OEDQ provides two different types of real time matching:
This topic provides a general guide to how real time matching works in OEDQ.
|
Note: If you wish to use OEDQ for real time duplicate prevention and/or data cleansing with Oracle Siebel UCM or CRM, Oracle provide a standard connector for this purpose. |
OEDQ's real time duplicate prevention capability assumes that the data being matched is dynamic, and therefore changes regularly (for example, customer data in a widely-used CRM system). For this reason, OEDQ therefore does not copy the working data. Instead, the data is indexed on the source system using the same clustering rules that are used in the match processor.
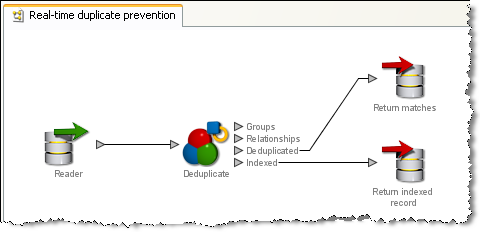
Real time duplicate prevention occurs in two stages - Clustering, and Group processing.
In the Clustering stage, OEDQ receives a new record on its real time interface and assigns it cluster keys using the clustering configuration of the Deduplicate match processor in the process that has been enabled for real time execution. It returns the cluster keys for the record using a Writer. The source system then receives this message and feeds back to OEDQ a set of all the records that have the same cluster keys.
OEDQ receives the message containing the records with the same cluster keys as the input record. Next, it selects the definite and possible matches to the new record from these candidate match records. The matching results are then returned using a second Writer. This response is then handled externally to determine how to update the system. Possible responses include declining the new (duplicate) record, merging the new record with its duplicate record, or adding the new record, but including a link to the duplicate record or records.
Note that the same process performs both clustering and matching on the records, with writers connected to different output filters to enable the different responses. An example process for real time de-duplication is shown below:

|
Note: In the case of the Siebel connector, OEDQ conforms with the constraints of the Siebel Data Quality interface, so the clustering is performed by configuring the query expressions on Siebel. OEDQ, therefore, only performs the Group processing stage of real time duplicate prevention, taking in the driving record and the candidate matches identified by Siebel, and returning the possible matches to the driving record along with a score (based on the match rule with which the candidate matched the driving record). |
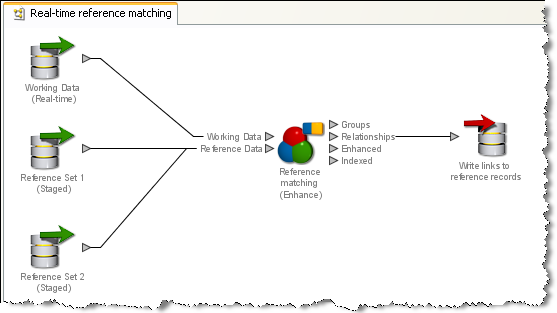
OEDQ's real time reference matching implementation matches new records against one or many reference sets. The data in the reference sets is assumed to be non-dynamic. That is, they are updated on a regular basis, but not constantly accessed and updated by multiple users (for example watch lists, rather than CRM data). Reference matching is a single stage process. Incoming records from a working real time source are matched against snapshots of reference records from one or more staged sources. A writer on the process then returns the output of the match processor back to the calling system. Note that the output returned may be any of the forms of output from the match processor. If you want only to link the new records to the reference sets, you can write back the Relationships output. If you want to enhance the new records by merging in data from the matching reference records, you can use the merge rules in the Enhance processor, and write back the Enhanced data output.
In the following example, the links to reference records are written:
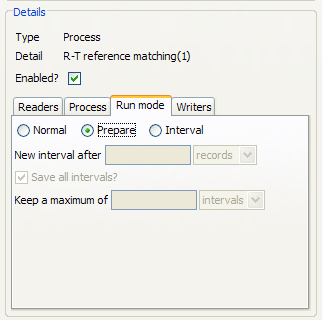
For a real time reference matching process to perform correctly, it must first be run in Prepare mode. This allows it to compare the inbound records quickly against the reference sets and issue a response. Running a process in Prepare mode will ensure that all the cluster keys for the reference data sets have been produced.
To run a process in Prepare mode, set up a job and add the relevant process as a task. Click on the process to set the configuration details. Click on the Run Mode tab, and select Prepare:
Real-time matching uses a cached and prepared copy of the reference data. This means that when updates are made to reference data, the snapshot must be re-run and the data re-prepared before the updates can be propagated to the matching process.
Re-preparing reference data involves:
Triggers, which can start and stop other jobs, can be used to create a job which includes all the above phases. Such a "Stop, re-prepare and restart" job would appear as follows:
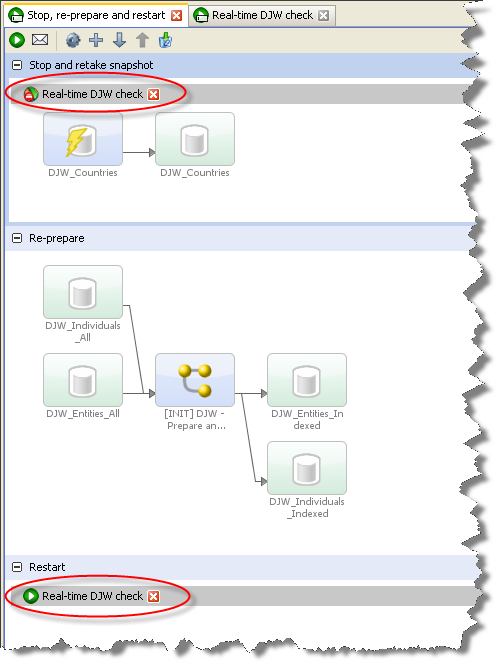
This job consists of three phases. The first stops the real-time match process and re-runs the reference data snapshot. The second runs the match process in Prepare mode. The third re-starts the real-time match process in Interval mode.
Triggers are configured to run either at the beginning of a phase or at the end, so it would be possible to include the restart trigger at the end of the second phase, just as the stop trigger is placed at the beginning of the first phase. However, placing the restart trigger in its own phase means you can configure the restart phase to run only if the re-prepare phase is successful.
see "Using Triggers" for more information on triggers.
In order to enable real time matching, you must configure a process containing a Deduplicate or Enhance processor. The process may contain other processors, but must only contain a single matching processor.
Normally, real time processes should be run in Interval mode. That is, they will run on a continuous basis, and write their results to the results database at regular intervals. See Execution Options.
Real time consumer and provider interfaces must also be configured to communicate with an external system, using either JMS or Web Services.
|
Note: For real time reference matching via a Web Service, you can use OEDQ's Web Service capability to generate the real time consumer and provider interfaces automatically. For real time duplicate prevention, the interfaces will normally need to be written manually, in order to cope with the separate calls for clustering and record matching. If you are using the Siebel Connector, pre-configured Web Services are provided. |
Oracle ® Enterprise Data Quality Help version 9.0
Copyright ©
2006,2011 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.