Round |
The Round processor allows you to round numeric values to a given number of decimal places.
Use Round where you need to transform numbers to a lower level of accuracy - for example in order to migrate numbers to a system that stores numbers differently.
A single Number attribute
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
Decimal places |
Integer |
Allows decimals to be rounded to a maximum number of decimal places |
2 |
|
Round to nearest |
Integer |
Allows integers to be rounded to the nearest aggregation of a given integer, such as the nearest 10, or the nearest 100. |
None |
|
Round type |
Selection (Up / Down / Nearest) |
Drives how rounding is performed; that is, whether to round up, down or to the nearest whole value. |
Nearest |
|
Note: If the Round to nearest value is set, this over-rides the value of the Decimal places option, and rounds values to the nearest aggregation of the given integer, such as the nearest 10 (that is, effectively sets Decimal places to 0). |
|
Data attribute |
Type |
Purpose |
Value |
|
[Attribute Name].Rounded |
Derived |
Stores the result of the rounding |
A numeric value with the result of the rounding operation |
None
|
Execution Mode |
Supported |
|
Batch |
Yes |
|
Real time Monitoring |
Yes |
|
Real time Response |
Yes |
The Round processor presents no summary statistics on its processing.
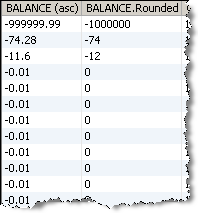
In the Data view, each input attribute is shown with the new roundedvalue to the right.
None. All records input are output.
In this example, the BALANCE attribute on the Customers table of the example Service Management data is rounded to 0 decimal places:
Oracle ® Enterprise Data Quality Help version 9.0
Copyright ©
2006,2011 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.