Globally Distributed AI Database
Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database is a single logical database that automatically distributes and replicates data across various nodes, regions, and countries. It helps organizations build always-on architectures and achieve high performance while addressing data residency requirements. Applications can use Oracle AI Database’s converged capabilities, strong consistency, and full SQL support without code changes. Globally Distributed AI Database is available as automated services in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), as well as part of multicloud and on-premises Oracle AI Database deployments.
* Oracle AI Database 26ai replaces Oracle Database 23ai. Features in 23ai are also available in 26ai.
-
![]() Announcing Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure
Announcing Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure
Automatically distribute Oracle databases across nodes, regions, and countries to help meet data residency, extreme availability, and performance needs.
-
![]() Deep-dive webinar on Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure
Deep-dive webinar on Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure
Get an exclusive, in-depth look at this new Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database service.
 Innovate with Globally Distributed AI Database
Innovate with Globally Distributed AI Database
See how Oracle enables hyperscalability across globally distributed databases.
 Build petabyte-scale, real-time applications
Build petabyte-scale, real-time applications
Understand how Oracle uses Globally Distributed AI Database for a service that stores petabyte of data and scale to millions of transactions per second.
 Addressing data residency challenges
Addressing data residency challenges
Learn how Oracle is helping customers address data residency challenges and strengthen compliance.
Why choose Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database?
Always-on architectures
Enable rapid failover within seconds and help eliminate data loss during outages with Raft replication and an Active-Active-Active distributed database architecture that’s designed for mission-critical applications.
Performance and scale
Reduce performance bottlenecks with independent and granularly scaled database compute, storage capacity, and data ingest rates for AI, transaction processing, and analytics.
Address data residency requirements
Help meet data residency requirements by implementing automated data distribution and access policies for data, replicas, backups, and encryption keys based on geography.
Simple to use and manage
All shards are presented to an application and administered as a single logical database, simplifying application development and database administration. Oracle AI Database workloads and data types that are supported include relational, AI vector, JSON, Graph, and Spatial.
More data distribution and replication methods
Choose from more data distribution and replication methods than other leading distributed databases to more easily address diverse application and business requirements.
Deploy in the cloud and your data center
Use Globally Distributed Autonomous AI Database and Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure in OCI, Oracle AI Database services on OCI in multicloud environments, and Oracle AI Database Enterprise Edition in customer data centers.
Globally Distributed AI Database features
Automated data distribution
Automate sharding and resharding of data
Six data distribution methods enable applications to optimally collocate data to address needs for low latency, high performance, extreme availability, data residency, and other criteria.
Features
- Data is automatically placed on the desired shard, saving time and eliminating manual rebalancing
- Composite sharding, which allows two levels of sharding with different sharding methods and keys
- Parallel data ingestion on all shards
- Parallel queries across all shards
- Select through the console on cloud services
Elastic scalability
Scale online, on demand
Handle peak workloads for agentic AI and hyperscale OLTP performance by scaling compute, memory, and storage independently on Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure.
Features
- Near-instant online addition and deletion of database nodes on Exascale Infrastructure
- No data copying when adding nodes on Exascale Infrastructure
- Decoupled compute and storage with Exascale
- Automated redistribution of data
- Automatic shard rebalancing
Centralized administration
Centrally manage and monitor sharded databases as a single logical database
A built-in shard catalog allows all shards in Globally Distributed AI Database to be managed as a single, logical database. Cloud services implement centralized administration through the cloud console.
Centralized features
- Sharded database configuration, including data distribution policies and the addition or removal of shards
- High availability configuration using a choice of replication methods and custom replication topologies, including by geography or application tier
- Database object management—simplified operations at scale via seamless integration with Oracle Enterprise Manager, OCI console, and automation frameworks
- Backup and recovery
- Security configuration
Automated application routing
Simplify application development and deployment
Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database is natively supported by Oracle AI Database client drivers. Developers can treat Globally Distributed AI Database as a single logical database, simplifying application development.
Features
- Automated request routing to shards
- Automated routing of multishard requests to coordinator
- Transaction support for multishard updates
- Support for JDBC, OCI, .Net drivers
- Automated failover to standbys
- Support for FAN events
- Automatic identification of sharding key (21 JDBC)
High availability
Minimize unplanned or planned downtime
Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database helps protect against unplanned outages and provides online mechanisms for planned administrative and maintenance operations, enabling applications to offer always-on availability.
Features
- Choice of automated replication technologies including Raft
- Automated failover
- Fault isolation
- Online patching and upgrade
- Backup and recovery
- Disaster protection
Globally Distributed AI Database deployment options
- Autonomous AI Database
- Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure
- Additional services
- Multicloud architecture
- Hybrid architecture
- On-premises
Autonomous AI Database
A fully automated distributed database
Oracle Globally Distributed Autonomous AI Database combines the shared-nothing scalability, data locality management, and extreme availability of a distributed database with the full automation of Oracle Autonomous AI Database. It helps customers meet data residency requirements, provide survivability for business-critical applications, and deliver cloud-scale database performance.
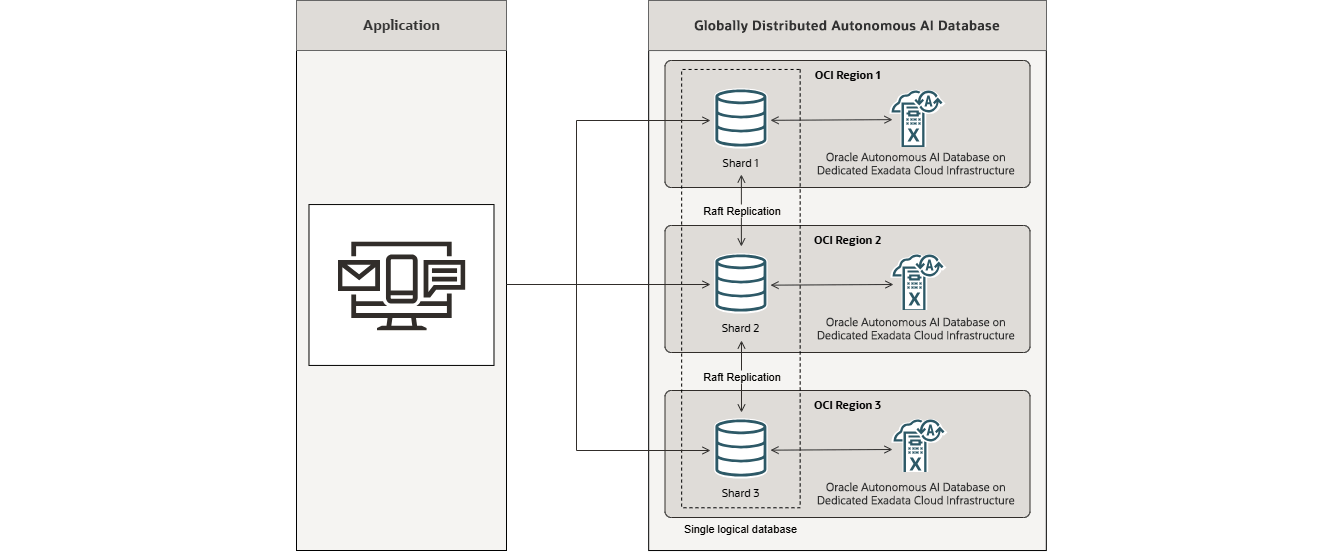
- Uses Autonomous AI Database’s self-managing, self-tuning, and self-scaling of nodes to reduce administrative overhead.
- Runs on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure for enhanced isolation and security.
- Simplifies management with automatic data distribution, automated application routing and centralized administration.
Resources:
Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure
Fast, efficient, and affordable
Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure delivers extreme availability, performance, and scalability for any type of Oracle AI Database workload. Each location uses pools of shared database-optimized compute and storage resources that enable performance scaling without copying data. It lets organizations minimize costs with small—yet powerful—configurations, granular elastic scaling, and pay-per-use economics.

- Deployed on secure and highly scalable multitenant resources.
- Independently scale database compute and storage—without downtime.
- Console-based automation helps automate data distribution, replication, resource scaling, and online maintenance
Resources:
Additional Oracle AI Database services on OCI
Use cloud applications with distributed databases
Oracle databases on OCI offer built-in access to globally distributed database capabilities. Existing Oracle AI Database applications can start using a distributed database without modifications. Consumption of database server licenses can be scaled up or down at any time without downtime, enabling users to optimize performance while reducing costs.

- Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database can be used with Oracle Database 19c or Oracle AI Database 26ai to gain Raft replication.
- Works with existing Oracle Exadata Database Service and Base Database Service environments.
- Provides administrator-based management of data distribution and replication.
Multicloud architecture
Distribute across clouds
Use Globally Distributed AI Database capabilities built into Oracle AI Database Enterprise Edition wherever it’s deployed. Deploy databases that span OCI, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to expand beyond the boundaries of any single cloud.

- Run Oracle AI Database Enterprise Edition deployed at Oracle Database multicloud partners.
- Each multicloud location provides low latency access to hyperscaler-specific services, tooling, and infrastructure.
- Use Oracle AI Database 26ai to access Raft replication.
Hybrid architecture
Distribute across clouds and your data center
Use Globally Distributed AI Database capabilities built into Oracle AI Database Enterprise Edition wherever it’s deployed. Deploy databases that span OCI, AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and your data centers to deploy closer to customers or in locations without cloud data centers.

- Works as part of Oracle databases deployed at Oracle AI Database multicloud partners.
- Provides low latency access to hyperscaler-specific services, tooling, and infrastructure.
- Leverage Exadata Database Machine, Exadata Cloud@Customer, Oracle Database Appliance, or non-Oracle infrastructure in your data center.
On-premises
A fully distributed database in your data center
Keep your data in your data center to help you meet data residency mandates, network latency, or high-throughput ingest requirements. Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database can be deployed on self-managed platforms or on Oracle-managed Exadata Cloud@Customer infrastructure wherever you need it.

Oracle offers the following choices for on-premises deployments of Globally Distributed AI Database:
- Exadata Database Machine
- Exadata Cloud@Customer
- Oracle Database Appliance
- Non-Oracle infrastructure

Munich Re HealthTech gives customers insights and control with OCI
What industry analysts are saying about Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database

“With the introduction of built-in RAFT-based replication, the new release brings the concept of database sharding to a new level of scalability and performance. A global, hyperscale database that is distributed and replicated across multiple geographical locations in real time is now a reality—and the data within it can be transparently localized according to complex rules.”
Alexei Balaganski
Lead Analyst and Chief Technology Officer, KuppingerCole Analysts

“Deploying successful agents with transactional systems is hard. With its scaling capacity, Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database on Exascale gives enterprises the capacity headroom so they can be confident they can scale in the AI era.”
Holger Mueller
Vice President and Principal Analyst, Constellation Research
Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database use cases
-
1Mission-critical availability (always-on/never-down)
Enable continuous operations and reduce data loss with sub–3-second failover across node, zone, or region outages—planned or unplanned.
-
2Data residency
Store and manage data across OCI regions or in your data centers to help meet data residency requirements— all while maintaining a unified, single-database view for applications and operations.
-
3Hyperscale OLTP workloads
Seamlessly scale out to handle petabytes of data and millions of transactions per second by elastically adding compute and storage.
-
4Petabyte-scale AI and analytics
Run AI vector searches and analytics on petabytes of data and support core backend services for agentic AI using decoupled compute and storage on Exascale’s intelligent, database-aware high performance storage.
-
5Low-latency user and device access
Improve response times by placing Globally Distributed AI Database nodes in OCI regions or private data centers near users and devices.
-
6Start small and grow
Achieve a low TCO while implementing always-on availability, addressing data residency requirements, and lowering your TCO by using cost-effective Exascale infrastructure in OCI or deploying on scalable infrastructure in your data center.
-
7Multicloud
Provide the ultimate in location flexibility by deploying scalable and highly available solutions that span all leading hyperscalers and your own data centers using Globally Distributed AI Database capabilities built into Oracle AI Database services and licenses.
-
8Economically run workloads with seasonal scalability
Easily scale up the performance of always-on workloads to meet peak demand and scale it back down afterwards using cost-effective Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure and your choice of software or bring your own license (BYOL) consumption models.
Experience Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database with Hands-On Labs


Announcing General Availability: Oracle Globally AI Distributed Database on Exascale Infrastructure
Pankaj Chandiramani, Senior Director, Product Management, OracleToday, Oracle is announcing the general availability of Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure, designed to simplify the deployment of distributed mission-critical applications across Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) regions worldwide. This purpose-built, enterprise-grade managed cloud database service automatically distributes, stores, and synchronizes data across multiple regions so applications can stay online even during regional outages. It provides full support of SQL, and helps customers meet diverse business needs for global data access, extreme scalability and performance, and data residency.
Read the complete postLatest Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database blogs
- August 11, 2025 How Can Organizations Benefit from Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure?
- May 22, 2025 Simplify Deployment of Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database on Containers Using Podman Compose
- October 23, 2024 Getting Started with Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database: Explore the Power of Free Images for Seamless Deployment
- September 26, 2024 Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database 26ai : Introducing Directory-Based Data Distribution to handle skewed data
- August 13, 2024 Introducing JSON Full-Text Search with Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database 26ai
Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database resources

Learning
- Press Release: Oracle Helps Customers Achieve Extreme Availability and Performance for Mission Critical and Agentic AI Applications
- Webcast: Deep Dive on Oracle Globally Distributed Exadata Database on Exascale Infrastructure
- Video: CUBE Conversation on Globally Distributed AI Database with Wei Hu, senior vice president, High Availability Technologies, Oracle (26:12)
- Optimizing Supply Chain Dynamics For Manufacturing & Logistics With Oracle’s Globally Distributed AI Database (PDF)
- Transforming Real-Time Payments with Oracle’s Distributed AI Database: Sovereignty, Scalability, and Survivability (PDF)
- JSON Full-Text Search with Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database 26ai (PDF)
- Oracle LiveLab: Learn How to Achieve Data Sovereignty with Oracle Globally Distributed Database 19c
- Oracle LiveLab: Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database – Hyperscale Globally Distributed AI Database Workshop
- Oracle LiveLab: Use Raft Replication with Distributed AI Database
Get started with Oracle Globally Distributed AI Database
Try Oracle Cloud Free Tier
Build, test, and deploy applications on Oracle Cloud for free.
Contact us
Interested in learning more? Contact one of our industry-leading experts.




