Oracle Text Document Section Searching
Overview
Purpose
This tutorial covers the following:
- Enabling Oracle Text Section Searching
- Oracle Text Section Types
- HTML Section Searching with Oracle Text
- XML Section Searching with Oracle Text
Time to Complete
Approximately 1 hour
Introduction
Section searching enables you to narrow text queries down to blocks of text within documents. Section searching is useful when your documents have internal structure, such as HTML and XML documents. You can also search for text at the sentence and paragraph level.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, you should:
Enabling Oracle Text Section Searching
The steps for enabling section searching for your document collection are:
- Create a Section Group
- Define Your Sections
- Index Your Documents
- Section Searching with the WITHIN Operator
Creating a Section Group
Section searching is enabled by defining section groups. You use one of the system-defined section groups to create an instance of a section group. Choose a section group appropriate for your document collection. You use section groups to specify the type of document set you have and implicitly indicate the tag structure. For instance, to index HTML tagged documents, you use the HTML_SECTION_GROUP. Likewise, to index XML tagged documents, you can use the XML_SECTION_GROUP. You use the CTX_DDL package to create section groups and define sections as part of section groups.
To create a a Section Group, perform the following steps:-
Open a SQL Worksheet using myuser_conn and enter the following code to create a table called docs1 having a single column called text which is VARCHAR2(80).
Click the Run Statement icon to run the query.CREATE TABLE docs1( text VARCHAR2(80));
-
Enter the following code to insert the data into the docs1 table and click Run Script icon to run the code.
INSERT INTO docs1 VALUES('<H1>Oracle</H1>');
INSERT INTO docs1 VALUES('<H1>California is a state in the US.</H1>');
INSERT INTO docs1 VALUES('<H1>Paris is a city in France.</H1>');
-
Create a section group with HTML_SECTION_GROUP using the following code:
begin
ctx_ddl.create_section_group('htmgroup', 'HTML_SECTION_GROUP');
end;
Define Your Sections
You define sections as part of the section group. Add a zone section called heading for all text within the <H1> tag:
begin
ctx_ddl.add_zone_section('htmgroup', 'heading', 'H1');
end;
Index Your Documents
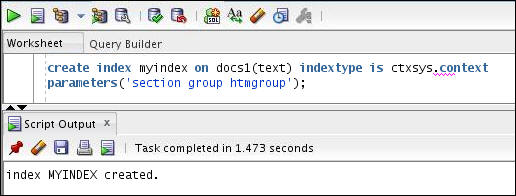
To index HTML documents, you need to specify your section group in the parameter clause of CREATE INDEX.
create index myindex on docs1(text) indextype is
ctxsys.context
parameters('section group htmgroup');
Section Searching with the WITHIN Operator
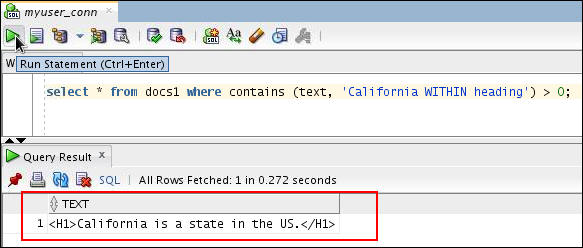
When your documents are indexed, you can query within sections using the WITHIN operator. Here, to find all the documents that contain the word California within their headings, enter the following query:
select * from docs1 where contains (text, 'California WITHIN heading') > 0;
Oracle Text Section Types
Zone Section
A zone section is a body of text delimited by start and end
tags in a document. The positions of the start and end tags
are recorded in the index so that any words in between the
tags are considered to be within the section.
Any instance of a zone section must have a start and an end
tag. Zone sections can nest, overlap, and repeat within a
document. You define sections as part of the section group.
The following example defines a zone section called heading
for all text within the HTML tag:
begin
ctx_ddl.add_zone_section('htmgroup', 'heading', 'H1');
end;
Note: Zone section has been already covered in the previous section.
Field Section
A field section is similar to a zone section in that it is a region of text delimited by start and end tags. Field sections are more efficient than zone sections and are different than zone sections in that the region is indexed separately from the rest of the document. You can create an unlimited number of field sections. Since field sections are indexed differently, you can also get better query performance over zone sections for when you have a large number of documents indexed.
Unlike zone sections, field sections have the following restrictions:- Field sections cannot overlap.
- Field sections cannot repeat.
- Field sections cannot nest.
Note: Repeated field sections are allowed, but WITHIN queries treat them as a
single section. To
have WITHIN queries
distinguish repeated sections, define them as zone
sections.
-
Create a table called authors using the following CREATE TABLE statement.
create table authors
(id number primary key, author_name varchar2(80));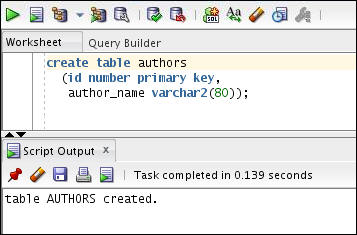
-
Insert data into the authors table using the following INSERT TABLE statement.
insert into authors values (1,'<author>John Irving</author>');
insert into authors values (2,'<author>Ken Belly</author>');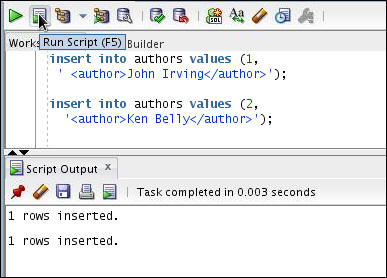
-
Create a section group called basicgroup of the BASIC_SECTION_GROUP type. Then add a field section in basicgroup called Author for the tag <author> and set the visible flag to FALSE to create an invisible section:
begin
ctx_ddl.create_section_group('basicgroup', 'BASIC_SECTION_GROUP');
ctx_ddl.add_field_section('basicgroup', 'Author', 'author', FALSE);
end;
-
Create an index on the authors table to index your documents and specify your section group in the parameter clause of CREATE INDEX.
create index myindx on authors (author_name) indextype is ctxsys.context
parameters ('section group basicgroup');
-
Execute the SELECT statement to find text within the Author section as follows:
select * from authors
where contains (author_name, 'Irving WITHIN Author') > 0;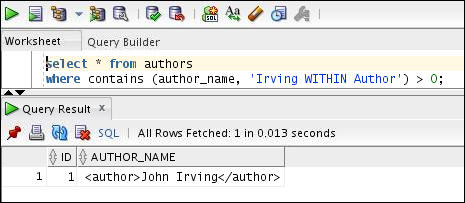
Note: You must use the WITHIN operator in the query when you set your field section as FALSE.
-
Create the section group of the BASIC_SECTION_GROUP type and set the visible flag to TRUE to create an visible section as follows:
begin
ctx_ddl.add_field_section('basicgroup', 'Author', 'author', TRUE);
end;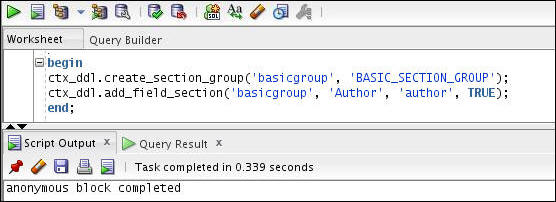
-
Drop and recreate the index on authors table.
drop index myindx;
create index myindx on authors (author_name) indextype is ctxsys.context
parameters ('section group basicgroup');
-
Execute the SELECT statement to find text within the Author section without specifying the WITHIN operator as follows:
select * from authors
where contains (author_name, 'Irving') > 0;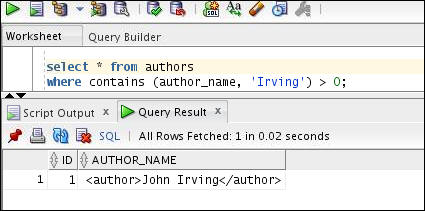
Note: If you want to query text within field sections without specifying WITHIN operator, you must set the visible flag to TRUE.
MDATA Section
An MDATA section is used to reference user-defined metadata for a document. Using MDATA sections can speed up mixed queries.MDATA sections are not tokenized. So "Black Dog" is indexed as a single string, rather than split into "black" and "dog" as would be the case for a field or zone section. MDATA can be updated (in a transactional manner) without affecting the rest of the index. So if a library application keeps track of the number of copies of a book it has in stock, then modifying that information does NOT require you to reindex the whole record.
Use CTX_DDL.ADD_MDATA_SECTION to add an MDATA section to a section group. MDATA values can be changed with CTX_DDL.ADD_MDATA and removed with CTX_DDL.REMOVE_MDATA. Also, MDATA sections can have multiple values. Only the owner of the index is allowed to call CTX_DDL.ADD_MDATA and CTX_DDL.REMOVE_MDATA.
-
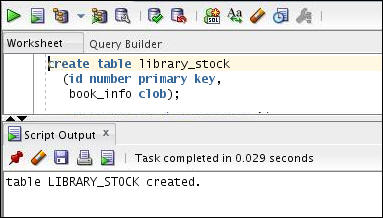
Create a table called library_stock using the following CREATE TABLE statement.
create table library_stock (id number primary key,
book_info clob);
-
Insert data into the library_stock table using the following INSERT TABLE statement.
insert into library_stock values (1,
'<title>A Prayer for Owen Meany</title>
<author>John Irving</author>
<status>In Stock</status>
<stocklevel>1</stocklevel>');
insert into library_stock values (2,
'<title>The World According to Garp</title>
<author>John Irving</author>
<status>In Stock</status>
<stocklevel>12</stocklevel>');
insert into library_stock values (3,
'<title>The Hotel New Hampshire</title>
<author>John Irving</author>
<status>Out of Stock</status>
<stocklevel>0</stocklevel>');
-
Create a section group called mysg of the HTML_SECTION_GROUP type. Then add a field section in mysg called title for the tag <title> and set the visible flag to TRUE. And create a MDATA sections called status and stocklevel.
begin
ctx_ddl.create_section_group('mysg', 'HTML_SECTION_GROUP');
ctx_ddl.add_field_section('mysg', 'title','title', TRUE);
ctx_ddl.add_mdata_section('mysg', 'status', 'status');
ctx_ddl.add_mdata_section('mysg', 'stocklevel','stocklevel');
end;
-
Create an index on the library_stock table to index your documents and specify your section group in the parameter clause of CREATE INDEX.
create index lib_index on library_stock (book_info)
indextype is ctxsys.context
parameters ('section group mysg');
-
Execute the SELECT statement to find text within the mdata and the field section as follows:
select book_info from library_stock
where contains (book_info, 'A Prayer for Owen Meany WITHIN title and mdata(status, In Stock)') > 0;

SDATA Section
The
value of an SDATA section is
extracted from the document text like other sections, but is
indexed as structured data, also referred to as SDATA.
Using SDATA sections supports
operations such as projection, range searches, and ordering.
It also enables SDATA indexing of
section data such as embedded tags, and detail table or
function invocations. This enables you to perform various
combinations of text and structured searches in one single SQL
statement.
SDATA operators should
only be used as descendants of AND operators that
also have non-SDATA children. SDATA operators are
meant to be used as secondary, checking or non-driving,
criteria. For instance, "find documents with DOG that also
have price > 5", rather than "find documents with rating
> 4". Other uses will operate properly, but may not have
optimal performance.
You
use CTX_DDL.ADD_SDATA_SECTION to add an SDATA section to a
section group. When querying within an SDATA section, you use
the CONTAINS operator. The following example creates a table
called items,
and adds an SDATA section called my_sec_group,
and then queries SDATA in the section.
-
Create a table called items using the following CREATE TABLE statement.
CREATE TABLE items
(id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, doc VARCHAR2(4000));
-
Insert data into the items table using the following INSERT TABLE statement.
INSERT INTO items VALUES (1, '
<description> Honda Pilot </description>
<category>Cars and Trucks </category>
<price>27000 </price> ');
INSERT INTO items VALUES (2, '<description> Toyota Sequoia </description>
<category>Cars and Trucks </category>
<price>35000 </price> ');
INSERT INTO items VALUES (3, '<description> Toyota Land Cruiser </description>
<category>Cars and Trucks </category>
<price>45000 </price> ');
INSERT INTO items VALUES (4, '<description> Palm Pilot </description>
<category>Electronics </category>
<price>5 </price> ');
INSERT INTO items VALUES (5, '<description> Toyota Land Cruiser Grill </description>
<category>Parts and Accessories </category>
<price> 100 </price> '); -
-
Create a section group called my_sec_group of the BASIC_SECTION_GROUP type. Then add a SDATA section in my_sec_group called category for the tag <category> and section price for the tag <price>.
BEGIN
CTX_DDL.CREATE_SECTION_GROUP('my_sec_group', 'BASIC_SECTION_GROUP');
CTX_DDL.ADD_SDATA_SECTION('my_sec_group', 'category', 'category', 'VARCHAR2');
CTX_DDL.ADD_SDATA_SECTION('my_sec_group', 'price', 'price', 'NUMBER');
END;
-
Create a CONTEXT index on the items table to index your documents and specify your section group in the parameter clause of CREATE INDEX.
CREATE INDEX items$doc
ON items(doc) INDEXTYPE IS CTXSYS.CONTEXT
PARAMETERS('SECTION GROUP my_sec_group');
-
Execute the SELECT statement to find text within the sdata section as follows:
SELECT id, doc
FROM items
WHERE contains(doc, 'Toyota
AND SDATA(category = ''Cars and Trucks'')
AND SDATA(price <= 40000 )') > 0;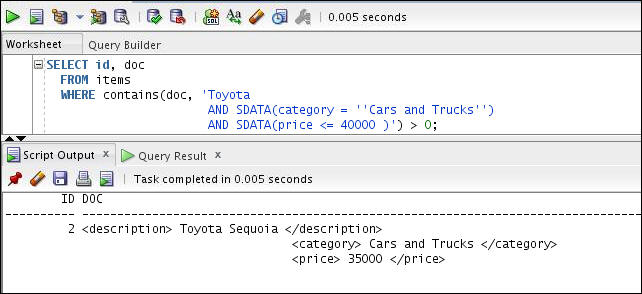
XML Section Searching with Oracle Text
Like HTML documents, XML documents have tagged text which you can
use to define blocks of text for section searching. The contents
of a section can be searched on with the WITHIN
or INPATH operators.
You can search XML attribute text in one of two ways:
- Create attribute sections with CTX_DDL.ADD_ATTR_SECTION
and then index with XML_SECTION_GROUP.
If you use AUTO_SECTION_GROUP
when you index, attribute sections are created automatically.
You can query attribute sections with the WITHIN
operator.
- Index
with the
PATH_SECTION_GROUPand query attribute text with theINPATHoperator.
In this tutorial, you will create attribute sections with CTX_DDL.ADD_ATTR_SECTION and then index with XML_SECTION_GROUP.
-
Create a table called books using the following CREATE TABLE statement.
create table books(id number, text clob);
-
Insert data into the books table using the following INSERT TABLE statement. Here, the XML file defines the <BOOK> tag with a TITLE attribute as follows:
insert into books values(1, '<BOOK TITLE="Tale of Two Cities">
It was the best of times. </BOOK>
<Author NAME="Charles Dickens">
Born in England in the town, Stratford_Upon_Avon </Author>');
-
Create a section group called myxmlgroup of the XML_SECTION_GROUP type. Then add a attribute section in myxmlgroup called booktitle for the tag <BOOK>.
begin
ctx_ddl.create_section_group('myxmlgroup', 'XML_SECTION_GROUP');
ctx_ddl.add_attr_section('myxmlgroup', 'booktitle', 'BOOK@TITLE');
end;
-
Create an index on the books table to index your documents and specify your section group in the parameter clause of CREATE INDEX.
CREATE INDEX myindex
ON books(text)
INDEXTYPE IS ctxsys.context
PARAMETERS ('datastore ctxsys.default_datastore
filter ctxsys.null_filter
section group myxmlgroup'
);
-
Execute the SELECT statement to find text within the booktitle attribute section as follows:
select * from books
where contains (text, 'Tale WITHIN booktitle') > 0;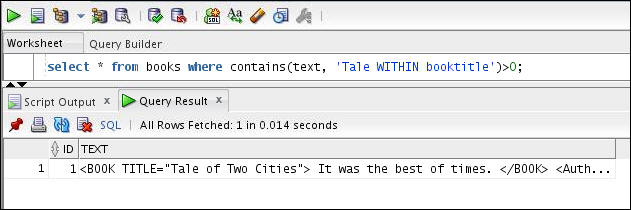
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned:
- Enabling Oracle Text Section Searching
- Oracle Text Section Types
- HTML Section Searching with Oracle Text
- XML Section Searching with Oracle Text
Resources
- Oracle Text Homepage on OTN
- Oracle Text Discussion Forums on OTN
- SearchTech Blog
- Oracle Text Application Developers' Guide
- To learn more about Oracle Text refer to additional OBEs in
the Oracle
Learning Library
Credits
- Lead Curriculum Developer: Dimpi Sarmah
- Other Contributors: Roger Ford
To navigate this Oracle by Example tutorial, note the following:
- Topic List:
- Click a topic to navigate to that section.
- Expand All Topics:
- Click the button to show or hide the details for the sections. By default, all topics are collapsed.
- Hide All Images:
- Click the button to show or hide the screenshots. By default, all images are displayed.
- Print:
- Click the button to print the content. The content that is currently displayed or hidden is printed.
To navigate to a particular section in this tutorial, select the topic from the list.