 文章
文章
 面向服务的架构
面向服务的架构
Oracle Service Bus 11g 的缓存策略
作者:William Markito Oliveira
合适的缓存策略可以在很大程度上改善应用程序性能。
2011 年 7 月发布
Oracle Service Bus 11g 提供内置的缓存功能(该功能利用 Oracle Coherence)为许多缓存策略提供一流的支持。本文通过一个示例来介绍如何使用此功能并探讨一个故障切换场景,该示例展示了缓存策略如何提高 Web 服务的速度甚至能够防止生产中断。
要求
- Oracle Service Bus 11.1.1.4
- Oracle Coherence 3.6
- Oracle WebLogic Server 10.3.4
- Linux 或 Windows
- Oracle Enterprise Pack for Eclipse (OEPE) 3.6
本文假定您具备以下方面的知识:
- Java 和 Web 服务
- Oracle Service Bus 基本知识
- Oracle WebLogic Server 基本管理
有问题的 Web 服务
在本案例研究中,我们有一个名为 CustomerService 的简单 Web 服务,它目前存在一些性能问题,对于每个请求,它都需要 9 秒钟才会作出响应。我们通过以下步骤来创建并模拟这个“有问题的”Web 服务:
- 启动 Oracle Enterprise Pack Eclipse。
- 在 New Project 窗口中,选择 Web Service Project 并单击 Next。
- 在 New Web Service Project 窗口中:
- 将项目名称设为 Customer
- 将 Target Runtime 设为 Oracle WebLogic Server 11gR1 PatchSet 3
- 单击 Finish。
- 右键单击 Customer 项目,创建一个名为 schemas 的新文件夹。
- 创建一个新的 XML 模式 CustomerType.xsd
- 将以下模式定义复制并粘贴到 CustomerType.xsd 文件中:
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.org/Customer"
xmlns:tns="http://www.example.org/Customer"
elementFormDefault="qualified"><element name="customer" type="tns:CustomerType"></element>
<complexType name="CustomerType">
<sequence>
<element name="id" type="int"></element>
<element name="firstname" type="string"></element>
<element name="lastname" type="string"></element>
<element name="address" type="tns:AddressType"></element>
</sequence>
</complexType>
<complexType name="AddressType">
<sequence>
<element name="street" type="string"></element>
<element name="country" type="string"></element>
<element name="city" type="string"></element>
</sequence>
</complexType>
</schema> - 将该内容粘贴到 CustomerType.xsd 中以后,右键单击该文件并选择 Generate > JAXB Classes。
- 将 Package 域设置为 com.oracle.examples.entities,然后单击 Finish。
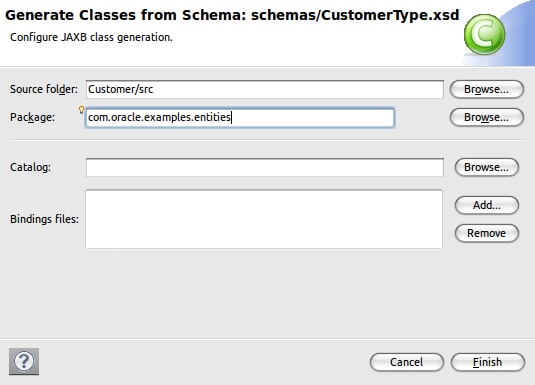
图 3 使用 JAXB 从 XML 模式生成 Java 类 - 控制台将输出以下结果:
compiling a schema...
com/oracle/examples/entities/AddressType.java
com/oracle/examples/entities/CustomerType.java
com/oracle/examples/entities/ObjectFactory.java
com/oracle/examples/entities/package-info.java
com/oracle/examples/entities/jaxb.properties
- 选择 Project Explorer 选项卡下的 Java Resources,单击 WebLogic Web Service 创建一个新的 Web 服务类。
- 在 New Web Service 窗口中进行以下设置:
Package:com.oracle.examples.service
Name:Customer - 将以下代码复制到刚创建的 Customer.java 类中。
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import com.oracle.examples.entities.AddressType;
import com.oracle.examples.entities.CustomerType;
import com.oracle.examples.entities.ObjectFactory;@WebService
public class Customer {@WebMethod
public CustomerType getCustomer(int id) {ObjectFactory factory = new ObjectFactory();
AddressType addressType = factory.createAddressType();
CustomerType customerType = factory.createCustomerType();switch (id) {
case 1:
addressType.setCity("São Paulo");
addressType.setCountry("BRA");
addressType.setStreet("Marginal Pinheiros");customerType.setId(1);
customerType.setFirstname("João");
customerType.setLastname("Silva");
customerType.setAddress(addressType);
break;
case 2:
addressType.setCity("San Francisco");
addressType.setCountry("USA");
addressType.setStreet("Some address");customerType.setId(2);
customerType.setFirstname("John");
customerType.setLastname("Lock");
customerType.setAddress(addressType);
break;
default:
break;
}
// forcing slow down
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(9000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}return customerType;
}
}
该 Web 服务将返回固定值,当然,现实中您应使用 JPA 和/或 Oracle TopLink 在数据库中进行实际的 Customer 搜索。同时,为了在我们的 Web 服务中模拟迟缓行为,这里进行了一个 Thread.sleep() 调用,这将导致该服务在 9 秒钟后才返回。 - 将此项目部署到一个正在运行的 WebLogic Server 实例,点击以下 URL 查看 WSDL 并使用 WebLogic Test Client 进行测试。 WSDL:http://localhost:7001/Customer/CustomerService?WSDL
- 调用服务方法 getCustomer 时,您将注意到它的确花了 9 秒钟来执行。

图 4 有问题的 Web 服务响应

图 1 新建 Web 服务项目

图 2 新建 XML 模式
Web 服务将采用与模式相同的数据结构。
TEST URL:http://localhost:7001/wls_utc/?wsdlUrl=http://localhost:7001/Customer/CustomerService?WSDL
注意:可以将此项目部署到将运行 Oracle Service Bus 的服务器上。
在下一节中,我们将该服务导入 Oracle Service Bus 中,然后将了解服务缓存如何降低这一性能问题的影响。
Oracle Service Bus 项目
在此节中,我们将导入先前创建的 Web 服务并在 Service Bus 项目中生成代理服务和业务服务。
导入 Web 服务资源
- 打开 Oracle Service Bus 控制台:http://localhost:7001/sbconsole
- 单击 Project Explorer,启动一个会话并创建一个新项目。将其命名为 Customer(举例来说)。
- 单击 Customer 项目,找到 Create Resource 组合框。选择 Bulk 下面的 Resources from URL。
- 使用以下信息填写表单:
- URL/Path:http://localhost:7001/Customer/CustomerService?WSDL
- Resource Name:CustomerWSDL
- Resource Type:WSDL
- 单击 Next,然后单击 Import。

图 5 将 WSDL 资源导入 Oracle Service BUS 中
创建代理服务和业务服务
- 单击 Customer 项目,找到 Create Resource 组合框。选择 Business Service。
- Service Name:CustomerBS
- Service Type:WSDL Web Service
- 在 Select WSDL 窗口中,选择 CustomerWSDL。
- 选择 CustomerPortBinding,然后单击 Submit。
- 保持协议为 HTTP,在 Endpoint URI 中设置 http://localhost:7001/Customer/CustomerService,这是上一节中创建的 Web 服务的 URL。

图 6 创建业务服务 - 单击 Last 然后单击 Save。
- 返回到 Customer 项目,找到 Create Resource 组合框,现在选择 Proxy Service
- Service Name:CustomerPS
- Service Type:Create From Existing Service
- 选择 Business Service 并指向 CustomerBS。
- 我们不需要修改代理服务中的任何设置,因此可以单击 Last,然后单击 Save。
激活和测试
- 单击 Activate 保存本会话中进行的更改,然后单击 Submit。
- 返回到 Customer 项目,单击 Actions 列下面的 Launch Test Console。
- 现在可以执行代理服务,这将调用我们这个有问题的 Web 服务。由于我们仅硬编码了两个 ID,所以您只有输入 1 或 2 才能获得某些响应数据。输入其他值将返回空的响应文档。

图 7 请求的执行存在性能问题
图 8 Web 服务在 9 秒后响应
注意,所有服务调用实际上都需要大约 9 秒钟来执行。有时可能需要更长的时间,如多 1 秒或 2 秒,但从来不会少于 9 秒,因为这是后端 Web 服务的“响应时间”。
在下一节,我们将演示如何集成 Oracle Service Bus 和 Oracle Coherence,以及如何使用进程外缓存策略升级解决方案。
Oracle Coherence 集成
Oracle Service Bus 一直有某种缓存机制,除了可以为代理服务和业务服务类提供对象缓存外,还可以提供 XQuery 和 XML bean 缓存。但自 11g 第 1 版之后,Oracle Service Bus 利用 Oracle Coherence 提供了一种结果缓存的集成解决方案。
Oracle Service Bus 中的结果缓存可用于业务服务。启用结果缓存时,业务服务将不会到达后端服务,响应将来自缓存项。缓存项可能过期,如果过期,下一个服务调用将实际到达后端服务并更新缓存项。

图 9 结果缓存的工作原理
有关 Oracle Service Bus 中结果缓存如何工作的详细信息,请参阅文档。
激活业务服务缓存
要为业务服务启用结果缓存,请执行以下步骤:
- 在 Oracle Service Bus 控制台中单击 Change Center 处的 Create,创建一个新的更改会话。
- 转到 Customer 项目,单击 CustomerBS Business Service。
- 单击 Message Handling Configuration 部分下面的 Edit。

图 10 启用业务服务结果缓存 - 展开 Advanced Settings,在 Result Caching 中选择 Supported。
- 设置 Cache Token Expression:fn:data($body/ser:getCustomer/arg0)

图 11 业务服务缓存设置这将把客户 ID 用作缓存项的唯一标记。另外,将 Expiration Time 设置为 10 minutes。
- 单击 Last >> 和 Save 确认对业务服务的修改。您可以激活更改会话。
- 现在单击 CustomerPS 代理服务的 Launch Test Console,我们来对配置进行测试。
第一次执行服务时,服务需要 9 秒钟来执行,并会填充缓存项。在 Test Console 中单击 Back,尝试再次执行;服务将直接从 Oracle Service Bus 内运行的内嵌 Oracle Coherence Server 中的缓存项立即显示结果。缓存的 Expiration Time(生存周期)在第 5 步中设为 10 分钟,因此在此期间,您的调用将不会抵达后端 Web 服务。
现在,我们已为这个存在问题的服务提供了一个解决方案。但如果您想了解缓存中发生了什么,或者想了解缓存服务器中有多少缓存项时,该怎么办呢?
Coherence Console 与 Service Bus Cache 的集成
Oracle Coherence 为有关缓存服务器的 JMX 和报表提供了很好的 API,这是监视巨大负载生产环境的必经之路。但对于开发环境和其他重要监视情形,可以使用 Coherence Console。
Coherence Console 是 Coherence 自带的一个命令行实用程序,可连接到特定的 Coherence 服务器。这是一个很好的工具,可以检查哪些服务器参与了集群,还可以浏览缓存数据。在本示例中,我们将使用此工具来监视缓存项和 Coherence 服务器。
为了集成 Coherence Console 与 Oracle Service Cache,需要指定以下几项内容:
- 创建一个名为 consoleOSB.sh 的文件并粘贴以下文本:
#!/bin/sh # Middleware home
MDW=/opt/oracle/osb11114
# Service Bus installation folder
OSB=$MDW/Oracle_OSB
# Domain home
DM=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------if [ -f $JAVA_HOME/bin/java ]; then
JAVAEXEC=$JAVA_HOME/bin/java
else
JAVAEXEC=java
fi
OPTS="-Xms64m -Xmx64m
-Dtangosol.coherence.override=$DM/config/osb/coherence/osb-coherence-override.xml
-Dtangosol.coherence.cacheconfig=$DM/config/osb/coherence/osb-coherence-cache-config.xml
-Dtangosol.coherence.distributed.localstorage=false
-Dtangosol.coherence.cluster=OSB-cluster
-Dtangosol.coherence.localhost=localhost
-DOSB.coherence.cluster=OSB-cluster"CP="$MDW/oracle_common/modules/oracle.coherence_3.6/coherence.jar"
注意: 您不必担心文件位置,可以将它放在任何位置。
CP=$CP:"$MDW/modules/features/weblogic.server.modules.coherence.server_10.3.4.0.jar"
CP=$CP:"$OSB/lib/osb-coherence-client.jar"
$JAVAEXEC -server -showversion $OPTS -cp $CP com.tangosol.net.CacheFactory $1 - 根据您的安装设置修改脚本变量。这些变量包括:
- 中间件主目录 — MDW
- Oracle Service Bus 安装目录 — OSB
- 域主目录 — DM
- 提供文件执行权限并在终端执行该脚本。您将看到类似下面的输出:
markito@anakin:~/Projects/PTS$ ./consoleOSB.sh
…2011-06-17 16:14:35.612/0.240 Oracle Coherence 3.6.0.4 <Info> (thread=main, member=n/a): Loaded operational configuration from "jar:file:/opt/oracle/osb11114/oracle_common/modules/oracle.coherence_3.6/coherence.jar!/tangosol-coherence.xml"
2011-06-17 16:14:35.621/0.249 Oracle Coherence 3.6.0.4 <Info> (thread=main, member=n/a): Loaded operational overrides from
"file:/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/osb/coherence/osb-coherence-override.xml"
2011-06-17 16:14:35.629/0.257 Oracle Coherence 3.6.0.4 <D5> (thread=main, member=n/a): Optional configuration override "/custom-mbeans.xml" is not specifiedOracle Coherence Version 3.6.0.4 Build 19111
Grid Edition: Development mode
Copyright (c) 2000, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates.All rights reserved.2011-06-17 16:14:36.127/0.755 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <Warning> (thread=main, member=n/a): Local address "127.0.0.1" is a loopback address;
this cluster node will not connect to nodes located on different machines
2011-06-17 16:14:36.136/0.764 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <D4> (thread=main, member=n/a): TCMP bound to /127.0.0.1:7892 using SystemSocketProvider
2011-06-17 16:14:36.445/1.073 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <Info> (thread=Cluster, member=n/a): This Member(Id=4, Timestamp=2011-06-17 16:14:36.262,
Address=127.0.0.1:7892, MachineId=26733, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:13130, Role=CoherenceConsole,
Edition=Grid Edition, Mode=Development, CpuCount=4, SocketCount=2) joined cluster "OSB-cluster" with senior Member(Id=1, Timestamp=2011-06-17 11:00:46.772,
Address=127.0.0.1:7890, MachineId=26733, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,
process:5603, Role=OSB-node, Edition=Grid Edition, Mode=Development, CpuCount=4, SocketCount=2)
2011-06-17 16:14:36.454/1.082 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <D5> (thread=Cluster, member=n/a): Member 1 joined Service Cluster with senior member 1
2011-06-17 16:14:36.454/1.082 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <D5> (thread=Cluster, member=n/a): Member 1 joined Service Management with senior member 1
2011-06-17 16:14:36.454/1.082 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <D5> (thread=Cluster, member=n/a): Member 1 joined Service ORA-OSB-deployments with senior member 1
2011-06-17 16:14:36.457/1.085 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <Info> (thread=main, member=n/a): Started cluster Name=OSB-clusterWellKnownAddressList(Size=2,
WKA{Address=127.0.0.1, Port=9999}
WKA{Address=127.0.0.1, Port=7890}
)MasterMemberSet
(
ThisMember=Member(Id=4, Timestamp=2011-06-17 16:14:36.262, Address=127.0.0.1:7892, MachineId=26733,
Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:13130, Role=CoherenceConsole)
OldestMember=Member(Id=1, Timestamp=2011-06-17 11:00:46.772, Address=127.0.0.1:7890,
MachineId=26733, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:5603, Role=OSB-node)
ActualMemberSet=MemberSet(Size=2, BitSetCount=2
Member(Id=1, Timestamp=2011-06-17 11:00:46.772, Address=127.0.0.1:7890, MachineId=26733,
Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:5603, Role=OSB-node)
Member(Id=4, Timestamp=2011-06-17 16:14:36.262, Address=127.0.0.1:7892, MachineId=26733,
Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:13130, Role=CoherenceConsole)
)
RecycleMillis=1200000
RecycleSet=MemberSet(Size=0, BitSetCount=0
)
)TcpRing{Connections=[1]}
IpMonitor{AddressListSize=0}2011-06-17 16:14:36.500/1.128 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <D5> (thread=Invocation:Management, member=4):
Service Management joined the cluster with senior service member 1Map (?):
现在已连接到与 Oracle Service Bus 相同的 Oracle Coherence 集群。Coherence Console 提供了各种不同的命令,有关完整列表,请查看文档。 - 我们来查看缓存项。键入 cache /osb/service/ResultCache,按 Enter 键:
Map (?): cache /osb/service/ResultCache
2011-06-17 16:27:25.807/770.435 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <Info> (thread=main, member=4): Loaded cache configuration from "file:/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/osb/coherence/osb-coherence-cache-config.xml"
2011-06-17 16:27:26.352/770.980 Oracle Coherence GE 3.6.0.4 <D5> (thread=DistributedCache:ORA-OSB-deployments, member=4): Service ORA-OSB-deployments joined the cluster with senior service member 1
<distributed-scheme>
<scheme-name>expiring-distributed</scheme-name>
<service-name>ORA-OSB-deployments</service-name>
<backing-map-scheme>
<local-scheme>
<scheme-ref>expiring-backing-map</scheme-ref>
</local-scheme>
</backing-map-scheme>
<autostart>true</autostart>
</distributed-scheme> - 键入 list 或 size 命令,如果您是按照我们的示例,将看到没有任何结果。这是因为我们的缓存项已过期(10 分钟,记得吗?),现在我们必须再次执行代理服务 CustomerPS 以填充缓存服务器项。如果缓存仍然有效(未过期),您将得到不同的结果,当然,您的缓存项将已经存在。
- 返回 Service Bus 控制台,再次启动 Test Client 并执行 CustomerPS。
- 转到 Coherence Console,键入 list 或 size 命令。您会看到以下输出(在测试之前和之后):
Map (/osb/service/ResultCache): size
0Map (/osb/service/ResultCache): size
1Map (/osb/service/ResultCache): list
PipelineResultCacheKey[BusinessService Customer/CustomerBS,getCustomer,1) = owner=BusinessService Customer/CustomerBS,value=[B@58c16b18 - 返回 Service Bus Test 客户端,尝试使用与前一次执行使用的不同客户 ID 执行。您会看到两个缓存项,10 分钟后,这两个缓存项过期。
从 WebLogic 控制台创建新的外部 Coherence 服务器
现在,我们已经启用了服务缓存,因此具有更好的吞吐性能,并且可以在系统中应对更多用户。但要记住,我们仍在使用进程内策略,这意味着我们将相同的 JVM 内存用于缓存项、WebLogic 服务(如 JDBC 或 JMS),以及 Oracle Service Bus 对象(如转换、代理服务和业务服务)。如果将缓存使用提升至一个很高的量,可能很容易出现内存耗尽的情况,这就会牺牲掉 Enterprise Service Bus 中的所有其他服务,甚至是未使用缓存功能的服务。
要解决这一问题,可以使用外部 Coherence 服务器,即拥有自己的 Coherence 服务器的专用 JVM。该解决方案可以提高整体架构的可伸缩性,支持更复杂的 Coherence 集群基础架构。Coherence 集群配置不在本文讨论范围之内,但本文对于可以针对自己的情形能实现哪些目标以及进行哪些调整提供了思路。
以下是使用 WebLogic 控制台添加新 Coherence 服务器的步骤:
- 登录 WebLogic 控制台:http://localhost:7001/console
- 如果在 WebLogic 中运行一个无关联计算机的域,则必须添加一个计算机并将 Coherence 服务器与该计算机相关联。在左侧菜单中展开 Environment,选择 Machines。
- 使用以下信息填写 New Machine 表单:
- Name:anakin [替换为您的计算机名]
- Machine OS:Unix [替换为您的操作系统]
- 单击 Next。
- 在 Node Manager Properties 表单中使用以下信息:
- Type:Plain [对于生产环境,请将其更改为 SSL 或 SSH]
- Listen Address:localhost
- Listen Port: 5556
- 单击 Finish。

图 13 Node Manager 属性
稍后我们将设置 Node Manager 脚本以完成此步骤。 - 展开 Environment,选择左侧菜单中的 Coherence Servers 并单击 New。
- 使用以下信息填写该表单:
- Name:server1
- Machine:anakin [或使用第 3 中所用的计算机名替换]
- Unicast Listen Address:localhost
- Unicast Listen Port: 9999
- 单击 Finish。
- 在 Coherence Servers 屏幕中,单击 server1。我们需要调整此服务器的类路径以便与 Oracle Service Bus 集成。
- 在 Settings for server1 屏幕中,单击 Server Start 选项卡并填写以下域:
- Java Home:/opt/oracle/jrockit-jdk1.6.0_20-R28.1.0-4.0.1
[设置为您的 java 主目录位置] - OSB Home:/opt/oracle/osb11114/
[设置为您的 Oracle Service Bus 安装目录] - Class Path: /opt/oracle/osb11114/modules/features/weblogic.server.modules.coherence.server_10.3.4.0.jar:/opt/oracle/osb11114/coherence_3.6/lib/coherence.jar:/opt/oracle/osb11114/Oracle_OSB/lib/osb-coherence-client.jar
[用您的 Oracle Service Bus 安装目录替换 /opt/oracle/osb11114/] - Arguments:
-Dtangosol.coherence.override=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/osb/coherence/osb-coherence-override.xml
-Dtangosol.coherence.cacheconfig=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/osb/coherence/osb-coherence-cache-config.xml
-Dtangosol.coherence.distributed.localstorage=true
-Dtangosol.coherence.cluster=OSB-cluster
-Dtangosol.coherence.localhost=localhost
-DOSB.coherence.cluster=OSB-cluster
[用您的 Oracle Service Bus 域目录替换 /opt/domains/osb11gR1/]
注意:为了将此 Coherence 服务器用作存储节点,tangosol.coherence.distributed.localstorage 属性需设置为 true。 - 单击 Save。

图 15 Coherence 服务器设置
- Java Home:/opt/oracle/jrockit-jdk1.6.0_20-R28.1.0-4.0.1
- 现在,需要将新服务器添加到 Oracle Service Bus 配置中 Coherence Servers 的 WKA (Well Known Address) 列表:
- 在命令终端,切换到 /opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/osb/coherence 目录
- 编辑 osb-coherence-override.xml 文件,根据以下代码段进行更新:
<!DOCTYPE coherence SYSTEM "coherence.dtd">
<coherence>
<cluster-config>
<!--
By specifying a well-known-address we disable the mutlicast listener.
This ensures that the Coherence cluster for OSB will be isolated to this machine only.
-->
<unicast-listener>
<well-known-addresses>
<socket-address id="1">
<address system-property="OSB.coherence.wka1">127.0.0.1</address>
<port system-property="OSB.coherence.wka1.port">7890</port>
</socket-address><socket-address id="2">
<address system-property="OSB.coherence.wka2">127.0.0.1</address>
<port system-property="OSB.coherence.wka2.port">9999</port>
</socket-address></well-known-addresses>
<address system-property="OSB.coherence.localhost">127.0.0.1</address>
<port system-property="OSB.coherence.localport">7890</port>
</unicast-listener>
<multicast-listener>
<time-to-live system-property="OSB.coherence.ttl">0</time-to-live>
</multicast-listener>
</cluster-config>
</coherence>
在此我们向 Oracle Coherence 集群添加一个新的套接字地址。由于安全和性能的原因,与 Oracle Service Bus 绑定的 Oracle Coherence 服务器使用 WKA 和 Unicast,因此对于添加到集群的每个新节点,都需要更新此文件,或者在尝试启动其他未列出的节点时确保此处指定的至少一个节点正在运行。在本例中,我们指定一个新的服务器,它监听 localhost 地址 (127.0.0.1) 和端口 9999。 - 保存并关闭 osb-coherence-override.xml。注意:还可以通过在 WebLogic 控制台中在 Coherence 服务器配置中再添加两个属性来执行与此步骤(第 9 步)中所示相同的配置:
-DOSB.coherence.wka2=localhost
-DOSB.coherence.wka2.port=9999
- 现在可以对以上所做的所有配置进行测试了,请执行以下操作:
- 关闭 Oracle Service Bus 域。
- 在命令终端中,切换到 /opt/oracle/osb11114/wlserver_10.3/server/bin 目录,其中 /opt/oracle/osb11114/ 是 Oracle Service Bus 安装目录。
- 执行以下脚本以启动 Node Manager:
./startNodeManager.sh - 启动 Oracle Service Bus 域。
- 转到 WebLogic Server 控制台:http://localhost:7001/console
- 展开左侧菜单中的 Environment,单击 Coherence Servers。
- 单击 Control 选项卡,标记 server1,然后单击 Start。
- 注意,State 列的值变为 Starting,数秒钟之后将变为 Running。

图 12 添加新计算机

图 14 创建一个新的 Coherence 服务器
祝贺您,新的 Coherence Server 已启动并且正在运行,该服务器与 Oracle Service Bus 集成,您可以通过 WebLogic 控制台并借助 Node Manager 管理该服务器。下面我们将对此集成进行测试并使用我们的缓存服务器。
使用外部 Coherence 服务器的进程外缓存
现在可以测试我们的进程外策略并再次执行那个有问题的 Web 服务。记住,与 Oracle Service Bus 绑定的内部服务器和外部的 server1 仍然都可以存储缓存数据,因为它们的 tangosol.coherence.distributed.localstorage 属性都设置为 true。
要测试进程外缓存,可以执行以下操作:
- 打开一个命令终端,找到先前创建的 consoleOSB.sh 脚本。执行该脚本,您会看到以下输出:
………
…
WellKnownAddressList(Size=2,
WKA{Address=127.0.0.1, Port=7890}
WKA{Address=127.0.0.1, Port=9999}
)MasterMemberSet
(
ThisMember=Member(Id=3, Timestamp=2011-06-20 15:03:22.947, Address=127.0.0.1:7894, MachineId=8417, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:11912, Role=CoherenceConsole)
OldestMember=Member(Id=1, Timestamp=2011-06-20 14:34:49.401, Address=127.0.0.1:7890, MachineId=8417, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:10716, Role=OSB-node)
ActualMemberSet=MemberSet(Size=3, BitSetCount=2
Member(Id=1, Timestamp=2011-06-20 14:34:49.401, Address=127.0.0.1:7890, MachineId=8417, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:10716, Role=OSB-node)
Member(Id=2, Timestamp=2011-06-20 14:47:55.749, Address=127.0.0.1:7892, MachineId=8417, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:11562,member:server1, Role=WebLogicWebLogicCacheServer)
Member(Id=3, Timestamp=2011-06-20 15:03:22.947, Address=127.0.0.1:7894, MachineId=8417, Location=site:localdomain,machine:localhost,process:11912, Role=CoherenceConsole)
)
RecycleMillis=1200000
RecycleSet=MemberSet(Size=0, BitSetCount=0
)
)TcpRing{Connections=[2]}
IpMonitor{AddressListSize=0} - 在 Oracle Coherence Console 中,在 Oracle Service Bus ResultCache 中输入:
Map (?): cache /osb/service/ResultCache - 在 Web 浏览器中,登录 Oracle Service Bus 控制台。http://localhost:7001/sbconsole。
- 单击 Project Explorer,转到 Customer 项目和 CustomerPS 代理服务的 Launch Test Console。
- 执行服务,首次调用时,您会经历 9 秒的执行时间。单击 Back,再次执行,结果会立即出现,就像先前一样。
- 在 Coherence Console 中键入 size 或 list,您将看到一个缓存项。
- 要验证外部缓存服务器并检查该服务器是否在工作,请关闭 Oracle Service Bus 域。
- 在 Coherence Console 中再次键入 size 或 list,您仍会看到一个缓存项。这就对了!外部 Coherence Server 现在将您的数据保存 10 分钟。
- 启动 Oracle Service Bus 域,登录到 sbconsole 并重新执行 CustomerPS 代理服务。您将看到立即响应,因为数据仍然来自缓存而不是后端服务。(注意:记住使用第 5 步中所尝试的客户 ID,否则您的调用可能会到达后端服务。)
注意,Well Know Address List 中现在有两个地址,Coherence 集群中有三个成员:OSB-node(内部)、server1(外部)和 CoherenceConsole(我们正在使用的控制台)。
将内部 Coherence 服务器存储设置为 False
我们在上一节中已经看到,外部 Coherence 服务器 (server1) 已负责管理缓存数据存储。但是缓存仍在两个 Coherence 服务器(内部和外部服务器)中进行,而对于生产环境,禁用内部 Coherence 服务器的缓存存储并释放一些 JVM 内存以便用于 JDBC、JMS 或服务处理等其他服务可能是一个好主意。这样更改之后,所有缓存数据将只存储在外部 Coherence 服务器 (server1) 中。
要执行这些设置,请执行以下步骤:
- 确保外部 Oracle Coherence (server1) 已运行并已启用存储。否则,您将在 Oracle Service Bus 日志中看到许多异常,抱怨“Service Result Caching functionality is disabled”。发生这种情况是因为在 Coherence 集群中没有已启用存储的缓存服务器,因此将无法进行缓存。
- 打开一个命令终端,进入 Oracle Service Bus 域目录。
- 在文本编辑器中打开 /opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/bin/startDomainEnv.sh,找到以下文本:
"${JAVA_OPTIONS} ${JAVA_PROPERTIES}
-Dwlw.iterativeDev=${iterativeDevFlag} -Dwlw.testConsole=${testConsoleFlag}
-Dwlw.logErrorsToConsole=${logErrorsToConsoleFlag} "
- 修改此文本使其如下所示:
JAVA_OPTIONS="${JAVA_OPTIONS} ${JAVA_PROPERTIES} -Dwlw.iterativeDev=${iterativeDevFlag} -Dwlw.testConsole=${testConsoleFlag}
-Dwlw.logErrorsToConsole=${logErrorsToConsoleFlag} -Dtangosol.coherence.distributed.localstorage=false "
- 保存并关闭 startDomainEnv.sh 文件。
- 重新启动 Oracle Service Bus 域以应用更改。
- 服务器启动之后,在 WebLogic 输出的启动信息中查找我们在第 3 步中修改过的行。
/opt/oracle/jrockit-jdk1.6.0_20-R28.1.0-4.0.1/bin/java -jrockit -Xdebug -Xnoagent -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,address=8453, server=y,suspend=n -Djava.compiler=NONE -Xms648m -Xmx768m -Dweblogic.Name=AdminServer -Djava.security.policy=/opt/oracle/osb11114/wlserver_10.3/server/lib/weblogic.policy -Xverify:none -da:org.apache.xmlbeans... -ea -da:com.bea... -da:javelin... -da:weblogic... -ea:com.bea.wli... -ea:com.bea.broker... -ea:com.bea.sbconsole... -Dplatform.home=/opt/oracle/osb11114/wlserver_10.3 -Dwls.home=/opt/oracle/osb11114/wlserver_10.3/server -Dweblogic.home=/opt/oracle/osb11114/wlserver_10.3/server -Dcommon.components.home=/opt/oracle/osb11114/oracle_common -Djrf.version=11.1.1 -Dorg.apache.commons.logging.Log=org.apache.commons.logging.impl.Jdk14Logger -Ddomain.home=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1 -Djrockit.optfile=/opt/oracle/osb11114/oracle_common/modules/oracle.jrf_11.1.1/jrocket_optfile.txt -Doracle.server.config.dir=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/fmwconfig/servers/AdminServer -Doracle.domain.config.dir=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/fmwconfig -Digf.arisidbeans.carmlloc=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/fmwconfig/carml -Digf.arisidstack.home=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/fmwconfig/arisidprovider -Doracle.security.jps.config=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml -Doracle.deployed.app.dir=/opt/oracle/domains/osb11gR1/servers/AdminServer/tmp/_WL_user -Doracle.deployed.app.ext=/- -Dweblogic.alternateTypesDirectory=/opt/oracle/osb11114/oracle_common/modules/oracle.ossoiap_11.1.1,/opt/oracle/osb11114/oracle_common/modules/oracle.oamprovider_11.1.1 -Djava.protocol.handler.pkgs=oracle.mds.net.protocol -Dweblogic.jdbc.remoteEnabled=false -Dem.oracle.home=/opt/oracle/osb11114/oracle_common -Djava.awt.headless=true -Dweblogic.management.discover=true -Dwlw.iterativeDev= -Dwlw.testConsole= -Dwlw.logErrorsToConsole= -Dtangosol.coherence.distributed.localstorage=false -Dweblogic.ext.dirs=/opt/oracle/osb11114/patch_wls1034/profiles/default/sysext_manifest_classpath:/opt/oracle/osb11114/patch_ocp360/profiles/default/sysext_manifest_classpath weblogic.Server - 现在执行 CustomerPS 代理服务。
- 返回命令终端,执行 consoleOSB.sh (Coherence Console) 并键入 size 或 list 命令。您仍然会在缓存中看到一个缓存项,但现在该缓存项只存储在外部 Coherence 服务器 (server1) 中,Oracle Service Bus 内部 Coherence 服务器现在只充当客户端节点。
总结
本文展示了两种不同的缓存策略以及对 Oracle Coherence 和 Oracle Service Bus 使用进程外缓存的优点。文中提供了一个 Web 服务示例,该服务在 Oracle Service Bus 中暴露出性能问题,而通过使用结果缓存,明显提高了响应速度。另外,Oracle Coherence Console 与 Oracle Service Bus 集成可作为开发和诊断服务缓存解决方案的另一种方法,可以显示运行中的服务器和缓存数据信息。
进程外缓存可以显著减少 Oracle Service Bus 域的 JVM 内存占用并提高架构的可伸缩性和故障切换能力,对于需要安全伸缩能力的项目,建议采用此方法。
William Markito Oliveira 是位于巴西的 Oracle 平台技术解决方案团队的资深技术专家,他致力于中间件、SOA 和 Java 技术。他还是官方《Java EE 6 教程》的撰稿人,提供有关 CDI、EJB 3.1 和 JAX-RS 的评论和代码示例。