![]()
|
|
Suspect Data Check |
The Suspect Data Check processor checks an attribute value for a variety of common data entry 'cheats', such as entering 'aaa' in a name field.
Specifically, it can check for any or all of the following:
Use the Suspect Data Check to check for common user ruses which result in suspect data in compulsory columns.
Where an empty value cannot be entered at the point of data entry, the user may enter a single character - for example a space, a full stop, or a random single character - to get past that point.
Alternatively, a single but repeating character may be entered - for example '9999' - or perhaps a repeating pattern of characters - for example 'asdasd'.
Note that this may not be the fault of the user, but of the business process and/or supporting applications. The user may not know or have available the complete set of data that the data entry application is requesting, but is required to enter the data into the system.
A single attribute that you wish to check for suspect data entries.
Repeating alphabetic characters
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
|
Check |
Yes/No |
Drives whether or not to check for repeating alphabetic characters |
Yes
|
|
|
Minimum repeat |
Number |
The minimum number of alphabetic characters that must be repeated for the check to identify a suspect entry |
3
|
Repeating numeric characters
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
|
Check |
Yes/No |
Drives whether or not to check for repeating numeric characters |
Yes |
|
|
Minimum repeat |
Number |
The minimum number of numeric characters that must be repeated for the check to identify a suspect entry |
2
|
Repeating non alphanumeric characters
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
Check |
Yes/No
|
Drives whether or not to check for repeating alphanumeric characters |
Yes
|
|
Minimum repeat |
Number |
The minimum number of numeric characters that must be repeated for the check to identify a suspect entry |
2 Note: This value must be at least 2 |
Repeating patterns
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
Check |
Yes/No |
Drives whether or not to check for repeating patterns of characters |
Yes |
|
Minimum pattern length |
Number |
The minimum number of pattern characters that must be repeated for the check to identify a suspect entry |
3 Note: This value must be at least 2 |
|
Minimum pattern repeat |
Number |
The number of times a pattern must occur for the data to be identified as suspect |
2 Note: This value must be at least 2 |
Minimum length
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
Minimum length |
Number |
The minimum length, in characters, for values in this attribute. Note that Null records are separately classified. |
0 |
None
|
Flag attribute |
Purpose |
Possible Values |
|
SuspectData |
Indicates which data passes the Suspect Data Check: Suspect Data, Valid Data and Null |
Y/N/- |
A Suspect Data Check's results may be published to the Dashboard.
The following interpretation of results is used by default:
|
Result |
|
|
Valid |
Pass |
|
Null |
Pass |
|
Suspect |
Alert |
|
Execution Mode |
Supported |
|
Batch |
Yes |
|
Real time Monitoring |
Yes |
|
Real time Response |
Yes |
The Suspect Data Check produces a summary view of its results, showing the following statistics:
|
Statistic |
Meaning |
|
Suspect records |
Records that were identified as having a suspect value in the attribute checked. Drill down to see a breakdown of the suspects by the check that identified them. Drill down again to see the records. |
|
Valid records |
Records that did not have a suspect value in the attribute checked |
|
Null records |
Records with a null value in the attribute checked |
The following output filters are available from a Suspect Data Check:
In this example, The Suspect Data Check is used to check a NAME attribute for suspect data entries:
Summary View
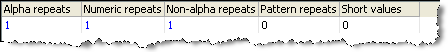
Drilldown on Alpha Repeats
![]()
Drilldown on Numeric Repeats
![]()
Oracle ® Enterprise Data Quality Help version 9.0
Copyright ©
2006,2011 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.