Fight Money Laundering with Graph Analytics
Why financial institutions and regulators should stop playing by the rules
Financial institutions are struggling to keep pace with malicious, global criminal networks that constantly devise new and more complex ways to launder funds through legitimate financial systems. Legacy, rules-only anti–money laundering (AML) systems are at their breaking point and are no longer sufficient to combat increasingly sophisticated international money laundering networks.
How a rules-only AML system works
- Applies AML rules to transaction data
- Identifies suspicious activity
- Alerts a human investigator about red flags
Limits of a rules-only AML system
- Doesn’t consider other types of data that may help prevent criminal activity
- Can’t make connections among entities
- Unable to recognize larger patterns and trends
- Inflexible, whereas criminals frequently adapt
- Doesn’t use the vast amounts of data stored at institutions
“The best place to hide is in plain sight, and money launderers know that especially well. They deploy tactics that are difficult to detect without a holistic view of wider networks and relationships. They have broken rules-only AML systems.”
Use graph analytics to beat money launderers at their own game
Financial institutions must fight money launderers in their own territory and operate beyond the constraints of rules-only AML systems. By leveraging graph analytics, banks can reveal complex webs of money laundering practices that might be overlooked by legacy systems. Now is the dawn of a new era when banks can boost security against invasive criminal activity to better protect their organizations, reputations, and customers.
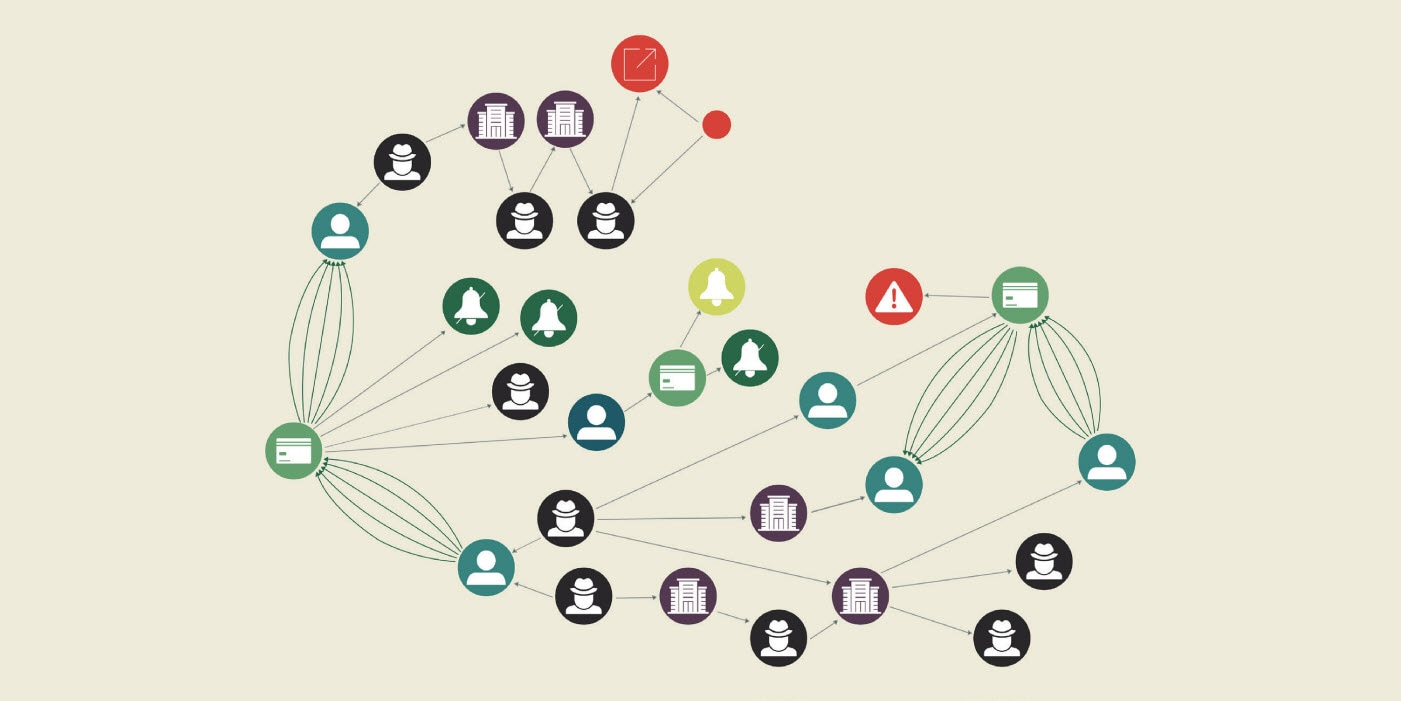
Graph analytics is a mathematical model that investigates information in graph format, plotting data points as nodes and sketching relationships among those data points as edges. With the ability to assess connections, no matter how complex or distant, this technology helps banks piece together patterns that were unidentifiable until recently.
Many industries use this technology to gain previously undiscoverable insights and adhere to AML rules. Chief compliance officers stand to benefit from graph analytics as the solution can be extremely effective against malicious networks of money launderers and can strengthen compliance management systems.
“The fight against money laundering has reached a tipping point as effective AML mitigation is becoming more challenging in an ever-evolving regulatory and business ecosystem. With heavy reliance on rules-based detection and highly manual investigative processes, the financial services industry is rapidly embracing graph analytics technology. By visually connecting customers and parties, related accounts and payments, and other data, graph analytics can deliver more-holistic customer profiles, uncover hidden risks, and optimize financial crime detection and investigations while simultaneously easing the burden on staffing and elevating the customer experience.”
Graph analytics from Oracle Financial Crime and Compliance Management Cloud Service
Oracle Financial Crime and Compliance Management incorporated graph analytics in 2018, based on research from Oracle Labs. Bolstered by our leadership in data, querying, processing, and visualizations, this technology strengthens institutions’ compliance with AML rules.
1. Data at the core
- Oracle’s financial crime and compliance management graph analytics tool is powered by Oracle Financial Services Data Foundation, which includes the most comprehensive anti–financial crime data models in the industry. This solution has been polished over the course of more than 20 years.
- Our integrated Financial Crime Graph Model works in tandem with our Financial Services Data Foundation, consolidating and indexing data so it can be visualized using graph analytics. The Financial Crime Graph Model is flexible and doesn’t operate on a predefined schema, ensuring the solution is useful even with sparse amounts of data.
- Users can leverage a multimodel configuration (such as Oracle Database) to flexibly decide how to query and manage data.
- The Financial Crime Graph Model obtains information from data lakes, relational databases, one-off datasets, and third-party data feeds. By facilitating a more holistic picture of customers and their relationships, this tool enables users to model connections among all their data sources.
- Our quantified integration offers on-demand, risk-rated information based on open source intelligence and external data sources.
- Data from the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (famous for releasing the Panama Papers) is integrated into the graph. This information helps users instantly detect and resolve potential bad actors.
2. Superior query language
- Graph query language is easy to use and simple to understand. It applies logic that simplifies the expression of patterns, regardless of whether data relationships are complex, indirect, or distant.
- Oracle’s proprietary, SQL-like language is called Property Graph Query Language (PGQL). The open source project expresses queries in a concise way, ensuring coding and processing are easier and faster.
- PGQL queries operate one to two orders of magnitude faster than similar queries run in SQL.
“With graphs, data can be managed in more intuitive ways, closer to how people organize their thoughts on a whiteboard. Our system takes advantage of parallel processing and the huge amounts of memory available in modern servers. This allows us to directly model the relationships among all our data.”
3. Faster processing
- Oracle uses a scalable, in-memory graph analytics engine called Oracle Parallel Graph Analytics (Oracle PGX).
- Oracle PGX delivers lightning-fast responses by tapping into parallel processing and huge amounts of available memory.
- While users have access to built-in algorithms to perform common queries, they can also create custom algorithms and constraints to suit their needs.
- Users who want to build their own algorithms can take advantage of an API for complete customization.
4. Powerful visualizations
- Users can click on nodes to intuitively explore relationships among various data points.
- Powered by open source data science notebooks, graph analytics visualizations are embedded in the Oracle Financial Services Enterprise Case Management application via the Oracle Financial Services Crime and Compliance Investigation Hub module.
- Real-time updates to visualizations help provide context for risk scores.
- By visualizing connections, data scientists can more easily create an algorithm. This is pivotal as implementing graph analytics into a machine learning ecosystem can improve accuracy.
Oracle Financial Crime and Compliance Management
Learn more about how our suite of anti–money laundering software solutions can protect the integrity of your financial institution and improve compliance management effectiveness.