The Java Language Environment
Java Base System and Libraries
CHAPTER 9
The complete Java system includes several libraries of utility classes and methods of use to developers in creating multi-platform applications. Very briefly, these libraries are:
Basic Java language classes--java.lang
The Input/Output package--java.io
The Java Utilities package--java.util
The Abstract Window Toolkit--java.awt
9.1 Java Language Classes
The java.lang package contains the collection of base types (language types) that are always imported into any given compilation unit. This is where you'll find the declarations of
Object (the root of the class hierarchy) and
Class, plus threads, exceptions, wrappers for the primitive data types, and a variety of other fundamental classes.
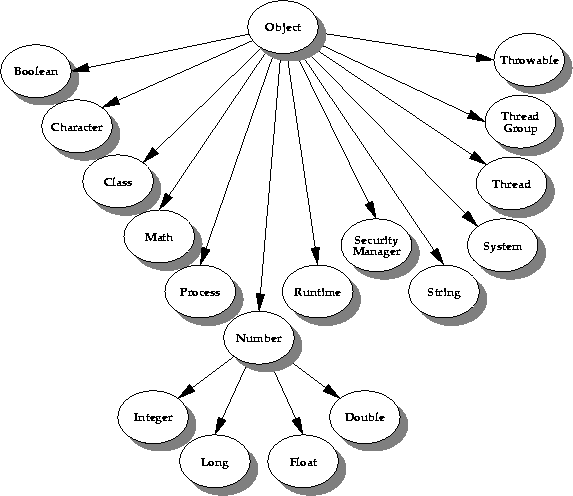
This picture illustrates the classes in java.lang, excluding all the exception and error classes.
Note the
Boolean,
Character, and
Number classes--these classes are "wrapper" classes for the primitive types. You use these classes in applications where the primitive types must be stored as objects. Note also the
Throwable class--this is the root class for all exceptions and errors.
9.2 Input Output Package
The
java.io package contains the declarations of classes to deal with streams and random-access files. This is where you find the rough equivalent of the Standard I/O Library you're familiar with on most UNIX systems. A further library is called
java.net, which provides support for sockets, telnet interfaces, and URLs.
This picture shows the class hierarchy of the I/O package.
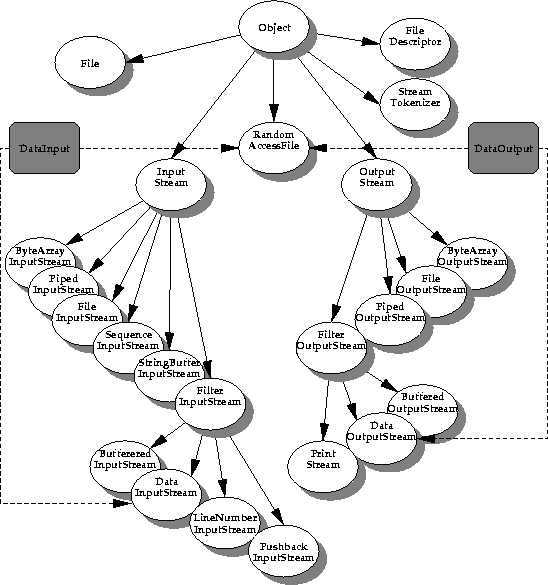
Note that the grayed out boxes with
DataInput and
DataOutput represent interfaces, not classes. Any new I/O class that subclasses one of the other classes can implement the appropriate interface if it needs to.
9.3 Utility Package
The java.util package contains various utility classes including collection classes such as Dictionary and Vector. Here you'll find common storage classes such as
HashTable and
Stack, as well as special use classes like
Date and
Time and classes to handle encoder and decoder techniques. This picture illustrates the useful classes contained in the
java.util package.
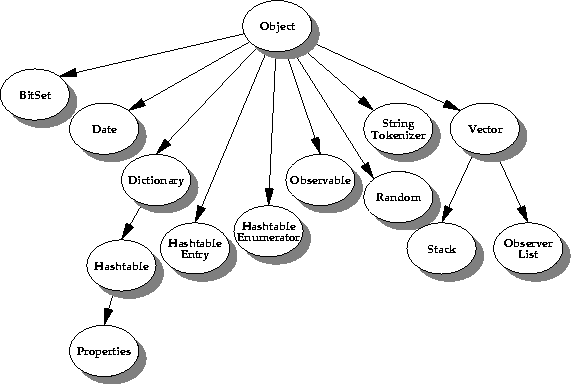
9.4 Abstract Window Toolkit
The
java.awt package is an Abstract Windowing Toolkit that provides a layer enabling you to port Java applications easily from one window system to another. This library contains classes for basic interface components such as events, colors, fonts, and controls such as buttons and scrollbars.
The following picture is a graphical depiction of the class hierarchy in the Abstract Window Toolkit.
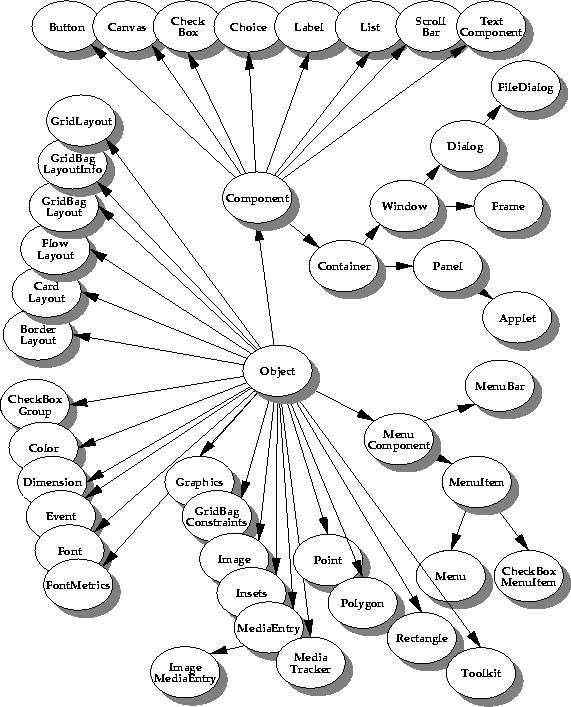
Familar interface elements such as windows and panels are subclasses of
Component. Layout classes provide varying degrees of control over the layout of interface elements.