Overview of Oracle's automated zero-downtime patching
Automated Patching Process - why is it important?
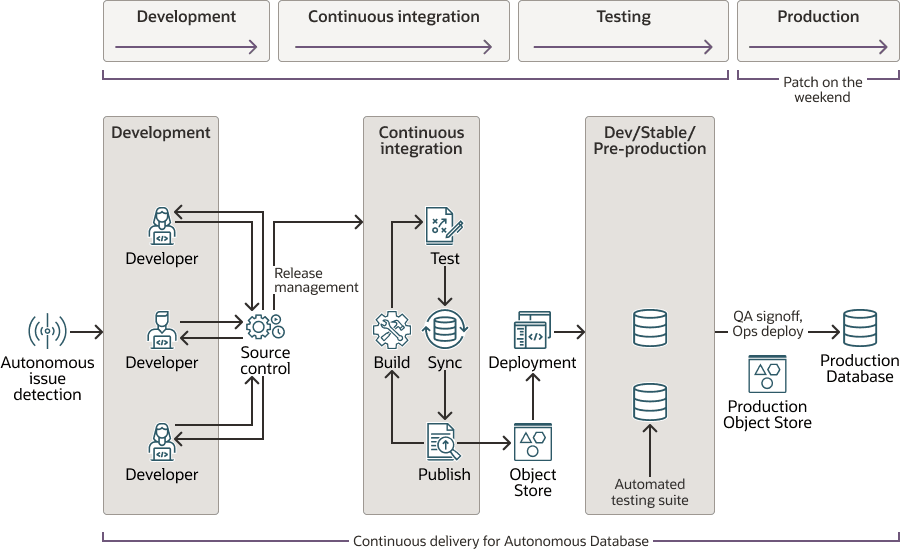
Autonomous Database instances are automatically patched on a regular bi-weekly cycle. The patches include new features, bug fixes, and security patches. By automating the patching process Oracle can ensure that your databases are always up-to-date with the latest security patches, which helps to protect your data from unauthorized access.
Automated patching is important for the following key reasons:
Security: Fully automated patching transparently fixes vulnerabilities that might be susceptible to cyberattacks, helping your organization reduce its security risk.
Database uptime: Fully automated patching ensures all software (database, O/S, storage servers etc) is kept up-to-date and runs smoothly, supporting system uptime requirements.
Compliance: With the continued rise in cyber-attacks, organizations are often required by regulatory bodies to maintain a certain level of compliance. Patch management is a necessary piece of adhering to compliance standards.
Feature and enhancements: Patching typically goes beyond delivering fixes and includes new feature/functionality updates. ADB Patches are critical to ensuring that you have the latest and greatest the database has to offer.
Oracle's Security-First Mindset
Oracle operates with a security-first mindset. Automating the patching process ensures that your databases are always up-to-date with the latest security patches, which helps to protect your data from unauthorized access.
With the continued rise in cyber-attacks, organizations are often required by regulatory bodies to maintain a certain level of compliance. Patch management is a necessary piece of adhering to compliance standards.
|
Maintenance and patching schedules
Maintenance and patching windows
All Autonomous Database instances are automatically assigned to a maintenance window and different instances can have different maintenance windows.
Autonomous Database uses these maintenance windows to patch the entire stack used to run your database, including the database software, database dictionary, operating systems, Exadata storage, firmware, and more.
Patches include bug fixes, security fixes, and new features. Critical security fixes are always applied as soon as they are available. Patches are deployed uniformly across all databases, so you do not need to track one-off patches. After a fix for an issue is implemented, for example an issue seen in one database, the fix is deployed to all Autonomous Database instances.
Features and enhancements
Patching goes beyond delivering fixes and includes new feature/functionality updates. Immediately take advantage of software updates that let you deliver solutions more quickly and easily.
Autonomous Database patching is backed by a zero-regression SLO
Autonomous Database instances are automatically patched on a regular bi-weekly cycle. Automated patching ensures all software (database, O/S, storage servers, etc.) is kept up-to-date and running smoothly, supporting system uptime requirements. Oracle provides a service level objective of zero regressions in your production database due to these patches.
After a patch is applied to a database on the Early patch level, if an issue is found and reported through a service request, Oracle will use commercially reasonable efforts to address the problem so that the same issue does not occur when the patch is applied to the production database.
|
|
|