Metaphone |
The Metaphone processor converts the values for a String attribute into a code which represents the phonetic pronunciation of the original string, using the Double Metaphone algorithm.
The Double Metaphone algorithm is a more general phonetic technique than Soundex (which is specifically designed for people’s names), and is more sophisticated and context-sensitive than the original Metaphone algorithm.
|
Note: For readability, the remainder of this documentation refers to 'Metaphone codes'. However, it is the Double Metaphone algorithm that is used throughout. |
Metaphone codes are particularly useful where spelling discrepancies may occur in words that sound the same, for example, where information has been captured over the telephone. By considering the pronunciation of the string instead of the exact string value, many minor variances can be overcome. A Metaphone code is therefore a good alternative to the raw data value when performing a duplicate check, making it is easier to identify possible duplicate or ‘equivalent’ values.
The processor allows you to specify the maximum length of the Metaphone code (up to a maximum of 12 characters) so that it can be focused solely on the first few syllables or words of complex data rather than the entire column, and so that you can control the sensitivity of the phonetic similarity between values.
Any String or String Array attributes.
Note that if you input an Array attribute, the transformation will be applied to all array elements, and an Array attribute will be output.
|
Option |
Type |
Purpose |
Default Value |
|
Maximum result length |
Number (1-12) |
Allows you to vary the maximum length of the Metaphone code to be produced |
12 |
|
Data attribute |
Type |
Purpose |
Value |
|
[Attribute Name].Metaphone |
Derived |
A new attribute with the Metaphone code derived from the input attribute. |
The original attribute value, converted to its Metaphone code. |
None
|
Execution Mode |
Supported |
|
Batch |
Yes |
|
Real time Monitoring |
Yes |
|
Real time Response |
Yes |
The Metaphone transformation processor presents no summary statistics on its processing.
In the Data view, each input attribute is shown with its new derived Metaphone attribute to the right.
None. All records input are output.
This example uses the Metaphone processor to transform the NAME attribute in the Customers table from the example Service Management data. In this case, the default maximum length of 12 characters was used:
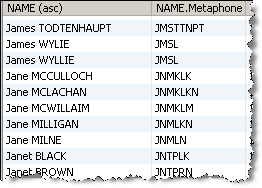
Note that James WYLIE and James WYLLIE have the same Metaphone code.
Oracle ® Enterprise Data Quality Help version 9.0
Copyright ©
2006,2011 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.