

Munich Re HealthTech builds AI chatbot for insurance analytics with Oracle AI
October 1, 2025 | 5 minute read
The author would like to thank Antonis Roussos, Head of Analytics, Munich Re HealthTech, for his contribution.

Munich Re HealthTech (MRHT) is a global provider of digital solutions for health insurance, serving clients across multiple continents for more than 30 years. With a flagship policy and claim administration system, comprehensive analytics platforms—including an advanced system for actuaries and underwriters called SMAART (Sophisticated Monitoring and Assessment of Risk Tool)—and an ongoing commitment to innovation, MRHT sought to further empower decision-makers within the health insurance industry.
The challenge for AI-powered analytics
Actuaries, who calculate risks in pricing; underwriters, who decide which policies to approve; and executives, who run the business, each need to make smart decisions by using the company’s own data with the latest AI technologies. Despite strong analytics capabilities, these business users struggled to access timely, actionable data insights. They often had to navigate multiple dashboards or depend on IT support to create new reports or KPIs. This delayed decision-making and created bottlenecks, especially for ad hoc queries crucial to dynamic risk assessment, premium pricing, and portfolio optimization.
Designing an AI solution
To simplify queries in natural language and get instant answers and insights in multiple languages, MRHT developed an AI-powered, natural language chatbot in its SMAART analytics platform using the suite of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) AI services:
- OCI Generative AI
- Oracle Autonomous Database
- Oracle Select AI
- Oracle AI Vector Search
- Oracle APEX
- OCI Object Storage
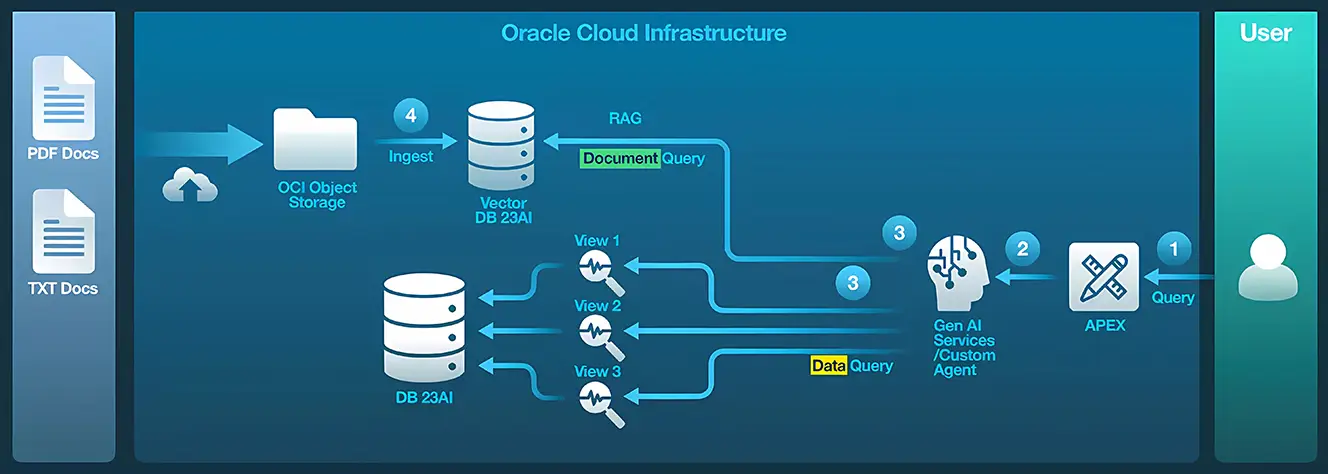
MRHT built the AI chatbot to answer two types of questions:
- Document-related: Using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), users can ask about available product features and instantly receive contextual answers and documentation links. The AI system ingests uploaded documentation (such as PDFs or TXT files) into OCI Object Storage and vectorizes them in Oracle Database 23ai for semantic search. Then the user asks a question in a chatbot, written in Oracle APEX, and the query is sent automatically to using the same embedding model that was used for the documentation, and the question’s vector is used by Oracle Database 23ai to perform a similarity search against the document vectors already stored in the database. The results of the search are individual portions of documents that have semantic meanings that are close to the question being asked. As a result, the end user has to look at only the best data.
- Data-driven analytics: Users query insurance policy performance data using natural language (such as, "Show me policies with high claims in 2023" or “What are the worst-performing policies over the last two years?”). Users receive tabular answers, intuitive charts, and personalized suggestions in seconds to optimize policy performance. The natural language queries are processed with Oracle Select AI, which turns them into SQL queries, returned by the LLM, then executed by Oracle Database 23ai. The formatted result set is presented using the APEX UI. In the case of data, the query is more complicated than documentation, because the query prompt also contains the metadata of the actual database. MRHT configured different views and tables for a category of questions raised by the user.
Insurance portfolio–related questions will be answered by View 1 for Portfolio Overview, while more granular questions about policies will be answered by View 2 for Policy Overview or View 3 for Claim Overview. The chatbot sets what is the appropriate view to use and the appropriate profile to connect to the LLM, then gets all the metadata that has been embedded in the database, along with the user query. Next, the chatbot goes to the LLM, and the LLM translates the query into a SQL statement. In many cases, MRHT has seen that the SQL statements are very sophisticated and role-based because staff have provided the user profile information as well. The SQL statement comes back to the LLM and is executed outside the LLM because the LLM is not connected to the database. Next, the statement goes to the APEX UI, and then it is forwarded to the 23ai database for execution. The result comes back to the APEX UI for the user. MRHT uses the Oracle Virtual Private Database security feature to control data access to help ensure that the right data goes to the right user every time to address security and compliance requirements.
Results
“Oracle’s AI innovation enhances decision-making, efficiency, and accessibility across global markets, making this a game changer in insurance portfolio management. Actuaries, underwriters, and executives can query data in natural language, receiving real-time insights, KPI analysis, and predictive recommendations without IT intervention,” says Antonis Roussos, Munich Re’s head of analytics.
- RAG-based document question answering: The GenAI chatbot scanned company documentation and knowledgebases for precise answers with direct links to increase collaboration and productivity.
- Natural language data queries: Select AI translated free-text queries into context-aware, metadata-enriched SQL executed on Autonomous Database 23ai with results displayed in APEX.
- Reduced IT dependency: Business users conducted complex analyses independently with instant response times, cutting development costs and increasing efficiency. In more than 90% of the queries, accurate answers were generated in seconds with next-level efficiency and insight.
- Enhanced decision-making: Instant, real-time access to vital KPIs, data visualizations with optimal charts or graphs, and recommendations empowered portfolio management and risk mitigation.
- Improved compliance and security: Role-based access and auditing kept data safe and helped to ensure regulatory alignment.
Lessons learned
- Model selection: Trade-offs exist between larger Llama LLMs with many attributes and parameters for accuracy, with lighter Cohere ones for faster response times.
- Granular access control: Robust metadata management and user-role mapping are crucial for accuracy and compliance.
- Future vision: Evolve from Q&A interactions to agentic workflows, where the AI system moves from “what happened?” to “what should we do next?” by identifying trends and anomalies and then coordinating multistep actions.
Conclusion
The collaboration between MRHT and Oracle transformed insurance analytics—allowing for natural language access to complex data, reducing time to insight, and supporting smarter, faster decisions for global insurers. This case demonstrates how enterprise-grade AI, coupled with secure and scalable database technology, redefines the possibilities for the insurance industry.
-
Peter Schutt
Senior Director, Oracle Product Management