GNR Parse |
The GNR Parse processor uses GNR’s parsing API to read in unstructured names (in a Full Name field) and to parse them into its best understanding of the constituent parts of the name.
Use GNR Parse with global name data which does not have a known Given Name and Surname structure.
Parsing names is normally done before using GNR Search, which requires a Given Name and Surname name structure.
The GNR Parse processor expects one or more name attributes as inputs. If multiple attributes are provided, the processor simply concatenates the values and treats the result as a name.
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
Reparse threshold |
Integer |
Drives the maximum number of attempts to find alternate parses for a single input name by reparsing. A value of 0 means that no reparsing will be attempted. A value of 1 or more will mean that reparsing will be attempted once. Note that reparsing is the process of re-parsing the name using the output of the initial parse. This may deliver an alternate parse of the same name with a higher confidence value. Setting the Reparse threshold higher might therefore lead to more records being successfully parsed. |
0 |
|
Confidence threshold |
Integer |
Drives which name parsing results are considered successful. Any name parses that are below the confidence threshold are suppressed. If no parses of the input name are above the threshold, parsing is unsuccessful, and no parsed name is output. |
60 |
Parsed names are added to the data as array attributes. This is because multiple parses of the same name may be output, and/or multiple names may be understood from the same input name. For example, the name the name ‘Stephen Martin’ may yield two alternate parsed names for the same individual, and the name ‘Mr and Mrs Alan and Susan Collins’ may yield multiple names for two individuals.
The array values may be further processed by other standard OEDQ processors – for example, the alternate and multiple parses of a name may be split into alternate records using Split Records from Array.
The gnr.NameIndex attribute indicates whether or not a parsed name is an alternative parse of a name, or another name. Any output names with the same gnr.NameIndex value are for the same individual.
Note that all attributes are arrays as there may be multiple parsed names returned by the API, either because of alternate parses of the same name, or because of multiple names in the input name.
|
Data attribute |
Type |
Value |
|
gnr.GivenName |
String Array |
The parsed Given Name(s) from the input name |
|
gnr.Surname |
String Array |
The parsed Surname from the input name |
|
gnr.Qualifier |
String Array |
The parsed Qualifier from the input name |
|
gnr.Title |
String Array |
The parsed Title from the input name |
|
gnr.Confidence |
String Array |
The confidence of the GNR parsing API in the parsed name |
|
gnr.NameIndex |
String Array |
An index value indicating whether the name is an alternate parse |
|
Flag |
Purpose |
Possible Values |
|
gnr.ParseSuccess |
Indicates the success or otherwise of parsing the input name, according to the configured confidence threshold |
Y - if name parsing was successful N - if name parsing was unsuccessful |
|
Execution Mode |
Supported |
|
Batch |
Yes |
|
Real-time Monitoring |
Yes |
|
Real-time Response |
Yes |
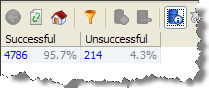
A summary view is included that summarizes the parsing results by success or failure (according to the configured Confidence Threshold):
|
Statistic |
Meaning |
|
Successful |
The input name was successfully parsed into one or more output names with a confidence value above the configured threshold. |
|
Unsuccessful |
The input name could not be parsed with a confidence value above the configured threshold |
The following output filters are available from the GNR Parse processor:
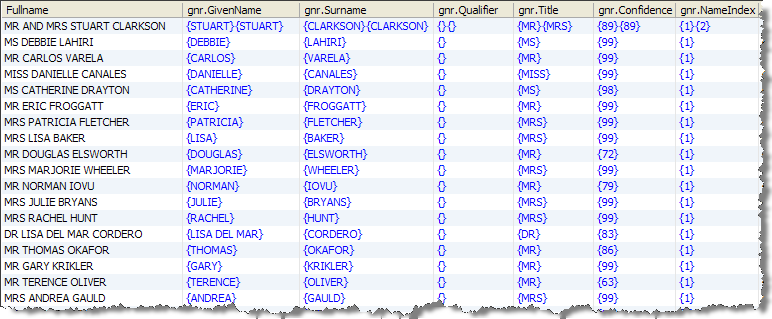
This example shows how GNR Parse parses out full names to a structured name format.
Summary View
Data View
Oracle ® Enterprise Data Quality Help version 9.0
Copyright ©
2006,2012 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.