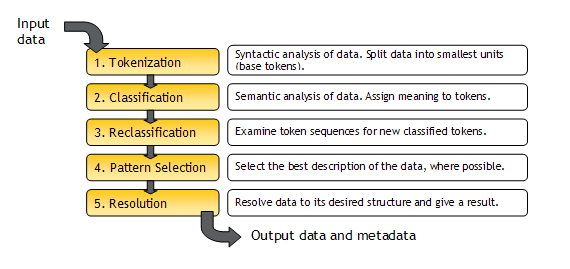
See the help pages for the OEDQ
Parse processor for full instructions on how to configure it.
Oracle ® Enterprise Data Quality Help version 9.0
Copyright ©
2006,2011 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.

