Private Service Access
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Private Service Access provides private secure access to one Oracle Cloud service API from within a VCN or on-premises network without traversing the internet.
Benefits of OCI Private Service Access

1. Per-service access
Instead of relying on a service gateway as a path to all Oracle service APIs within a region, OCI Private Service Access can be used to access a single OCI service API in that region.
2. Uses private IP
OCI Private Service Access uses a private IP from your network as the path to reach an OCI service API, rather than the public IP for that API.
3. No code changes required
Once you create a private service access (PSA) for a given OCI service API, any existing workloads in the private network will start using the PSA with no code changes required. This is because the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is now mapped in private DNS to the private IP of the PSA.
4. Secure
With OCI Private Service Access, you can configure network security groups and/or zero trust security attributes to a PSA, allowing for granular, per-service network access controls. Furthermore, in-tenancy credentials are enforced when accessing a service through a PSA, blocking cross-tenancy credential use and cross-tenancy Object Storage PAR access.
5. Performance
Each PSA will support up to 8 Gb/sec of throughput and 25 Gb/sec for Object Storage.
6. Availability
OCI Private Service Access is backed by the resilient OCI Cloud architecture, with fault domain and availability domain failover built in.
7. No gateway required
When using OCI Private Service Access, you do not need to configure a gateway on your private network to reach the target service. All the traffic for that service goes via the PSA.
8. Can coexist with gateways
While not required, you may have a service gateway that coexists with the PSA. Services enabled for PSA will use that PSA, while services not enabled for PSA would use the service gateway.
9. No charge
There is no separate charge for using OCI Private Service Access.
How does OCI Private Service Access work?
Within the virtual cloud network (VCN), you can determine what OCI services you wish to access via your private network. From the VCN user interface, create a PSA to each service you want to use.
Upon creation, the PSA exists as a private IP address within a subnet in your VCN. You control the lifecycle of the PSA and can delete it when it’s no longer needed. Each PSA results in a private DNS mapping to associate the service FQDN to the private IP address.
Control access to the service by configuring NSGs or zero trust security attributes as you would for any virtual NIC in a subnet.
Create multiple PSAs if you need access to multiple services (one PSA for each service).
Resources in an on-premises network will travel over a virtual private network or FastConnect dedicated circuit (private peering) to a dynamic routing gateway, and then to the private endpoint in the appropriate subnet. Network traffic remains within OCI and does not traverse the public internet. From the on-premises network, forward your DNS lookups for the regional OCI services to a listening endpoint in the VCN resolver to have the private IP returned and used for service communication.
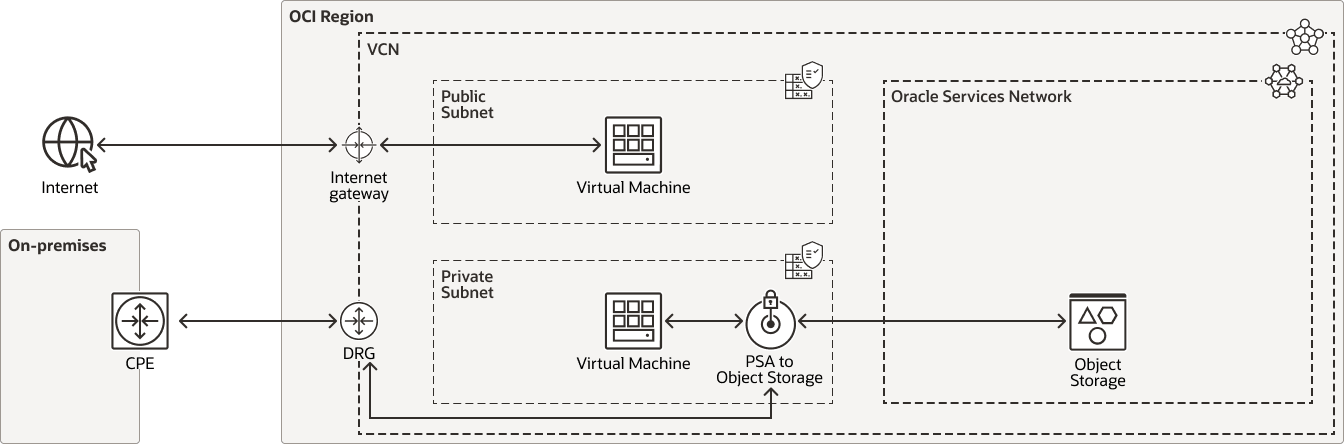
This image shows a logical layout of resources and connections in a typical scenario for OCI Private Servide access.
An OCI region is shown that contains a virtual cloud network with an attached internet gateway, dynamic routing gateway, and Private Service Access.
The virtual cloud network contains a public-facing subnet with a virtual machine resource. The virtual machine has access to the internet through the internet gateway.
The virtual cloud network also contains a private subnet with a virtual machine resource. Also within the private subnet is a private service access component that consumes an IP address in the subnet.
Within the region is a grouping of Oracle-managed resources, called the Oracle Services Network. This includes OCI Object Storage. The Object Storage service can be reached via the PSA endpoint without leaving the network in the region.
Resources in the private subnet can access a service when the corresponding PSA is created to that service. If multiple services are to be accessed, each would need its own PSA endpoint.
Resources

Pages
- There is no additional charge for OCI Private Service Access.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Economics
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Pricing
- Billing and Payment Tools Overview

How can we help you?

Oracle Cloud Infrastructure training
Get started with OCI Private Service Access work
Oracle Cloud Free Tier
Build, test, and deploy applications on Oracle Cloud—for free. Sign up once, get access to two free offers.
Contact sales
Interested in learning more about Oracle Cloud Infrastructure? Let one of our experts help.